

Brihadeeswarar Temple - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia - Waterfox. The Peruvudaiyar Kovil ( Tamil : தஞ்சைப் பெருவுடையார் கோயில்), also known as Thanjavur Periya Kovil,[1] Brihadeeswara Temple, RajaRajeswara Temple and Rajarajeswaram,[2] at Thanjavur in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, is a Hindu temple dedicated to Shiva.
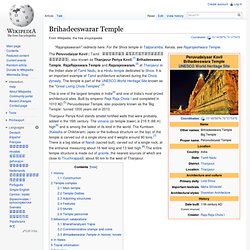
It is an important example of Tamil architecture achieved during the Chola dynasty. The temple is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site known as the "Great Living Chola Temples".[3] This is one of the largest temples in India[4] and one of India's most prized architectural sites. Caral - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia - Waterfox. This article is about the archaeological site.
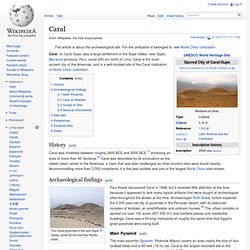
For the civilization it belonged to, see Norte Chico civilization Caral, or Caral-Supe, was a large settlement in the Supe Valley, near Supe, Barranca province, Peru, some 200 km north of Lima. Caral is the most ancient city of the Americas, and is a well-studied site of the Caral civilization or Norte Chico civilization. Chichen Itza - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia - Waterfox. Chichen Itza (/tʃiːˈtʃɛn iːˈtsɑː/,[1] Spanish: Chichén Itzá [tʃiˈtʃen iˈtsa], from Yucatec Maya: Chi'ch'èen Ìitsha' [tɕʰɨɪʼtɕʼeːn˧˩ iː˧˩tsʰaʲ];[2] "at the mouth of the well of the Itza") was a large pre-Columbian city built by the Maya people of the Post Classic.
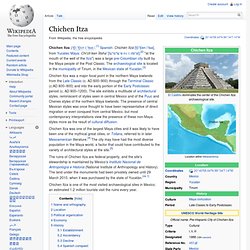
The archaeological site is located in the municipality of Tinum, in the Mexican state of Yucatán.[3] Chichen Itza was a major focal point in the northern Maya lowlands from the Late Classic (c. AD 600–900) through the Terminal Classic (c.AD 800–900) and into the early portion of the Early Postclassic period (c. AD 900–1200). The site exhibits a multitude of architectural styles, reminiscent of styles seen in central Mexico and of the Puuc and Chenes styles of the northern Maya lowlands. Chichen Itza - Waterfox. Khuzestan Province - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia - Waterfox. Domes like this are quite common in Khuzestan province.
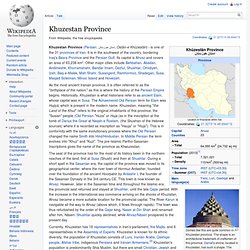
The shape is an architectural trademark of craftsmen of this province. Daniel's shrine, located in Khuzestan, has such a shape. Koh Ker - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia - Waterfox. Koh Ker (Khmer: ប្រាសាទកោះកេរ្ដិ៍) is a remote archaeological site in northern Cambodia about 120 kilometres (75 mi) away from Siem Reap and the ancient site of Angkor.
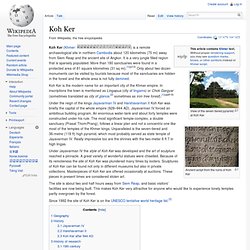
It is a very jungle filled region that is sparsely populated. More than 180 sanctuaries were found in a protected area of 81 square kilometres (31 sq mi).[1](p13) Only about two dozen monuments can be visited by tourists because most of the sanctuaries are hidden in the forest and the whole area is not fully demined. Koh Ker is the modern name for an important city of the Khmer empire. In inscriptions the town is mentioned as Lingapua (city of lingams) or Chok Gargyar (sometimes translated as city of glance,[2] sometimes as iron tree forest).[1](pp8–9) Sacsayhuamán - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia - Waterfox. Sideways view of the walls of Saksaywaman showing the details of the stonework and the angle of the walls.
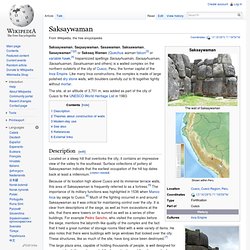
The site, at an altitude of 3,701 m, was added as part of the city of Cusco to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1983. Description[edit] Located on a steep hill that overlooks the city, it contains an impressive view of the valley to the southeast. Surface collections of pottery at Saksaywaman indicate that the earliest occupation of the hill top dates back at least a millennium. [citation needed] Teotihuacan - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia - Waterfox. Coordinates: Teotihuacan /teɪˌoʊtiːwəˈkɑːn/,[1] also written Teotihuacán (Spanish teotiwa'kan ), was a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican city located in the Basin of Mexico, 30 miles (48 km) northeast of modern-day Mexico City, which is today known as the site of many of the most architecturally significant Mesoamerican pyramids built in the pre-Columbian Americas.
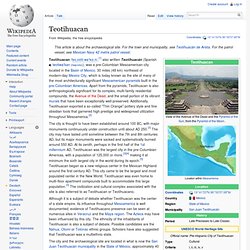
Apart from the pyramids, Teotihuacan is also anthropologically significant for its complex, multi-family residential compounds, the Avenue of the Dead, and the small portion of its vibrant murals that have been exceptionally well-preserved. Additionally, Teotihuacan exported a so-called "Thin Orange" pottery style and fine obsidian tools that garnered high prestige and widespread utilization throughout Mesoamerica.[2] Name[edit] What is the Pyramid - Waterfox. Borobudur - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia - Waterfox. Borobudur, or Barabudur, is a 9th-century Mahayana Buddhist Temple in Magelang, Central Java, Indonesia.
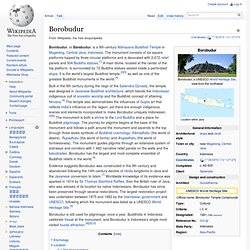
The monument consists of six square platforms topped by three circular platforms and is decorated with 2,672 relief panels and 504 Buddha statues.[1] A main dome, located at the center of the top platform, is surrounded by 72 Buddha statues seated inside a perforated stupa. It is the world’s largest Buddhist temple,[2][3] as well as one of the greatest Buddhist monuments in the world.[4] Evidence suggests Borobudur was constructed in the 9th century and abandoned following the 14th-century decline of Hindu kingdoms in Java and the Javanese conversion to Islam.[7] Worldwide knowledge of its existence was sparked in 1814 by Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles, then the British ruler of Java, who was advised of its location by native Indonesians.
Borobudur has since been preserved through several restorations. Etymology[edit]