

What are Scalar Waves? What are Scalar Waves? « Electromagnetic Frequencies. Posted by healthyself in Beneficial frequencies, Biological Activity, Biological Effects, Blogroll, Cell phone safety, Definitions, Electrosensitivity, Healing, Health, Health related, Mitigation, Solutions, Vibration, Vibrational Medicine, Waves. Trackback ….”The term scalar was used by Nikola Tesla at the end of the last century as a part of powerful non-Hertzian energy (without frequencies) which he referred to as cosmic waves. Einstein gave reference to the scalar energies in the 1920’s.
Yet even today modern physics textbooks and scholarly publications do not mention scalar energies. This is understandable. Tesla's Scalar Waves Still Beaming On! The superluminal (faster than light) scalar or longitudinal waves Nikola Tesla used to magnify and wirelessly transmit power are not just a thing of the past.
IEEE engineer, Steve Jackson, discusses and demonstrates how they can be utilized today, and he is open sourcing it here! By Hank MillsPure Energy Systems News Nikola Tesla is the father of the modern age. Scalar field. Quartic interaction. This article refers to a type of self-interaction in scalar field theory, a topic in quantum field theory.
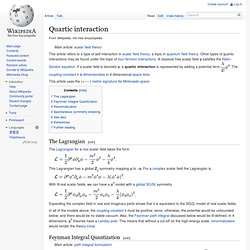
Other types of quartic interactions may be found under the topic of four-fermion interactions. A classical free scalar field φ satisfies the Klein–Gordon equation. Equation of motion in a scalar field. In the Nordström's second theory of gravitation, the field equation is \varphi \,\square \left( \varphi \right) =4\,\pi { \it GT}_{{m}} where \square is the D'Alembertian operator defined in the Minkowskian spacetime with metric (+,-,-,-), T_m is the trace of the material contribution to the total stress-energy-momentum tensor T_{{\mu \nu }} and finally we have \varphi implying the potential.
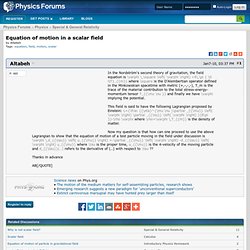
This field is said to have the following Lagrangian proposed by Einstein: L={\frac {{\eta}^{\mu \nu }\partial _{{\mu}} \left( \varphi \right) \partial _{{\nu}} \left( \varphi \right) }{8\pi }}-\rho \varphi. Gradient of a scalar field. Algebra. Scalar field theory. Law prohibiting electromagnetic and mind control weapons in Europe. What is HAARP IS HAARP Dangerous HAARP and Weather Control.flv. Untitled. Undefined undefined Published in Commander X's Guide To Incredible Conspiracies Alternatively invisible moving barriers and globes made of plasma (produced by crossed scalar beams) could destroy any nuclear missile easily while it moves towards the target and failing all these, it could be destroyed by entering the target's territory by passing through a Tesla shield which would explode anything entering its airspace.

