


http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=URUJD5NEXC8
Related: Komórka i metabolizm • ETLV • Science Video • Human body • Biologie/EnseignementPDB-101: About Molecule of the Month The RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month by David S. Goodsell (RCSB PDB-Rutgers and The Scripps Research Institute) presents short accounts on selected molecules from the Protein Data Bank. Each installment includes an introduction to the structure and function of the molecule, a discussion of the relevance of the molecule to human health and welfare, and suggestions for how visitors might view these structures and access further details. This feature provides an easy introduction to the RCSB PDB for all types of users, but especially for teachers and students. It is used in many classrooms to introduce structures to students, and is an integral part of the protein modeling event at the Science Olympiad. It is not intended to be a comprehensive index to entries in the PDB archive, nor necessarily represent the historical record.
A Giant-Sized History of Biotechnology Historically, biotech has been primarily associated with food (agtech), addressing such issues as malnutrition and famine. Today, biotechnology is most often associated with the development of drugs. But drugs are hardly the future of biotech. We’ve entered the Fourth Industrial Revolution (#4IR), and genetics are on a new level. Biotech is paving a way for a future open to imagination, and that’s kind of scary. How your digestive system works - Emma Bryce The digestive system is a marvel of evolution. The NIH provides a helpful overview on its different parts and how they all work together. If you want more detail on the individual organs, see these sources about the gastrointestinal tract, the long organ that incorporates the esophagus, the stomach, the small intestine and large intestine, anus and rectum. Then there’s also the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder, each playing their vital parts in breaking food down. You can also learn more about the recently distinguished mesentery organ, which acts as a scaffold for the various parts of the digestive system. And of course, don’t forget your mouth--the gaping hole through which all food enters in the first place!
Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer: Specialized Microscopy Techniques - Fluorescence Digital Image Gallery - Human Bone Osteosarcoma Cells (U-2 OS) Fluorescence Digital Image Gallery Human Bone Osteosarcoma Cells (U-2 OS Line) The U-2 OS cell line, originally known as the 2T line, was derived from the bone tissue of a fifteen-year-old human female suffering from osteosarcoma. Established by J. About Microbiology – Fungi Fungi can be single celled or very complex multicellular organisms. They are found in just about any habitat but most live on the land, mainly in soil or on plant material rather than in sea or fresh water. A group called the decomposers grow in the soil or on dead plant matter where they play an important role in the cycling of carbon and other elements.
What does the pancreas do? - Emma Bryce So what does this internal health coach look like? To find out, take a look at the organ and see where it lives in the body. Its prime position close to the stomach allows it to help us digest our food, with the aid of the enzymes—amylase, protease, and lipase—present in the special pancreatic juice it makes. Why is digestion important anyway, and how does the pancreas fit into this process?
Earth - How much of your body is your own? This story is part of BBC Earth's "Best of 2016" list, our greatest hits of the year. Browse the full list. • Bill Gates is actually worth $1,956• Canadian pop star Justin Bieber has five times fewer cells in his brain than in his liver• Top tennis player Serena Williams has 24.5 trillion red blood cells powering her body• Internet and social media pioneer Mark Zuckerberg’s body contains 800MB of data• President Barack Obama’s head rules his heart; his brain weighs 1.4kg, his heart just 0.4kg Welcome to The Making of Me and You, a unique, new digital interactive from BBC Earth that details extraordinary personalised facts.
5 Creative Ways to Teach the Cell 5 Creative Ways to Teach the Cell 1. 3 D Cell – this is a standard project for entry level biology classes, where students use various objects from around the house to design a three dimensional cell. Popular models are made of clay, cardboard, or styrofoam. Pros: Students seem to enjoy the project and you end up with a lot of amazing models. Cons: Can be expensive, difficult to store, or attract bugs if they are made of candy or other perishables, mostly done as individual projects. 2. The Living Body With meticulous and startling detail, The Living Body examines the miracle of the human species from birth to death. The journey of a human life - the inner processes that bind us all - has rarely been rendered with such stunning clarity and insight. An Emmy-winning feature length documentary produced by Naked Science, The Living Body utilizes 3D computerized graphics, cutting-edge special effects and exploratory footage from actual human subjects to dramatize the manner by which our complex design accommodates each milestone phase of human development.
There Are Three Surviving Elephant Species And They Have A Mammoth Inheritance There are three living species of elephants, not two, and their family tree is more complex than anyone realized, genetic analysis has revealed. The finding is important because it adds urgency to the quest to save the African forest elephant. It also represents the debut of a genetic technique that could help us understand other animals' heritage. Elephants famously come in African and Asian species, with differences in size and whether the females have tusks. However, biologists have suspected for some time that Africa hosts two species, the forest (Loxodonta cyclotis) and savannah (Loxodonta africana) elephant. Troublingly, not all relevant agencies have acknowledged the difference, often treating the two as subspecies.
What Makes You, YOU 150 Years American Museum of Natural History Share OLogy Home search Type keyword(s) to search OLogy How the heart actually pumps blood - Edmond Hui The technique of demonstrating the pumping mechanism of the heart was first shown in public in this TEDx Talk.The detailed scientific description of the technique was published in the European journal, Science in School. There is a beautiful app from Touch Press by Martin Clayton on Leonardo Da Vinci’s anatomical studies, explaining the difficulties he had trying to understand the heart.This book by Thomas Wright describes the discovery of circulation by William Harvey, a hundred years after Leonardo Da Vinci. Harvey was also the first to prove that the heart is a pump, but he did it by lethal and gory demonstrations on live dogs. Many animals would have been saved if he had discovered this technique!
Enzyme Lab Name:________________________________________ Date:__________ Objectives Measure the effects of changes in temperature, pH, and enzyme concentration on reaction rates of an enzymeExplain how environmental factors affect the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. INTRODUCTION: What would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical?
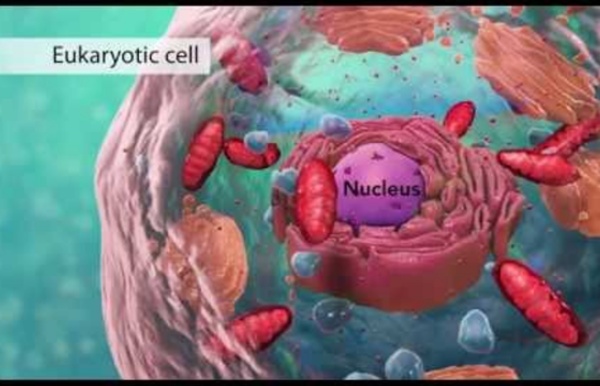
A 7 min introduction to cell structure. Too much detail but 1st 2 mins are fine and the animation is clear. Distinction between plant/animal. So covers everything needed and more. Take notes with care. by davidne Oct 9