

Granite Stone,Granite Slabs,Granite Tiles,Natural Granite Stone,Granite Tiles Exporters. Looking for Stones Suppliers?
Let us help you find the right suppliers! Free, Easy, Simple way to find Suppliers. Granite, from igneous rock, is a very hard, crystalline, and primarily composed of feldspar, quartz accompanied by one or more dark minerals. It is visibly homogeneous in texture. The term "Granite" means "grain" in Latin word "Granum" because of its granular nature. Granite is the hardest building stone, and granite slabs and granite tiles occupy a prominent place among dimensional stones.
The principal characteristics of granite also include high load bearing capacity, crushing strength, abrasive strength, amenability to cutting and shaping without secondary flaws, ability to yield thin and large slabs and - above all - durability. Due to highly dense grain, it is impervious to stain. Limestone Rocks,Natural Limestone,Limestone Properties,Limestone Suppliers. Looking for Stones Suppliers?
Let us help you find the right suppliers! Free, Easy, Simple way to find Suppliers. Limestone is calcareous sedimentary rocks formed at the bottom of lakes and seas with the accumulation of shells, bones and other calcium rich goods. It is composed of calcite (CaCO3). The organic matter upon which it settles in lakes or seas, are preserved as fossils. The rock which contain more than 95% of calcium carbonate is known as high-calcium limestone. Slate Stone,Natural Slate Stone,Slate Stone Suppliers,Slate Stone Exporters.
Looking for Stones Suppliers?
Let us help you find the right suppliers! Free, Easy, Simple way to find Suppliers. Slates are dense and fine grained rock. GCSE Bitesize: Uses of limestone. Chemical Properties of Sandstone,Sandstone Chemical Properties,Chemical Composition of Sandstone. Home » Chemical Properties of Sandstone Sandstone is basically a sedimentary rock which is primarily composed of tiny minerals or rock grains.
A majority of sandstones are composed of minerals like quartz and feldspar which are present in the earth's crust in abundance. The common constituents of sand are quartz and feldspar. The sand may also consists of organic matter or rock fragments. As sandstones are made of sand, the properties of sand and the sandstones are almost the same. The percentage of various constituents of sandstone varies between the following ranges: Metamorphic rocks. Granite: Igneous Rock - Pictures, Definition. What is Granite?
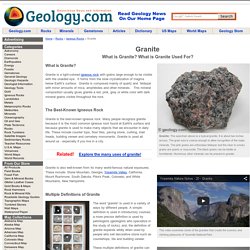
Granite is a light-colored igneous rock with grains large enough to be visible with the unaided eye. It forms from the slow crystallization of magma below Earth’s surface. Sandstone: Sedimentary Rock - Pictures, Definition. What is Sandstone?
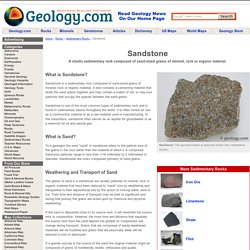
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed of sand-sized grains of mineral, rock or organic material. It also contains a cementing material that binds the sand grains together and may contain a matrix of silt- or clay-size particles that occupy the spaces between the sand grains. Sandstone is one of the most common types of sedimentary rock and is found in sedimentary basins throughout the world.
It is often mined for use as a construction material or as a raw material used in manufacturing. In the subsurface, sandstone often serves as an aquifer for groundwater or as a reservoir for oil and natural gas. Slate: Metamorphic Rock - Pictures, Definition & More. What is Slate?

Slate is a fine-grained, foliated metamorphic rock that is created by the alteration of shale or mudstone by low-grade regional metamorphism. It is popular for a wide variety of uses such as roofing, flooring and flagging because of its durability and attractive appearance. Composition of Slate Slate is composed mainly of clay minerals or micas depending upon the degree of metamorphism to which it has been subjected. The original clay minerals in shale alter to micas with increasing levels of heat and pressure. Sedimentary rock. Sedimentary rock is one of the three main rock groups (along with igneous and metamorphic rocks) and is formed in four main ways: by the deposition of the weathered remains of other rocks (known as 'clastic' sedimentary rocks); by the accumulation and the consolidation of sediments; by the deposition of the results of biogenic activity; and by precipitation from solution.

Sedimentary rocks include common types such as chalk, limestone, sandstone, clay and shale. Sedimentary rocks cover 75% of the Earth's surface. Limestone: Rock Uses, Formation, Composition, Pictures. What is Limestone?
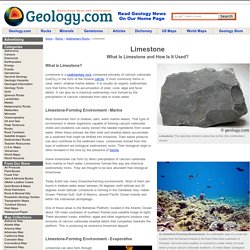
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) in the form of the mineral calcite. It most commonly forms in clear, warm, shallow marine waters. It is usually an organic sedimentary rock that forms from the accumulation of shell, coral, algal and fecal debris. It can also be a chemical sedimentary rock formed by the precipitation of calcium carbonate from lake or ocean water. Limestone-Forming Environment - Marine Most limestones form in shallow, calm, warm marine waters. Some limestones can form by direct precipitation of calcium carbonate from marine or fresh water. Today Earth has many limestone-forming environments.
One of these areas is the Bahamas Platform, located in the Atlantic Ocean about 100 miles southeast of southern Florida (see satellite image at right). Limestone-Forming Environment - Evaporative Limestone can also form through evaporation. Composition of Limestone The "Acid Test" for Carbonate Minerals. Obsidian: Igneous Rock - Pictures, Uses, Properties. What is Obsidian?
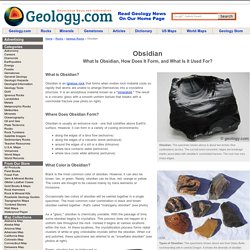
Obsidian is an igneous rock that forms when molten rock material cools so rapidly that atoms are unable to arrange themselves into a crystalline structure. It is an amorphous material known as a "mineraloid. " The result is a volcanic glass with a smooth uniform texture that breaks with a conchoidal fracture (see photo on right). Where Does Obsidian Form? Obsidian is usually an extrusive rock - one that solidifies above Earth's surface. Along the edges of a lava flow (extrusive)along the edges of a volcanic dome (extrusive)around the edges of a sill or a dike (intrusive)where lava contacts water (extrusive)where lava cools while airborne (extrusive) Pictures of Foliated and Non-Foliated Types.
Home » Rocks » Metamorphic Rocks Pictures of Foliated and Non-Foliated Rock Types Amphibolite is a non-foliated metamorphic rock that forms through recrystallization under conditions of high viscosity and directed pressure. It is composed primarily of hornblende (amphibole) and plagioclase, usually with very little quartz. The specimen shown above is about two inches (five centimeters) across. Chemical Formula - Obsidian. Sandstone Facts.