

Tcpdump. Tcpdump es un herramienta en línea de comandos cuya utilidad principal es analizar el tráfico que circula por la red.
Permite al usuario capturar y mostrar a tiempo real los paquetes transmitidos y recibidos en la red a la cual el ordenador está conectado. Está escrito por Van Jacobson, Craig Leres, y Steven McCanne que trabajaban en ese momento en el Grupo de Investigación de Red del Laboratorio Lawrence Berkeley. Más tarde el programa fue ampliado por Andrew Tridgell. Existe una adaptación de tcpdump para los sistemas Windows que se llama WinDump y que hace uso de la biblioteca Winpcap. En UNIX y otros sistemas operativos, es necesario tener los privilegios del root para utilizar tcpdump. El usuario puede aplicar varios filtros para que sea más depurada la salida.
Utilización frecuente de tcpdump[editar] Para depurar aplicaciones que utilizan la red para comunicar.Para depurar la red misma.Para capturar y leer datos enviados por otros usuarios u ordenadores. Funcionamiento[editar] SAPs. The protocol for each layer is concerned with providing a peer-to-peer service with the corresponding layer at the other end of the path (a hop for the lower three layers, end-to-end for the upper four).
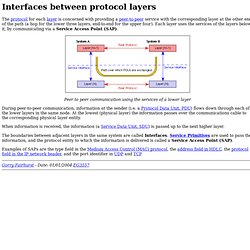
Each layer uses the services of the layers below it, by communicating via a Service Access Point (SAP). Peer to peer communication using the services of a lower layer During peer-to-peer communication, information at the sender (i.e. a Protocol Data Unit, PDU) flows down through each of the lower layers in the same node. Nptelhrd's Channel. Lecture - 17 Data Link Control. Data Link Layer (Layer 2) I know everyone hates ads.
But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :) If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads. If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. Thanks for your understanding! Sincerely, Charles Kozierok Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide. Hamming distance. Examples[edit] The Hamming distance between: "karolin" and "kathrin" is 3.
" OSI model. Model with 7 layers to describe communications systems The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology.
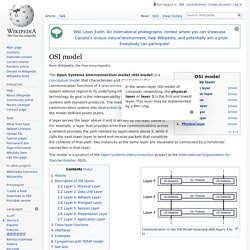
Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard protocols. Piggybacking (data transmission) Piggybacking is a bi-directional data transmission technique in the network layer (OSI model).
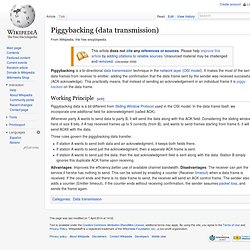
It makes the most of the sent data frames from receiver to emitter, adding the confirmation that the data frame sent by the sender was received successfully (ACK acknowledge). This practically means, that instead of sending an acknowledgement in an individual frame it is piggy-backed on the data frame. Piggybacking data is a bit different from Sliding Window Protocol used in the OSI model. In the data frame itself, we incorporate one additional field for acknowledgment (called ACK). Whenever party A wants to send data to party B, it will send the data along with this ACK field. Packet switching. Packet switching is a digital networking communications method that groups all transmitted data – regardless of content, type, or structure – into suitably sized blocks, called packets.
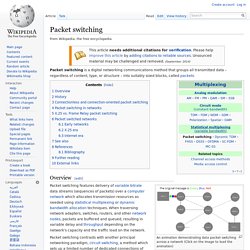
Overview[edit] An animation demonstrating data packet switching across a network (Click on the image to load the animation) Packet switching features delivery of variable bitrate data streams (sequences of packets) over a computer network which allocates transmission resources as needed using statistical multiplexing or dynamic bandwidth allocation techniques. When traversing network adapters, switches, routers, and other network nodes, packets are buffered and queued, resulting in variable delay and throughput depending on the network's capacity and the traffic load on the network. History[edit] First proposed for military uses in the early 1960s and implemented on small networks in 1968, packet switching became one of the fundamental networking technologies behind the Internet and most local area networks.
Protocol data unit. MAC layer PDU becomes physical layer SDU In telecommunications, the term protocol data unit (PDU) has the following meanings: Context in the OSI model[edit] PDUs are relevant in relation to each of the first 4 layers of the OSI model as follows:[2] Given a context pertaining to a specific OSI layer, PDU is sometimes used as a synonym for its representation at that layer.
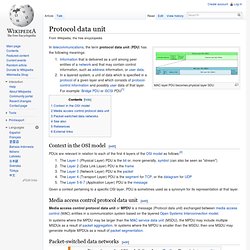
Flow control.