

Rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that results in a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks flexible (synovial) joints.
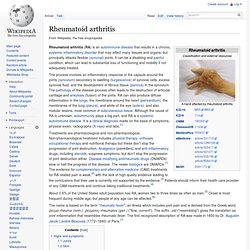
It can be a disabling and painful condition, which can lead to substantial loss of functioning and mobility if not adequately treated. The process involves an inflammatory response of the capsule around the joints (synovium) secondary to swelling (turgescence) of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development of fibrous tissue (pannus) in the synovium. The pathology of the disease process often leads to the destruction of articular cartilage and ankylosis (fusion) of the joints.
RA can also produce diffuse inflammation in the lungs, the membrane around the heart (pericardium), the membranes of the lung (pleura), and white of the eye (sclera), and also nodular lesions, most common in subcutaneous tissue.