

Rainbow. Double rainbow and supernumerary rainbows on the inside of the primary arc.
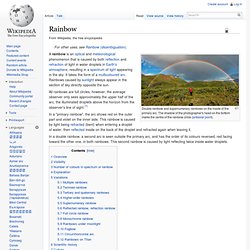
The shadow of the photographer's head on the bottom marks the centre of the rainbow circle (antisolar point). All rainbows are full circles, however, the average observer only sees approximately the upper half of the arc, the illuminated droplets above the horizon from the observer's line of sight.[1] In a "primary rainbow", the arc shows red on the outer part and violet on the inner side. This rainbow is caused by light being refracted (bent) when entering a droplet of water, then reflected inside on the back of the droplet and refracted again when leaving it. Aurora (astronomy) Natural light display that occurs in the sky, primarily at high latitudes (near the Arctic and Antarctic) Images of auroras from around the world, including those with rarer red and blue lights Aurora australis from the ISS, 2017.
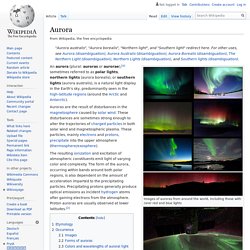
Video of this encounter: [2] An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae),[a] sometimes referred to as polar lights, northern lights (aurora borealis), or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in the Earth's sky, predominantly seen in the high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic).
Auroras are the result of disturbances in the magnetosphere caused by solar wind. Aurora borealis. Rainbow cloud towers over Mount Everest. By Daily Mail Reporter Updated: 12:31 GMT, 16 March 2011 Hovering in the sky, this rainbow cloud over Mount Everest took an astonished astronomer by surprise.

Oleg Bartunov, 51, caught the spectacle on camera during a Himalayas expedition in Nepal.