

2011. OPERA experiment. The Oscillation Project with Emulsion-tRacking Apparatus (OPERA) is an instrument used in a scientific experiment for detecting tau neutrinos from muon neutrino oscillations.
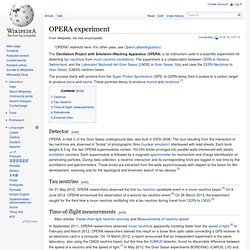
The experiment is a collaboration between CERN in Geneva, Switzerland, and the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso (LNGS) in Gran Sasso, Italy and uses the CERN Neutrinos to Gran Sasso (CNGS) neutrino beam. The process starts with protons from the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) at CERN being fired in pulses at a carbon target to produce pions and kaons. These particles decay to produce muons and neutrinos.[1] Faster-than-light neutrino anomaly. Fig. 1 What OPERA saw.
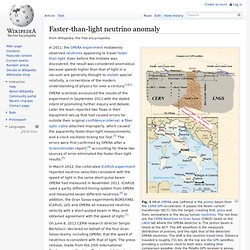
Leftmost is the proton beam from the CERNSPS accelerator. It passes the beam current transformer (BCT), hits the target, creating first, pions and then, somewhere in the decay tunnel, neutrinos.