

Genetic switch for limbs and digits found in ancient fish. Public release date: 11-Jul-2011 [ Print | E-mail Share ] [ Close Window ] Contact: Robert Mitchumrobert.mitchum@uchospitals.edu 773-795-5227University of Chicago Medical Center.

Heaviest elements yet join periodic table - physics-math - 03 June 2011. Elements 114 and 116 have been officially added to the periodic table, becoming its heaviest members yet.
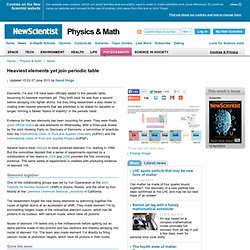
570-Million-Year-Old Fossils Hint at Origins of Animal Kingdom. New research suggests that fossils thought to represent some of the earliest multicellular life are instead single-celled, amoeba-like organisms.
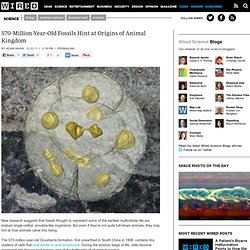
But even if they’re not quite full-blown animals, they may hint at how animals came into being. The 570-million-year-old Doushanto formation, first unearthed in South China in 1998, contains tiny clusters of cells that look similar to animal embryos. During the embryo stage of life, cells become organized into tissues and organs, one of the hallmarks of all animal species. Using a technique called x-ray tomographic microscopy, researchers captured an unprecedented level of detail in the Doushanto fossils, imaging internal and external features down to a ten-thousandth of an inch. The World's Oldest Mattress. The capitalist network that runs the world - physics-math - 19 October 2011. AS PROTESTS against financial power sweep the world this week, science may have confirmed the protesters' worst fears.

An analysis of the relationships between 43,000 transnational corporations has identified a relatively small group of companies, mainly banks, with disproportionate power over the global economy. The study's assumptions have attracted some criticism, but complex systems analysts contacted by New Scientist say it is a unique effort to untangle control in the global economy. Pushing the analysis further, they say, could help to identify ways of making global capitalism more stable. The idea that a few bankers control a large chunk of the global economy might not seem like news to New York's Occupy Wall Street movement and protesters elsewhere (see photo).
The sharp eyes of Anomalocaris, a top predator that lived half a billion years ago. Before killer whales and polar bears, before sharks and tyrannosaurs, the world’s top predator was probably a bizarre animal called Anomalocaris.
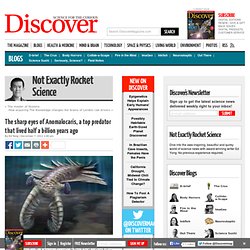
It lived in the Cambrian period, over half a billion years ago, when life was confined to the seas and animals took on bizarre shapes that haven’t been seen since. Many scientists believe that Anomalocaris ruled this primordial world as a top predator. At up to a metre in length, it was the largest hunter of its time. It chased after prey with undulating flaps on its sides and a large fan-shaped tail. First ancient proteome revealed. Mammoth bones have yielded proteins that could help to elucidate the animals' evolutionary history.

An international group of scientists has managed to identify 126 distinct protein sequences from a 43,000-year old bone from a woolly mammoth ( ). The study, in the 1 , unleashes the field of palaeoproteomics by identifying prehistoric protein sequences that could be used to help identify species, evolutionary relationships and even, perhaps, ancient diseases.
Proteomic analysis could therefore be used as an alternative to DNA analysis in samples that are too degraded to contain any genetic material. Protein sequences have previously been published for dinosaur fossils, including a 68-million-year-old 2 and an 80-million-year-old hadrosaur 3 , but the results have proved controversial (see Origin of ‘ ’ protein questioned ). Previous analysis of the same mammoth's DNA had revealed that the animal probably had a dark-coloured coat 4 . Prolific proteins. Wired.com. First Superpredator Had Enormous Eyes on Stalks. (Credit: Katrina Kenny, University of Adelaide) The world's first superpredator was a giant crustacean with enormous eyes and a razor sharp mouth, according to a new study in the journal Nature.
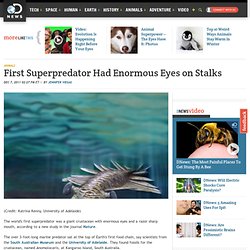
The over 3-foot-long marine predator sat at the top of Earth's first food chain, say scientists from the South Australian Museum and the University of Adelaide. They found fossils for the crustacean, named Anomalocaris, at Kangaroo Island, South Australia. NEWS: Ancient Animal Explosion Gets Bigger With New Finds. Arbitrary, Development-Obsessed Environmental Policy-Making Threatening Turkey's Ecosystems.
A New Hominin – A. sediba. Following the branching bush of human evolution is getting increasingly difficult.
When I studied human evolution in college, things were much simpler. There were a few Australopithecus species followed by a few Homo species, leading to modern humans. It was recognized at the time that these fossil species probably did not represent a nice clean straight line to Homo sapiens, but it seems the family tree has become much bushier than was imagined at the time. RNA dynamics deconstructed. RNA plays a critical role in directing the creation of proteins, but there is more to the life of an RNA molecule than simply carrying DNA’s message.

