

Physicochemical Properties of Beef Extract Powder Volume 5 • Issue 4 • 1000389 J Nutr Food Sci ISSN: 2155-9600 JNFS, an open access journal Open Access Research Article Nutrition and Food Sciences o u r n a l f t i d c e s Mahendra et al., J Nutr Food Sci 2015, 5:4 *Corresponding author: Shrikant P, Trivedi Global Inc., 10624 S Eastern Avenue Suite A-969, Henderson, NV 89052, USA, Tel: 1602-531-5400; E-mail: publication@trivedieffect.com Received June 02, 2015; Accepted June 18, 2015; Published June 23, 2015 Citation: Mahendra KT, Gopal N, Shrikant P, Rama MT, Snehasis J, et al. (2015) Bio-eld Treatment: An Effective Strategy to Improve the Quality of Beef Extract and Meat Infusion Powder. Copyright: © 2015 Mahendra KT, et al. under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Bio-field Treatment: An Effective Strategy to Improve the Quality of Beef Extract and Meat Infusion Powder
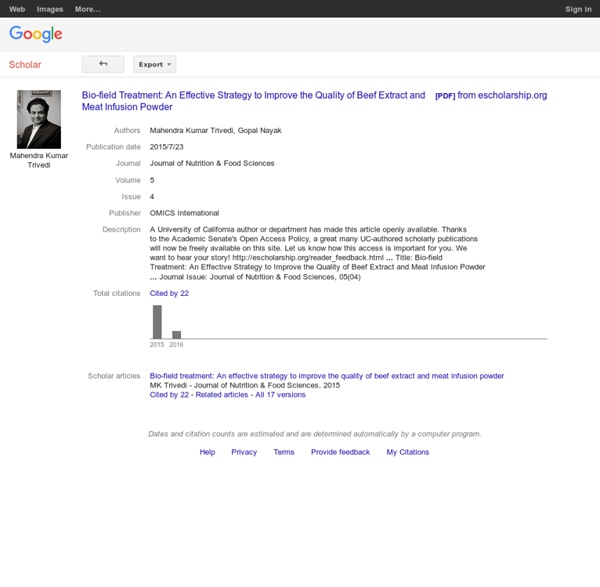
Standard Quality of Beef Extract- Biofield Impact Citation: Mahendra KT, Gopal N, Shrikant P, Rama MT, Snehasis J, et al. (2015) Bio-eld Treatment: An Effective Strategy to Improve the Quality of Beef Extract and Meat Infusion Powder. J Nutr Food Sci 5: 389. doi:10.4172/2155-9600.1000389 Page 8 of 8 Volume 5 • Issue 4 • 1000389 J Nutr Food Sci ISSN: 2155-9600 JNFS, an open access journal melting temperature in BEP and MIP of treated powders as compared to control. observed in treated samples (BEP and MIP) as compared to control. It is postulated that no extra energy or heat was required in order to raise the powder temperature as the treated samples were already in high energy state due to bio-eld treatment. temperature and maximum thermal decomposition temperature of treated samples showed the higher thermal stability. results achieved, we conclude that, the removal of triglycerides could lead to an improvement in the aroma and food quality of beef extract and meat infusion powder. Acknowledgement We thank Dr. References 1. Chem 187: 563-571. 2.
