

Titanium. Titanium is a chemical element with symbol Ti and atomic number 22.
It is a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density and high strength. It is highly resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia and chlorine.
Titanium compounds. Halides. Organometallic complexes. History. Production and fabrication. Applications. Bioremediation. Precautions. Titanium in Africa. Titanium in Africa From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search Titanium mining in Africa has been beset by environmental problems due to the polluting nature of processing rutile, a principal titanium ore.
Titanium alloy. Titanium alloys are metals that contain a mixture of titanium and other chemical elements.
Such alloys have very high tensile strength and toughness (even at extreme temperatures). They are light in weight, have extraordinary corrosion resistance and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures. However, the high cost of both raw materials and processing limit their use to military applications, aircraft, spacecraft, medical devices, highly stressed components such as connecting rods on expensive sports cars and some premium sports equipment and consumer electronics. Although "commercially pure" titanium has acceptable mechanical properties and has been used for orthopedic and dental implants, for most applications titanium is alloyed with small amounts of aluminium and vanadium, typically 6% and 4% respectively, by weight. Titanium Metals. Titanium Metals Corporation (formerly NYSE: TIE), founded in 1950, is an American manufacturer of titanium-based metals products, focusing primarily on the aerospace industry.
In November 2012, it was announced the company was being purchased for $2.9 billion by Precision Castparts.[1] Its major U.S. operations are based in Morgantown, Pennsylvania; Henderson, Nevada; Vallejo, California; and Toronto, Ohio. Its overseas operations are primarily based in the United Kingdom (in the cities of Waunarlwydd and Swansea and the village of Witton) and France. The company's current headquarters are located in Dallas, Texas.[2] Titanium ring.
Titanium rings are jewelry rings or bands which have been primarily constructed from titanium.
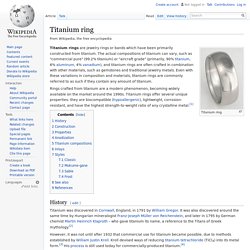
The actual compositions of titanium can vary, such as "commercial pure" (99.2% titanium) or "aircraft grade" (primarily, 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, 4% vanadium), and titanium rings are often crafted in combination with other materials, such as gemstones and traditional jewelry metals. Even with these variations in composition and materials, titanium rings are commonly referred to as such if they contain any amount of titanium. Titanium sublimation pump. A titanium sublimation pump (TSP) may be used as a component of ultra high vacuum systems.
Principle of operation[edit] Since the TSP filament has a finite lifetime, TSPs commonly have multiple filaments to allow the operator to switch to a new one without needing to open the chamber. Replacing used filaments can then be combined with other maintenance jobs.[1] The effectiveness of the TSP depends on a number of factors. Titanium in zircon geothermometry. Optical microscope photograph; the length of the zircon crystal is about 250 µm.
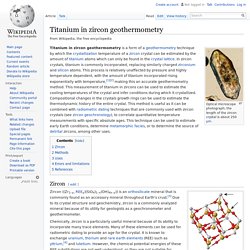
Titanium in zircon geothermometry is a form of a geothermometry technique by which the crystallization temperature of a zircon crystal can be estimated by the amount of titanium atoms which can only be found in the crystal lattice. In zircon crystals, titanium is commonly incorporated, replacing similarly charged zirconium and silicon atoms. This process is relatively unaffected by pressure and highly temperature dependent, with the amount of titanium incorporated rising exponentially with temperature,[1][2] making this an accurate geothermometry method. This measurement of titanium in zircons can be used to estimate the cooling temperatures of the crystal and infer conditions during which it crystallized. Compositional changes in the crystals growth rings can be used to estimate the thermodynamic history of the entire crystal.