

Performing Engineering Operations 001.docx. Performing Engineering Operations Supplement.docx. Performing Engineering Operations 001-02.docx. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Employers have duties concerning the provision and use of personal protective equipment (PPE) at work.
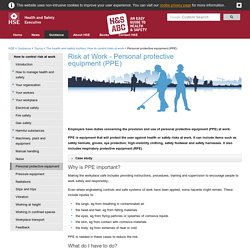
PPE is equipment that will protect the user against health or safety risks at work. It can include items such as safety helmets, gloves, eye protection, high-visibility clothing, safety footwear and safety harnesses. It also includes respiratory protective equipment (RPE). Why is PPE important? Making the workplace safe includes providing instructions, procedures, training and supervision to encourage people to work safely and responsibly. Even where engineering controls and safe systems of work have been applied, some hazards might remain. The lungs, eg from breathing in contaminated air the head and feet, eg from falling materials the eyes, eg from flying particles or splashes of corrosive liquids the skin, eg from contact with corrosive materials the body, eg from extremes of heat or cold PPE is needed in these cases to reduce the risk.
What do I have to do? Selection and use Eyes Note. Personnel Protective Equipment Leaflet. Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 (PUWER) - Work equipment and machinery. These Regulations, often abbreviated to PUWER, place duties on people and companies who own, operate or have control over work equipment.
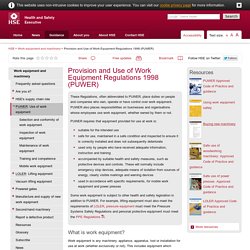
PUWER also places responsibilities on businesses and organisations whose employees use work equipment, whether owned by them or not. PUWER requires that equipment provided for use at work is: suitable for the intended use safe for use, maintained in a safe condition and inspected to ensure it is correctly installed and does not subsequently deteriorate used only by people who have received adequate information, instruction and training accompanied by suitable health and safety measures, such as protective devices and controls. These will normally include emergency stop devices, adequate means of isolation from sources of energy, clearly visible markings and warning devices used in accordance with specific requirements, for mobile work equipment and power presses What is work equipment?
What you must do What you should know. Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations 2013 - RIDDOR - HSE. Hazard symbols and hazard pictograms - Chemical classification. Hazard pictograms alert us to the presence of a hazardous chemical.
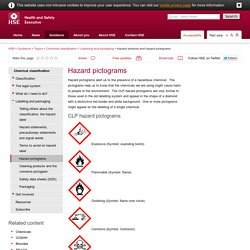
The pictograms help us to know that the chemicals we are using might cause harm to people or the environment. The CLP hazard pictograms are very similar to those used in the old labelling system and appear in the shape of a diamond with a distinctive red border and white background. One or more pictograms might appear on the labelling of a single chemical. Explosive (Symbol: exploding bomb) Flammable (Symbol: flame) Oxidising (Symbol: flame over circle) Corrosive (Symbol: Corrosion) Acute toxicity (Symbol: Skull and crossbones) Hazardous to the environment (Symbol: Dead tree and fish) You’ll see that the old 'harmful/irritant' symbol is missing.
Health hazard/Hazardous to the ozone layer (Symbol: Exclamation mark) A couple of new pictograms have also been introduced: Serious health hazard (Symbol: health hazard) Gas under pressure (Symbol: Gas cylinder)