Spectroscopic Characterization of Biofield Treated Metronidazole and Tinidazole *The embed functionality can only be used for non commercial purposes. In order to maintain its sustainability, all mass use of content by commercial or not for profit companies must be done in agreement with figshare. Description Metronidazole and tinidazole are widely used antimicrobial drugs against Gram-negative and Gram-positive anaerobic bacteria. The present study was aimed to evaluate the impact of biofield treatment on metronidazole and tinidazole using FT-IR and UV spectroscopy. Comments (0) Published on 09 Sep 2015 - 10:57 (GMT) Filesize is 941.62 KB License (what's this?) Cite "Filename" Place your mouse over the citation text to select it Embed "Spectroscopic Characterization of Biofield Treated Metronidazole and Tinidazole" Show filename on top Place your mouse over the embed code to select and copy it
Changes in Beef Powder Characteristics Description The present research work investigated the influence of bio-field treatment on two common flavoring agents used in food industries namely beef extract powder (BEP) and meat infusion powder (MIP). The treated powders were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), particle size analysis, surface area analysis, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The FT-IR results showed disappearance of triglycerides peaks in both the treated powders as compared to control. XRD results corroborated the amorphous nature of both control and treated samples. The BEP showed enhanced average particle size (d50) and d99 (size exhibited by 99% of powder particles) by 5.7% and 16.1%, respectively as compared to control. Citation Information
Spectroscopic Characterization of Pharmaceuticals Compound Description The stability of any pharmaceutical compound is most desired quality that determines its shelf life and effectiveness. The stability can be correlated to structural and bonding properties of compound and any variation arise in these properties can be easily determined by spectroscopic analysis. The present study was aimed to evaluate the impact of biofield treatment on these properties of four pharmaceutical compounds such as urea, thiourea, sodium carbonate, and magnesium sulphate, using spectroscopic analysis. Each compound was divided into two groups, referred as control and treatment. Citation Information Mahendra Kumar Trivedi.
Antimicrobial Sensitivity Pattern of Pseudomonas fluorescens after Biofield Treatment Antimicrobial Sensitivity Pattern of Pseudomonas fluorescens after Biofield Treatment Trivedi MK1, Patil S1, Shettigar H1, Gangwar M2 and Jana S2* 1Trivedi Global Inc., 10624 S Eastern Avenue Suite A-969, Henderson, NV 89052, USA 2Trivedi Science Research Laboratory Pvt. *Corresponding author: Snehasis Jana, Trivedi Science Research Laboratory Pvt. 462026 Madhya Pradesh, India, Tel: +91-755-6660006; E-mail: publication@trivedisrl.com Received date: June 18, 2015; Accepted date: June 27, 2015; Published date: July 4, 2015 Copyright: © 2015 Trivedi. distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Abstract Global emergence of Pseudomonas fluorescens (P. fluorescens) displays a mechanism of resistance to all existing antimicrobials. strategy. of P. fluorescens. Type Culture Collection (ATCC 49838) number. denoted as A and B. (revived); likewise, ATCC-B was labeled as Gr.III (lyophilized). Voges-Proskauer in Gr.II. Keywords: Pseudomonas fluorescens
Magnesium Sulphate FT-IR Analysis- Energy Treatment Assessment 0WordPress0CiteULike0 New The stability of any pharmaceutical compound is most desired quality that determines its shelf life and effectiveness.The stability can be correlated to structural and bonding properties of compound and any variation arise in these properties can be easily determined by spectroscopic analysis. The present study was aimed to evaluate the impact of biofield treatment on these properties of four pharmaceutical compounds such as urea, thiourea, sodium carbonate,and magnesium sulphate, using spectroscopic analysis. Your session has expired but don’t worry, your message has been saved.Please log in and we’ll bring you back to this page. Your evaluation is of great value to our authors and readers. Review When you're done, click "publish" Only blue fields are mandatory. Your mailing list is currently empty.It will build up as you send messagesand links to your peers. No one besides you has access to this list. Your message has been sent. Description Leave a comment
Variation in Spectral Properties of Pharmaceuticals Compound Title: An Impact of Biofield Treatment on Spectroscopic Characterization of Pharmaceutical Compounds Publication: Modern Chemistry & Applications Select license: Creative Commons Attributions-NonCommercial-ShareAlike Updated: January 16th, 2017 Abstract: The stability of any pharmaceutical compound is most desired quality that determines its shelf life and effectiveness.The stability can be correlated to structural and bonding properties of compound and any variation arise in these properties can be easily determined by spectroscopic analysis.
bibtexkey :: mahendrakumartrivedi :: biofield BibTeX keymahendrakumartrivedi publications (hide) Mahendra Kumar Trivedi. Thermodynamics & Catalysis (August 2015)Founder of The Trivedi Effect and Trivedi Science.Mahendra Kumar Trivedi. Physical and Structural Characterization of Biofield Treated Imidazole Derivatives (September 2015)Aim of present study was to evaluate the impact of biofield treatment on two imidazole derivatives (i.e., imidazole and 2-methylimidazole) by various analytical methods..