To begin with, defense using scalar technology could intercept it before it even landed. Antigravitywg024.jpg (JPEG Image, 600 × 662 pixels) - Scaled (87%) Vortex Ring Collision. Water has Memory. How to make a fire tornado. Magnetic Reconnection (Wikipedia) Magnetic Reconnection: This view is a cross-section through four magnetic domains undergoing separator reconnection.
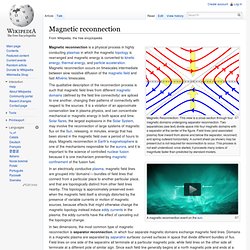
Two separatrices (see text) divide space into four magnetic domains with a separator at the center of the figure. Field lines (and associated plasma) flow inward from above and below the separator, reconnect, and spring outward horizontally. Real reason NASA bombed the moon. Electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation.[4] The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object has a different meaning, and is instead the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object.
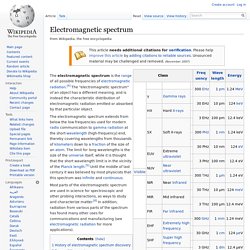
Most parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are used in science for spectroscopic and other probing interactions, as ways to study and characterize matter.[6] In addition, radiation from various parts of the spectrum has found many other uses for communications and manufacturing (see electromagnetic radiation for more applications). History of electromagnetic spectrum discovery The first discovery of electromagnetic radiation other than visible light came in 1800, when William Herschel discovered infrared radiation.[7] He was studying the temperature of different colors by moving a thermometer through light split by a prism. He noticed that the highest temperature was beyond red. Where:
Matter is Vibrating. Extraordinary Toroidal Vortices. SolarBeat. Triangle wave. A bandlimited triangle wave pictured in the time domain (top) and frequency domain (bottom).
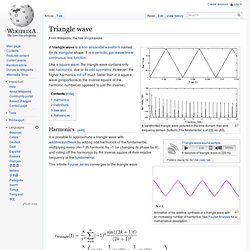
The fundamental is at 220 Hz (A3). A triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape. It is a periodic, piecewise linear, continuous real function. Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics, due to its odd symmetry. However, the higher harmonics roll off much faster than in a square wave (proportional to the inverse square of the harmonic number as opposed to just the inverse). Wave. In physics, a wave is a disturbance or oscillation that travels through space and matter, accompanied by a transfer of energy.
Wave motion transfers energy from one point to another, often with no permanent displacement of the particles of the medium—that is, with little or no associated mass transport. They consist, instead, of oscillations or vibrations around almost fixed locations. Waves are described by a wave equation which sets out how the disturbance proceeds over time. The mathematical form of this equation varies depending on the type of wave. Phase space. Phase space of a dynamic system with focal instability, showing one phase space trajectory A plot of position and momentum variables as a function of time is sometimes called a phase plot or a phase diagram.
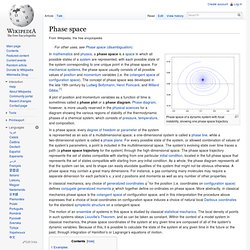
Phase diagram, however, is more usually reserved in the physical sciences for a diagram showing the various regions of stability of the thermodynamic phases of a chemical system, which consists of pressure, temperature, and composition. In classical mechanics, any choice of generalized coordinates q i for the position (i.e. coordinates on configuration space) defines conjugate generalized momenta pi which together define co-ordinates on phase space. Wave–particle duality. Origin of theory[edit] The idea of duality originated in a debate over the nature of light and matter that dates back to the 17th century, when Christiaan Huygens and Isaac Newton proposed competing theories of light: light was thought either to consist of waves (Huygens) or of particles (Newton).

Through the work of Max Planck, Albert Einstein, Louis de Broglie, Arthur Compton, Niels Bohr, and many others, current scientific theory holds that all particles also have a wave nature (and vice versa).[2] This phenomenon has been verified not only for elementary particles, but also for compound particles like atoms and even molecules. For macroscopic particles, because of their extremely short wavelengths, wave properties usually cannot be detected.[3] Brief history of wave and particle viewpoints[edit] Photon. Nomenclature[edit] In 1900, Max Planck was working on black-body radiation and suggested that the energy in electromagnetic waves could only be released in "packets" of energy.
In his 1901 article [4] in Annalen der Physik he called these packets "energy elements". Wave equation. Spherical waves coming from a point source. The wave equation is an important second-order linear partial differential equation for the description of waves – as they occur in physics – such as sound waves, light waves and water waves. It arises in fields like acoustics, electromagnetics, and fluid dynamics. Historically, the problem of a vibrating string such as that of a musical instrument was studied by Jean le Rond d'Alembert, Leonhard Euler, Daniel Bernoulli, and Joseph-Louis Lagrange.[1][2][3][4] In 1746, d’Alambert discovered the one-dimensional wave equation, and within ten years Euler discovered the three-dimensional wave equation.[5] Introduction[edit] where ∇2 is the (spatial) Laplacian and where c is a fixed constant.
7 Functions of the Pyramid. Synchronized probes explore Bermuda Triangle's swirling vortices. (Phys.org) -- Some might say that University of Washington oceanographers did well to only lose one of 21 underwater probes, given that they were deployed near the notorious Bermuda Triangle, where boats and airplanes have been known to disappear without a trace. The scientists chose the location to research its swirling whirlpools via a pioneering experiment that repeatedly sent the probes deep into the ocean and back to the surface in unison. “Nothing like this has ever been done,” said Tom Sanford, an oceanographer at the UW’s Applied Physics Laboratory. “It will be the paradigm for future experiments.” Typically, oceanographers may deploy an instrument in one place and then travel by boat to another spot to launch it again. Lost Pyramids and Other Hidden Ancient Artifacts. Zero-point energy.
Zero-point energy, also called quantum vacuum zero-point energy, is the lowest possible energy that a quantum mechanical physical system may have; it is the energy of its ground state. "Giza Power Plant" Part 1 by Chris Dunn. Nuclear Reactors. The Becker-Hagens Grid. By Bethe Hagens 1984 from Montalk Website. Earth's Grids - Typography - Vile Vortexes. Earth's Grid Systems Science and Pseudoscience. Ley Lines & the Earth's Vertices 2. World Grid.