One can imagine that an RNA molecule is born, matures, and, eventually, meets its demise. Researchers at the Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT have developed an approach that offers many windows into the life cycle of these essential molecules and will enable other scientists to investigate what happens when something in a cell goes wrong. They describe their approach, which offers high resolution and a comprehensive scope, in a Nature Biotechnology article published online on April 24. Box jellyfish stable-eyes vision to hunt prey : Neurophilosophy. Protein flaws responsible for complex life, study says. 19 May 2011Last updated at 09:13 By Jason Palmer Science and technology reporter, BBC News Some proteins have remained largely unchanged since they first appeared Tiny structural errors in proteins may have been responsible for changes that sparked complex life, researchers say.

A comparison of proteins across 36 modern species suggests that protein flaws called "dehydrons" may have made proteins less stable in water. Mammals first evolved big brains for better sense of smell. Friday, May 20, 2011 CT scans of modern short-tailed opossum (upper left) and Hadrocodium (bottom right) brains (pink) through cut-away skulls.
Turkey opens restaurant for vultures. The first vulture restaurant has opened in Turkey, and already it is acquiring customers. Photo courtesy of Çağan Şekercioğlu The site selected for the restaurant is in Iğdır, in view of Mount Ağrı, near the border with Armenia in Eastern Anatolia (see map below). The area is home to four vulture species–the Egyptian, bearded, griffon and black vultures. Ancient primate fossil unearthed. 2 August 2011Last updated at 16:35 The researchers say the skull belongs to a creature called Ugandapithecus major. ?Doğanın ücretsiz ekosistem hizmetlerini yok edersek, medeniyetler de çöker? Human Ancestors in Eurasia Earlier than Thought. Jellyfish Blooms Increase Carbon Emissions, Upend Marine Food Webs. Photo credit: Jaymi Heimbuch/Creative CommonsJellyfish are taking over the world's oceans.
Warming waters and the elimination of key predators like sharks and tuna, hav made conditions ideal for the soft, brainless, organisms and their numbers have increased steadily for years—with populations occasionally exploding in "blooms. " Now, new research shows that jellyfish are upending marine food webs—and disrupting ocean ecosystems' ability to sync carbon in the process.SLIDESHOW: Jellyfish: Future Rulers of the Oceans?
The problem is that jellyfish are voracious predators that consume plankton rapidly and in huge quantities. This effectively prevents small fish from finding the food the need to thrive, collapsing an important low-ring of the chain. "This restricts the transfer of energy up the food chain," explained Rob Condon, who led the study, "because jellyfish are not readily consumed by other predators. " Photo credit: Jaymi Heimbuch/Creative Commons. The challenge of microbial diversity: Out on a limb. Two Ultraheavy Elements Added to Periodic Table. By Mark Brown, Wired UK. Australopithecus sediba may be an ancestor of modern humans. Three new bat species discovered in Indochina. Three new bat species have been discovered after an international team of scientists from the Hungarian Natural History Museum (HNHM) and Fauna & Flora International (FFI) embarked on a study in southern Indochina.
Scientists discover 12 new frog species in India. Years of combing tropical mountain forests, shining flashlights under rocks and listening for croaks in the night have paid off for a team of Indian scientists which has discovered 12 new frog species plus three others thought to have been extinct. It's a discovery the team hopes will bring attention to India's amphibians and their role in gauging the health of the environment. Worldwide, 32 percent of the world's known amphibian species are threatened with extinction, largely because of habitat loss or pollution, according to the group Global Wildlife Conservation. Mouse Genomes Catalogued. Fossil eyes show wraparound three-dimensional vision, half a billion years ago. Early hunters killed mastodons with mastodons (Also, you can chuck a bone spear through a car. Who knew?) Near-perfect young Dinosaur fossil found in Bavaria. The world’s longest cells? Speculations on the nervous systems of sauropods « Sauropod Vertebra Picture of the Week.
May 23, 2011. 1118669109.full. The eyes have it – incredible ways of seeing the world. New “Evil Spirit” Dino Bridges Evolutionary Gap. Modern humans in Arabia >100,000 years ago. First Wolves Tagged for GPS Tracking in Turkey.