Biofield Impact on Klebsiella Pneumoniae Characteristics Citation: Trivedi MK, Branton A, Trivedi D, Shettigar H, Gangwar M, et al. (2015) Antibiogram Typing and Biochemical Characterization of Klebsiella Pneumonia after Bioeld Treatment. J Trop Dis 3: 173. doi:10.4173/2329891X.1000173 Page 2 of 6 Volume 3 • Issue 4 • 1000173 J Trop Dis ISSN: 2329-891X JTD, an open access journal the bioeld treatment has considerably altered the susceptibility of antimicrobials and biotype of microbes [18-20]. above mentioned facts and literature reports on bioeld treatment, the present work was undertaken to evaluate the impact of bioeld treatment on antimicrobials susceptibility, biochemical reactions pattern, and biotype of MDR isolates of K. pneumoniae. Materials and Methods Experimental design and bacterial isolates MDR clinical lab isolates (i.e. pneumoniae were obtained from stored stock cultures in Microbiology Lab, Hinduja Hospital, Mumbai. into two groups i.e. control and treatment. identication media and antimicrobial agents were checked prior to the [22].
Klebsiella Pneumoniae Characteristics | Effects of External Energy Description Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) is a common nosocomial pathogen causing respiratory tract (pneumoniae) and blood stream infections. Multidrug-resistant (MDR) isolates of K. pneumoniae infections are difficult to treat in patients in health care settings. Aim of the present study was to determine the impact of Mr. Trivedi’s biofield treatment on four MDR clinical lab isolates (LS) of K. pneumoniae (LS 2, LS 6, LS 7, and LS 14). Samples were divided into two groups i.e. control and biofield treated. Citation Information Mahendra Kumar Trivedi.
Evaluation of Biofield Treatment on Physical, Atomic and Structural Characteristics of Manganese (II, III) Oxide Research Article Open Access Patil et al., J Material Sci Eng 2015, 4:4 Material Science & Engineering o u r n a l f t e i c s g Volume 4 • Issue 3 • 1000177 J Material Sci Eng ISSN: 2169-0022 JME, an open access journal Evaluation of Biofield Treatment on Physical, Atomic and Structural Characteristics of Manganese (II, III) Oxide Trivedi MK, Nayak G, Patil S*, Tallapragada RM and Latiyal O Trivedi Global Inc., 10624 S Eastern Avenue Suite A-969, Henderson, NV 89052, USA *Corresponding author: Patil S, Trivedi Global Inc., 10624 S Eastern Avenue Suite A-969, Henderson, NV 89052, USA, Tel: +1 602-531-5400; E-mail: publication@trivedieffect.com Received May 25, 2015; Accepted June 23, 2015; Published July 03, 2015 Citation: Trivedi MK, Nayak G, Patil S, Tallapragada RM, Latiyal O (2015) Evaluation of Bioeld Treatment on Physical, Atomic and Structural Characteristics of Manganese (II, III) Oxide. Copyright: © 2015 Trivedi MK, et al. analysis Introduction [1]. etc. Abstract
Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biochemical Analysis 0WordPress0CiteULike0 6 Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) is a common nosocomial pathogen causing respiratory tract (pneumoniae)and blood stream infections. Multidrug-resistant (MDR) isolates of K. pneumoniae infections are difficult to treat inpatients in health care settings. Aim of the present study was to determine the impact of Mr. Your session has expired but don’t worry, your message has been saved.Please log in and we’ll bring you back to this page. Your evaluation is of great value to our authors and readers. Review When you're done, click "publish" Only blue fields are mandatory. Your mailing list is currently empty.It will build up as you send messagesand links to your peers. No one besides you has access to this list. Enter the e-mail addresses of your recipients in the box below. Your message has been sent. Description Title : Antibiogram Typing and Biochemical Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae after Biofield TreatmentAuthor(s) : Mahendra Kumar Trivedi Leave a comment