

Earth Floor: Biomes. Arctic Tundra: Animals Not many kinds of animals live year-round in the Arctic tundra.

Most birds and mammals only use the tundra as a summer home. Mammals that do live year-round in the tundra include the muskox, Arctic wolf, and brown bear; and each has its own way of adapting to the extreme climatic conditions. Animals need to find ways to stay warm and to provide nourishment for themselves in order to survive the long, cold, winter months. Animal adaptations Migration and hibernation are examples of behavioral adaptations used by animals in the Arctic tundra. The fact that many animals do not live year-round in the tundra means they leave or migrate for a length of time to warmer climates. Hibernation is a combination of behavioral and physical adaptations. A physical adaptation used by the Musk Ox is the growth of two layers of fur--one short and the other long. Back | Next. Tundra Biome. Earth Floor: Biomes. Arctic Tundra Arctic tundra is found across northern Alaska, Canada, and Siberia.

This biome has long cold winters and short cool summers. The Arctic tundra has low precipitation (less than 10 inches per year) and dry winds. These conditions make the Arctic tundra a desert-like climate (see climograph). *Tundra encroachment by tundra due to climate change. In Alaska, trees growing at the very edge of their northern range may be influenced by warming climate.
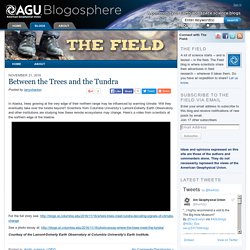
Will they eventually take over the tundra beyond? Scientists from Columbia University’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory and other institutions are studying how these remote ecosystems may change. Here’s a video from scientists at the northern edge of the treeline. Dirty, isolated and freezing: life in Arctic circle city – in pictures. Lennox Island residents may be the first climate change refugees in Canada. As sea level rise threatens homes, indigenous people living on tiny Lennox Island face the possibility of becoming Canada‘s first climate change refugees. 450 Mi’kmaq people reside there, and have tried to protect their coasts with rock.

Ultimately, however, loss of land will likely force them to relocate. Lennox Island, which is right by Prince Edward Island, is losing land as sea levels creep upwards. In 1880, the island was around 1,500 acres big. Land surveys reveal the tiny island has now lost nearly 300 acres of that land. At least 77 acres were lost just between 1968 and 2010. Related: Tiny Alaskan village votes to abandon 400-year-old ancestral home because of climate change Residents have stacked boulders on the shores of the island in an attempt to guard against erosion, but such a tactic will likely only work for so long. Via VICE Images via Wikimedia Commons and Larry on Flickr. The Köppen Climate Classification System. In: The Cold Climate Updated 29 Jan 2013 Did you know that the Arctic Tundra is the world's youngest biome?
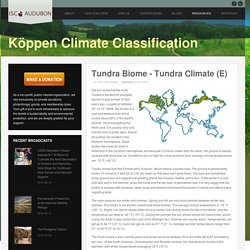
It was formed 10,000 years ago. Located at latitudes 55° to 70° North, the tundra is a vast and treeless land which covers about 20% of the Earth's surface, circumnavigating the North pole. It is usually very cold, and the land is pretty stark. Tundra comes from the Finnish word "tunturia", which means a barren land. The main seasons are winter and summer. The Arctic tundra is also a windy place and winds can blow between 30 to 60 miles (48 to 97 kilometers) per hour. The tundra is basically like a desert when it comes to precipitation.
There is barely any vegetation in the tundra, only about 1,700 different species, which isn't very much. Tundra Biome. Tundra Climate. The tundra biome. Online exhibits : The world's biomes The tundra biome Tundra is the coldest of all the biomes.

Tundra comes from the Finnish word tunturi, meaning treeless plain. It is noted for its frost-molded landscapes, extremely low temperatures, little precipitation, poor nutrients, and short growing seasons. Dead organic material functions as a nutrient pool. Characteristics of tundra include: Extremely cold climate Low biotic diversity Simple vegetation structure Limitation of drainage Short season of growth and reproduction Energy and nutrients in the form of dead organic material Large population oscillations. Major Weather Patterns - Tundra. Arctic Tundra And Polar Desert.