

Msoute/vertx-deploy-tools: vertx-deploy-tools. GitHub - msoute/vertx-deploy-tools: vertx-deploy-tools. Square Open Source. Bugsnag - Detect and diagnose crashes in your applications. Sentry: Track exceptions with modern error logging for JavaScript, Python, Ruby, Java, and Node.js. GitHub - vert-x3/vertx-openshift-diy-quickstart. GitHub - vert-x3/vertx-openshift-cartridge.
h5bp/server-configs-nginx. Vert.x Reading data from request. There are several objects in Vert.x that allow items to be read from and written.

In previous versions the streams.adoc package was manipulating Buffer objects exclusively. From now, streams are not anymore coupled to buffers and work with any kind of objects. In Vert.x, calls to write item return immediately and writes are internally queued. It’s not hard to see that if you write to an object faster than it can actually write the data to its underlying resource then the write queue could grow without bound - eventually resulting in exhausting available memory. To solve this problem a simple flow control capability is provided by some objects in the Vert.x API. Any flow control aware object that can be written-to implements ReadStream, and any flow control object that can be read-from is said to implement WriteStream. Let’s take an example where we want to read from a ReadStream and write the data to a WriteStream.
We’re almost there, but not quite. And there we have it. ReadStream WriteStream. JS: How to read the complete request. On 29/09/12 00:12, Jochen Bedersdorfer wrote: > For the life of me I couldn't find an example in JavaScript where a > request JSON payload is being read.
> > So here is a simple echo example (without error handling and stuff): > > load('vertx.js'); > var server = vertx.createHttpServer(); > var routeMatcher = new vertx.RouteMatcher(); > routeMatcher.post('/api/echo', function(req) { > *req.bodyHandler(function (data) { Vert.x 3 MongoDB Conf. The client is configured with a json object.

The following configuration is supported by the mongo client: db_name Name of the database in the mongoDB instance to use. Defaults to default_db useObjectId Toggle this option to support persisting and retrieving ObjectId’s as strings. The mongo client tries to support most options that are allowed by the driver. Connection_string The connection string the driver uses to create the client. Specific driver configuration options Driver option descriptions host The host the mongoDB instance is running. Port The port the mongoDB instance is listening on. Hosts An array representing the hosts and ports to support a mongoDB cluster (sharding / replication) A host in the cluster The port a host in the cluster is listening on replicaSet The name of the replica set, if the mongoDB instance is a member of a replica set maxPoolSize.
Vert.x. What is Vert.x?

Vert.x is a polyglot, non-blocking, event-driven application platform that runs on the JVM. Some of the key highlights include: Polyglot. You can write your application components in JavaScript, Ruby, Groovy, Java or Python, and you can mix and match several programming languages in a single application.Simple actor-like concurrency model.
Vert.x. Tomcat vs Vert.x. Tomcat, at least with the 2.x servlet version is using a thread per request model of execution.
Basically each request that is received from a client uses and blocks a thread in your tomcat jvm as long as the request is being processed (same with e.g. apache with worker mpm model), so that the number of client connections is directly related to the number of used threads. Depending on the memory consumption of the servlet threads, you will usually have a rather limited number of threads available (e.g. 100 or 250), which limits the number of clients that can connect. This is not an issue when you have a "normal" web 1.0 application, plus you will usually move the static files to another server, either a cdn or at least an apache or nginx server that is running before the tomcat or is running on an alternate address on the same machine. Undertow, Vert.x, and Netty Benchmarks - Miles to go 2.0 ... 90 frameworks (including web application platforms, full-stack frameworks, and micro-frameworks) are compared using 230 tests by Tech Empower.
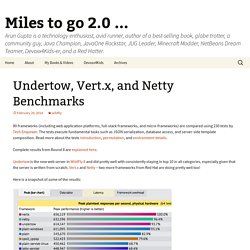
The tests execute fundamental tasks such as JSON serialization, database access, and server-side template composition. Read more about the tests introduction, permutation, and environment details. Complete results from Round 8 are explained here. Undertow is the new web server in WildFly 8 and did pretty well with consistently staying in top 10 in all categories, especially given that the server is written from scratch.
Vert.x and Netty – two more frameworks from Red Hat are doing pretty well too! Here is a snapshot of some of the results: Top 3 frameworks here are by Red Hat WildFly 8 was recently released and uses Undertow as the web server.