

An Introduction To Financial Functions In Excel 2010. Time Value of Money. This page covers the following topics regarding the calculation of the present value of an annuity: 1.

Formula and Definition The formula below calculates the current value of a stream of equal payments made at regular intervals over a specified period of time. This value is referred to as the present value (PV) of an annuity. The PV of an annuity formula is used to calculate how much a stream of payments is worth currently where "currently" does not necessarily mean right now but at some time prior to a specified future date. Internal rate of return. Definition[edit] The internal rate of return on an investment or project is the "annualized effective compounded return rate" or "rate of return" that makes the net present value (NPV as NET*1/(1+IRR)^year) of all cash flows (both positive and negative) from a particular investment equal to zero.
Discount rate. Discount rate may refer to: An interest rate (the term "discount" does not refer to the common meaning of the word, but to the meaning in computations of present value) The central bank's discount window interest rateThe annual effective discount rate, an alternative measure of interest rates to the standard Annual Percentage Ratein investment financing, discounted cash flowtheoretical or observed rates at which people discount future payoffsin environmental economics, and more generally in assessing the general welfare impacts of government policies, social discount rate (the basic mathematics is the same as discounted cash flow, but the cash value of human lives etc. can only be crudely estimated)Fees charged for accepting payments other than in banknotes and coins: bankers' acceptance rates for accepting bankers' acceptances.
Time Value of Money. This page covers the following topics regarding the calculation of the present value of a single sum: 1.
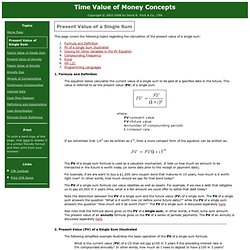
Formula and Definition The equation below calculates the current value of a single sum to be paid at a specified date in the future. This value is referred to as the present value (PV) of a single sum. If we remember that 1/xn can be written as x-n, then a more compact form of the equation can be written as: The PV of a single sum formula is used as a valuation mechanism. 2. The following simplified example illustrates the basic operation of the PV of a single sum formula. What is the current value (PV) of a CD that will pay $100 in 3 years if the prevailing interest rate is 5% compounded annually? Drawn from the the perspective of the investor, the problem is illustrated below. The arrow drawn pointing away from the time line (labeled "100.00") represents a cash inflow to the investor. FV = 100.00 i = 0.05 n = 3 3.
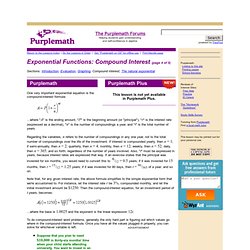
The FV of a single sum is discussed in more detail here. 4. 5. 7. Exponential Functions: Compound Interest. Exponential Functions: Compound Interest (page 4 of 5) Sections: Introduction, Evaluation, Graphing, Compound interest, The natural exponential This lesson is not yet availablein Purplemath Plus.
Present value. Present value, also known as present discounted value, is a future amount of money that has been discounted to reflect its current value, as if it existed today.
The present value is always less than or equal to the future value because money has interest-earning potential, a characteristic referred to as the time value of money.[1] Time value can be described with the simplified phrase, “A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow”. Here, 'worth more' means that its value is greater. A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow because the dollar can be invested and earn a day's worth of interest, making the total accumulate to a value more than a dollar by tomorrow. Interest can be compared to rent.[2] Just as rent is paid to a landlord by a tenant, without the ownership of the asset being transferred, interest is paid to a lender by a borrower who gains access to the money for a time before paying it back. Years' Purchase[edit] Background[edit] Interest Rates[edit] Where.
Present and Future Value Using Excel. Financial Functions Using Microsoft Excel FV(rate,nper,pmt,pv,type) Rate is the interest rate per period.

Nper is the total number of payment periods in an annuity. Pmt is the payment made each period; it cannot change over the life of the annuity. Pmt must be entered as a negative number.