

War Doctor by David Nott From Afghanistan to Libya, Sierra Leone to Haiti, surgeon David Nott stood amidst trauma and bloodied chaos to deliver extraordinary care, often at astonishing personal risk, and this is his vivid, haunting and humbling story. Waterstones Non-Fiction Book of the Month for January 2020 For more than twenty-five years, David Nott has taken unpaid leave from his job as a general and vascular surgeon with the NHS to volunteer in some of the world's most dangerous war zones. The conflicts he has worked in form a chronology of twenty-first-century combat: Afghanistan, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Darfur, Congo, Iraq, Yemen, Libya, Gaza and Syria. Driven both by compassion and passion, the desire to help others and the thrill of extreme personal danger, he is now widely acknowledged to be the most experienced trauma surgeon in the world. War Doctor is his extraordinary story. Publisher: Pan Macmillan ISBN: 9781509837052 Number of pages: 320 Weight: 264 g Dimensions: 198 x 130 x 25 mm Show more
Bucharest Early Intervention Project The Bucharest Early Intervention Project (BEIP) was a randomized controlled trial of foster care as an intervention for children abandoned at or around the time of birth and placed in one of six institutions for young children in Bucharest, Romania (Zeanah, et al., 2003). The BEIP began in 2000 with a comprehensive baseline assessment of 136 children and their caregiving environments. Following this assessment, half the children were randomly assigned to high-quality foster care (designed specifically for this study) and the other half to remain in institutional care. We have found in data collected on children through 54 months of age that early institutionalization leads to profound deficits and delays in cognitive (i.e., IQ) and socio-emotional behaviors (i.e., attachment), a greatly elevated incidence of psychiatric disorders and impairment, and differences in brain electrical activity. The BEIP is supported by the National Institute of Mental Health, the John D. and Catherine T.
On the Dangers of the Internet Views: 4064 Over the past century, technologies have completely changed the way we connect with each other. The benefits of the internet are obvious and all around us. The news is the best distraction ever invented. The Young Doctor Summer Internship The internship will take place on 23rd July – 1st August 2021 OR 20th – 29th August 2021. You can choose either the Half Internship (5 days) or the Full Internship (10 days). The Live Online Internship will take place 31st July - 4th August 2021. Listed on the table below is a breakdown of the pricing options and what is included. In select circumstances, we can offer payment by instalments, which requires a 50% deposit. The internship will take place on 23rd July – 1st August 2021 OR 20th – 29th August 2021. The Live Online Internship will take place 31st July - 4th August 2021. Listed on the table below is a breakdown of the pricing options and what is included. In select circumstances, we can offer payment by instalments, which requires a 50% deposit.
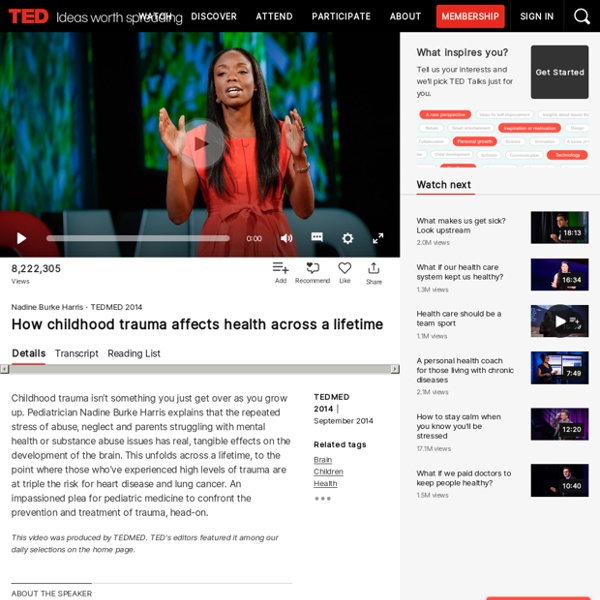
What's the difference between these two brains? Neurologists are beginning to understand exactly how a baby’s interaction with their mother determines how, and indeed whether, the brain grows in the way that it should. Professor Allan Schore, of UCLA, who has surveyed the scientific literature and has made significant contributions to it, stresses that the growth of brain cells is a “consequence of an infant’s interaction with the main caregiver [usually the mother]”. The growth of the baby’s brain “literally requires positive interaction between mother and infant. The development of cerebral circuits depends on it.” Prof Schore points out that if a baby is not treated properly in the first two years of life, the genes for various aspects of brain function, including intelligence, cannot operate, and may not even come into existence. Nature and nurture cannot be disentangled: the genes a baby has will be profoundly affected by the way it is treated. This discovery has enormous implications for social policy.
Free Audio Lessons | Lavinia Plonka Each month we will explore a somatic approach toward improving the quality of life. I believe that since body and mind are intimately connected, when you learn more about how you function physically, you discover insights about your psychological self as well. Therefore, sometimes these lessons will offer ways to think about the movements from a mental and emotional as well as physical point of view. This Week’s Lesson Where is Your Head? This lesson will put your head back in its place – you’ll feel taller, lighter and of course, smarter! Past Lessons Shoulder Clock Take a few moments to relax your shoulder and discover ease with this simple movement. Take a Walk A mini-lesson designed to put your feet where they need to go. A Longer Spine You can’t just “command” your skeleton back into balance. A Trip Around the Sit Bones Discover simple strategies to improve your posture and make sitting more comfortable. Relax the Hand Eyes Sitting At Your Desk Share this with a friend:
Alcohol's Effects on the Body Drinking too much – on a single occasion or over time – can take a serious toll on your health. Here’s how alcohol can affect your body: Brain: Alcohol interferes with the brain’s communication pathways, and can affect the way the brain looks and works. These disruptions can change mood and behavior, and make it harder to think clearly and move with coordination. Heart: Drinking a lot over a long time or too much on a single occasion can damage the heart, causing problems including: Cardiomyopathy – Stretching and drooping of heart muscle Arrhythmias – Irregular heart beat Stroke High blood pressure Research also shows that drinking moderate amounts of alcohol may protect healthy adults from developing coronary heart disease. Liver: Heavy drinking takes a toll on the liver, and can lead to a variety of problems and liver inflammations including: Steatosis, or fatty liver Alcoholic hepatitis Fibrosis Cirrhosis Mouth Esophagus Throat Liver Breast Learn more about alcohol’s effects on the body.
Alcohol Facts and Statistics For more information, please visit: www.niaaa.nih.gov 1 Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). 2014 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). Table 2.41B—Alcohol use in lifetime, past year, and past month among persons aged 18 or older, by demographic characteristics: Percentages, 2013 and 2014. Available at: 2 Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). 2014 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). 3 Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). 2014 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). 4 Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). 2014 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). 5 Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). 2014 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). 9 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 38 U.S. 39 U.S.