

Chord (distributed hash table) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedi. In computing, Chord is a protocol and algorithm for a peer-to-peer distributed hash table.
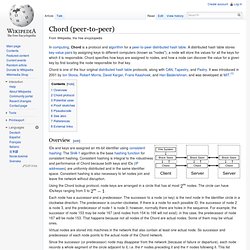
A distributed hash table stores key-value pairs by assigning keys to different computers (known as "nodes"); a node will store the values for all the keys for which it is responsible. Chord specifies how keys are assigned to nodes, and how a node can discover the value for a given key by first locating the node responsible for that key. IDs and keys are assigned an -bit identifier using consistent hashing. Paxos algorithm. Consensus protocols are the basis for the state machine approach to distributed computing, as suggested by Leslie Lamport[2] and surveyed by Fred Schneider.[3] The state machine approach is a technique for converting an algorithm into a fault-tolerant, distributed implementation.
Ad-hoc techniques may leave important cases of failures unresolved. The principled approach proposed by Lamport et al. ensures all cases are handled safely. The Paxos protocol was first published in 1989 and named after a fictional legislative consensus system used on the Paxos island in Greece.[4] It was later published as a journal article in 1998.[5] The Paxos family of protocols includes a spectrum of trade-offs between the number of processors, number of message delays before learning the agreed value, the activity level of individual participants, number of messages sent, and types of failures.