

Stussybrah. Brain Chip Helps Quadriplegics Move Robotic Arms with Their Thoughts. Reach out: In a clinical trial, a woman used a brain-chip system to control a robotic arm with her thoughts and reach for a drink of coffee.
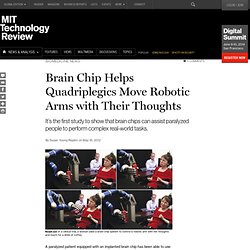
A paralyzed patient equipped with an implanted brain chip has been able to use a robotic arm to reach for and pick up a bottle of coffee, bring it close enough to her face so she could drink from a straw, and then place the bottle back on the table. The quadriplegic patient was outfitted with an electronic brain implant that can drive a robotic arm to reach and grasp objects (see video). A study published today in the journal Nature shows that people with the brain chips can use the devices to perform complex three-dimensional tasks that could be helpful in daily life.
Cyber war. Shankargallery. Aloharmobile.com. Singularity-Emergence A.I. Josh.bushong. Science/Math. Make A Cheap & Easy Solar USB Charger. Photos by Joshua Zimmerman The craftster behind the very popular $3 solar-powered emergency radio is back with a new awesome project: a cheap solar battery charger with a USB plug.
Get Paid to Travel. Travel Writing — By Lost Girls on January 30, 2011 at 2:20 pm.
VS 2nd place - Canadian Forces Remix. The Rise of Nimble Medicine. Editor’s note: This guest post was written by Dave Chase, the CEO of Avado.com, a patient portal & relationship management company that was a TechCrunch Disrupt finalist.

Previously he was a management consultant for Accenture’s healthcare practice and founder of Microsoft’s Health platform business. You can follow him on Twitter @chasedave. What's Your "Minimum Viable Concept?" Eric Ries's Lean Startup book famously promotes the "Minimum Viable Product" as a way for start-ups to think about how to spend limited resources to get a product out the door.
Physics, Cosmology, Astronomy. Physics, Cosmology, Astronomy. Harvesting Iron Asteroids and bringing them down from orbit? Harvesting asteroids. Physics, Cosmology, Astronomy. Sky. Large Hadron Collider scientists think they may have disproved a law of physics by breaking the speed of light. ASTONISHED scientists are in complete shock after they apparently blew apart one of the basic laws of physics.
Researchers say they have recorded particles travelling faster than the speed of light – something that was understood to be impossible. OPERA experiment. The Oscillation Project with Emulsion-tRacking Apparatus (OPERA) is an instrument used in a scientific experiment for detecting tau neutrinos from muon neutrino oscillations.
The experiment is a collaboration between CERN in Geneva, Switzerland, and the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso (LNGS) in Gran Sasso, Italy and uses the CERN Neutrinos to Gran Sasso (CNGS) neutrino beam. The process starts with protons from the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) at CERN being fired in pulses at a carbon target to produce pions and kaons. These particles decay to produce muons and neutrinos.[1] Special relativity. Special relativity implies a wide range of consequences, which have been experimentally verified,[2] including length contraction, time dilation, relativistic mass, mass–energy equivalence, a universal speed limit, and relativity of simultaneity.
It has replaced the conventional notion of an absolute universal time with the notion of a time that is dependent on reference frame and spatial position. Rather than an invariant time interval between two events, there is an invariant spacetime interval. Combined with other laws of physics, the two postulates of special relativity predict the equivalence of mass and energy, as expressed in the mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, where c is the speed of light in vacuum.[3][4]
Albert Einstein. Albert Einstein (/ˈælbərt ˈaɪnʃtaɪn/; German: [ˈalbɐrt ˈaɪnʃtaɪn]; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist.
Einstein's work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science.[4][5] He developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics (alongside quantum mechanics).[3][6]:274 Einstein is best known in popular culture for his mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2 (which has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation").[7] He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics for his "services to theoretical physics", in particular his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect, a pivotal step in the evolution of quantum theory.[8] Near the beginning of his career, Einstein thought that Newtonian mechanics was no longer enough to reconcile the laws of classical mechanics with the laws of the electromagnetic field. This led to the development of his special theory of relativity.
Life Early life and education Death. DIY / Physical computing / Electonics. Self-Replicating Repairing Robots ( Boston Dynamics: Dedicated to the Science and Art of How Things. Shadow Robot Company: Home Page. Robotics. Robotics is the branch of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering and computer science that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots,[1] as well as computer systems for their control, sensory feedback, and information processing.
These technologies deal with automated machines that can take the place of humans in dangerous environments or manufacturing processes, or resemble humans in appearance, behavior, and/or cognition. Many of today's robots are inspired by nature contributing to the field of bio-inspired robotics. The concept of creating machines that can operate autonomously dates back to classical times, but research into the functionality and potential uses of robots did not grow substantially until the 20th century.[2] Throughout history, robotics has been often seen to mimic human behavior, and often manage tasks in a similar fashion.
Etymology[edit] History of robotics[edit] Robotic aspects[edit] Components[edit] Power source[edit] Welcome to DEKA Research and Development. Le Site des Robots, de la Robotique, des Exosquelettes et de leu. ASIMO - The World's Most Advanced Humanoid Robot. Hirose and Fukushima Laboratory. Introduction. Hirose Fukushima Lab. Spécialiste de la conception de minis robots poissons autonomes. 22 EU Countries Ratify ACTA, Key Parliament Member Calls it a 'Charade' Most member states of the European Union have signed the Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement (ACTA) at a ceremony in Tokyo, Japan on Thursday, Jan. 26. ACTA is a global treaty that tries to normalize copyright protection and IP standards. It's similar to SOPA and PIPA, proposed U.S. laws which have recently been dropped after massive internet protests, but in many ways even more dangerous.
Unfortunately (and unlike SOPA and PIPA), ACTA has been signed by many states without a wide, open public discussion. Australia, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Morocco, New Zealand, Singapore and the United States signed the ACTA on 1 Oct 2011. Streamie.