

Jews. The Jews (Hebrew: יְהוּדִים ISO 259-3 Yehudim Israeli pronunciation [jehuˈdim]); (בני ישראל, Standard: Bnai Yisraʾel; Tiberian: Bnai Yiśrāʾēl; ISO 259-3: Bnai Yiśraʾel, translated as: "Children of Israel" or "Sons of Israel"), also known as the Jewish people, are a nation and ethnoreligious group[14] originating from the Israelites (Hebrews) of the Ancient Near East. The world Jewish population reached a peak of 16.7 million prior to World War II,[25] but 6 million Jews were killed in the Holocaust.
Moses. Moses (Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה, Modern Moshe Tiberian Mōšéh ISO 259-3 Moše ; Syriac: ܡܘܫܐ Moushe; Arabic: موسى Mūsā ) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the Qur'an, and Baha'i scripture, a former Egyptian prince and warrior,[citation needed] later turned religious leader, lawgiver, and prophet, to whom the authorship of the Torah is traditionally attributed.
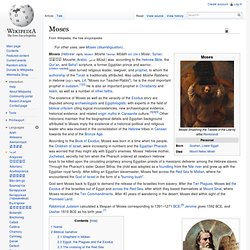
Also called Moshe Rabbenu in Hebrew (מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּנוּ, Lit. "Moses our Teacher/Rabbi"), he is the most important prophet in Judaism.[1][2] He is also an important prophet in Christianity and Islam, as well as a number of other faiths. According to the Book of Exodus, Moses was born in a time when his people, the Children of Israel, were increasing in numbers and the Egyptian Pharaoh was worried that they might ally with Egypt's enemies. God sent Moses back to Egypt to demand the release of the Israelites from slavery.
Name. History of the Jews during World War II. Group of Jewish parachutists under British command, who was sent into Slovakia.
Palestine, wartime World War II is the most tragic period in Jewish history. German Nazi occupied Europe[edit] By World War II, nearly all Jewish companies had either collapsed under financial pressure and declining profits, or had been forced to sell out to the Nazi-German government as part of the "Aryanization" policy inaugurated in 1937. Nazism. Nazism, or National Socialism in full (German: Nationalsozialismus), is the ideology and practice associated with the 20th-century German Nazi Party and state as well as other related far-right groups.
Usually characterised as a form of fascism that incorporates scientific racism and antisemitism, Nazism originally developed from the influences of pan-Germanism, the Völkisch German nationalist movement and the anti-communist Freikorps paramilitary culture in post-First World War Germany, which many Germans felt had been left humiliated by the Treaty of Versailles. German Nazism subscribed to theories of racial hierarchy and social Darwinism, asserted the superiority of an Aryan master race, and criticised both capitalism and communism for being associated with Jewish materialism.
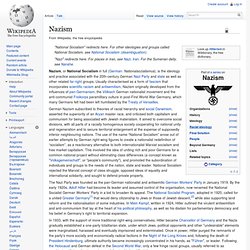
The Nazi Party was founded as the pan-German nationalist and antisemitic German Workers' Party in January 1919. Etymology. Adolf Hitler. Adolf Hitler (German: [ˈadɔlf ˈhɪtlɐ]; 20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the leader of the Nazi Party (German: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei (NSDAP); National Socialist German Workers Party).

He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945 and Führer (leader) of Nazi Germany from 1934 to 1945. As effective dictator of Nazi Germany, Hitler was at the centre of World War II in Europe, and the Holocaust. Hitler was a decorated veteran of World War I. He joined the precursor of the NSDAP, the German Workers' Party, in 1919 and became leader of the NSDAP in 1921. In 1923 he attempted a coup in Munich to seize power. Hitler actively sought Lebensraum ("living space") for the German people.
Early years Ancestry. Anne Frank. Nazi Camps. INTRODUCTION Between 1933 and 1945, Nazi Germany established about 20,000 camps to imprison its many millions of victims.
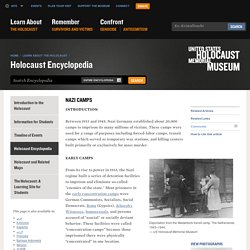
These camps were used for a range of purposes including forced-labor camps, transit camps which served as temporary way stations, and killing centers built primarily or exclusively for mass murder. EARLY CAMPS From its rise to power in 1933, the Nazi regime built a series of detention facilities to imprison and eliminate so-called "enemies of the state.
" Most prisoners in the early concentration camps were German Communists, Socialists, Social Democrats, Roma (Gypsies), Jehovah's Witnesses, homosexuals, and persons accused of "asocial" or socially deviant behavior. These facilities were called “concentration camps” because those imprisoned there were physically “concentrated” in one location. German Jews during the Holocaust. 1933-1939 In January 1933, some 522,000 Jews by religious definition lived in Germany.
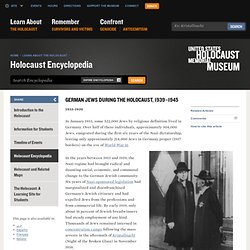
Over half of these individuals, approximately 304,000 Jews, emigrated during the first six years of the Nazi dictatorship, leaving only approximately 214,000 Jews in Germany proper (1937 borders) on the eve of World War II. In the years between 1933 and 1939, the Nazi regime had brought radical and daunting social, economic, and communal change to the German Jewish community. Six years of Nazi-sponsored legislation had marginalized and disenfranchised Germany's Jewish citizenry and had expelled Jews from the professions and from commercial life. By early 1939, only about 16 percent of Jewish breadwinners had steady employment of any kind. Escape of the Jewish People from Europe. Even before the beginning of World War II, many Jews sought to escape from countries under Nazi control.
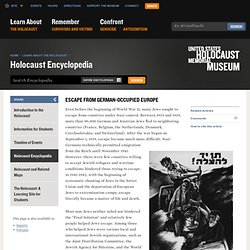
Between 1933 and 1939, more than 90,000 German and Austrian Jews fled to neighboring countries (France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Denmark, Czechoslovakia, and Switzerland). After the war began on September 1, 1939, escape became much more difficult. Nazi Germany technically permitted emigration from the Reich until November 1941. However, there were few countries willing to accept Jewish refugees and wartime conditions hindered those trying to escape. Antisemitism. Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is prejudice, hatred of, or discrimination against Jews for reasons connected to their Jewish religion or heritage.[1] A person who holds such positions is called an "antisemite".
As Jews are an ethnoreligious group, antisemitism is generally considered a form of racism. While the term's etymology might suggest that antisemitism is directed against all Semitic people, the term was coined in the late 19th century in Germany as a more scientific-sounding term for Judenhass ("Jew-hatred"),[2] and that has been its normal use since then.[3] For the purposes of a 2005 U.S. governmental report, antisemitism was considered "hatred toward Jews—individually and as a group—that can be attributed to the Jewish religion and/or ethnicity. "[4]