

Neuron - Triangulating the Neural, Psychological, and Economic Bases of Guilt Aversion. To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription.

Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect. Figure 1 Trial Timeline (A) Schematic of Trust Game (TG) with beliefs. Player 1 decides how much of their endowment they want to invest in Player 2 (S1) and has an expectation about the amount of money that Player 2 will return (E1S2). Growing a Brain in a Dish : Dean's Corner. Source.
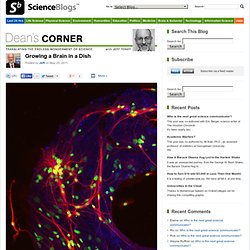
That doughnut shape decorated with bright green spots, some connected by red pathways, amidst sky blue neighbors could be an artist’s creation, but is the result of a creative scientific attempt to grow an active brain in a dish, complete with memories. Really. Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh published this stunning study in the journal Lab on a Chip {the full paper can be accessed here.} In Vivo Monitoring of Adult Neurogenesis in Health and Disease. Introduction The existence of adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain has been demonstrated almost half of a century ago (Altman and Das, 1965), nevertheless, broad attention to this process only arose after the discovery of pools of neural stem-like cells residing in discrete brain regions (Reynolds and Weiss, 1992).

In most adult mammals, proliferating neural stem cells can be detected in two neurogenic niches, the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricle wall and the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the hippocampal dentate gyrus (see Ma et al., 2009 for a recent review). The SVZ constitutes the most active site of neurogenesis (Conover and Allen, 2002). Young neural progenitor cells (NPCs), also known as neuroblasts, are generated throughout the entire SVZ and subsequently migrate along the rostral migratory stream (RMS) into the olfactory bulb (OB) where they differentiate into new interneurons (Lois and Alvarez-Buylla, 1994).
Table 1. Direct Labeling Using Iron Oxide Particles. Age-related memory deficits linked to circuit-specific disruptions in the hippocampus. Author Affiliations Edited by Edward E.
Smith, Columbia University, New York, NY, and approved April 15, 2011 (received for review January 27, 2011) Abstract Converging data from rodents and humans have demonstrated an age-related decline in pattern separation abilities (the ability to discriminate among similar experiences). Human Thought Controls Neurons in Brain. Neuroscience research involving epileptic patients with brain electrodes surgically implanted in their medial temporal lobes shows that patients learned to consciously control individual neurons deep in the brain with thoughts.
Subjects learned to control mouse cursors, play video games and alter focus of digital images with their thoughts. The patients were each using brain computer interfaces, deep brain electrodes and software designed for the research. The article below offers more detail. Controlling Individual Cortical Nerve Cells by Human Thought. Anger Can Make Us More Rational. A recent study in Cognition and Emotion found that anger can sometimes make us more critical thinkers by inhibiting our confirmation bias.
Instead of only searching for information that supports our beliefs, anger can create a “moving against” tendency that motivates us to seek alternative information that opposes our assumptions. The study had participants do two different experiments (which they thought were unrelated). In the first experiment, Group A wrote about an experience that made them angry, while Group B wrote about a mundane, ordinary experience.
This has shown in previous research to facilitate a mood change. In the next experiment, each participant was asked to evaluate their opinions on hands-free mobile kits. By the end of the experiment, those who were primed to be angry were more likely to shift from their original opinions. A similar study was also conducted in 2008 regarding the election between Obama and McCain. ‘Can you hear me now?’ Researchers Detail How Neurons Decide How to Transmit Information. There are billions of neurons in the brain and at any given time tens of thousands of these neurons might be trying to send signals to one another.
Much like a person trying to be heard by his friend across a crowded room, neurons must figure out the best way to get their message heard above the din. Researchers from the Center for the Neural Basis of Cognition, a joint program between Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Pittsburgh, have found two ways that neurons accomplish this, establishing a fundamental mechanism by which neurons communicate. The findings have been published in an online early edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). “Neurons face a universal communications conundrum. They can speak together and be heard far and wide, or they can speak individually and say more. Neurons communicate by sending out electrical impulses called action potentials or “spikes.”
Notes about this neuroscience article. Love Study: Brain Reacts To Heartbreak Same As Physical Pain. Reflections on Mirror Neurons. In 1992, a team at the University of Parma, Italy discovered what have been termed “mirror neurons” in macaque monkeys: cells that fire both when the monkey took an action (like holding a banana) and saw it performed (when a man held a banana).

Giacomo Rizzolati, the celebrated discoverer, will deliver the Keynote Address at the APS Convention in Washington DC, USA, on May 26, 2011, and report on his latest findings. To tide us over until then, here’s a report on the state of mirror neuron science. Like monkeys, humans have mirror neurons that fire when we both perceive and take an action. Locating the tiny cells means attaching electrodes deep inside the brain. Neuroscientists decode crucial component in brain signal processing. A team of Neuroscientists from NeuroCure Cluster of Excellence at Charité -- Universitätsmedizin Berlin and Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, have made a major breakthrough in understanding how signals are processed in the human brain.

The paper, published in the current issue of the scientific journal Neuron, shows that a certain type of protein -- the "vesicular glutamate transporter" (VGLUT) plays a crucial part in the strength regulation of synaptic connections. This regulation enables synapses to vary in strength. Synapses transmit the communication between different neurons within the central nervous system and depending on their function in the brain, they operate differently. For example, the cerebral cortex bundles a vast amount of information and in order to process this, neurons need to dose or regulate the information. "A neuron can be compared to a music enthusiast. MicroRNA’s Role In Risk Factor For Panic Disorder.
A new study implicates microRNAs as a possible molecular switch which could contribute to a risk factor for panic disorder.
While 40% of the risk for panic disorder is heritable, according to a number of twin studies, it remains unclear the manner in which genes contribute to an overall risk factor. While variations in a number of genes have been considered as risks for developing panic disorder, individually the impact of each gene is small. This new study considers that at least four miRNAs could act as potential switches which control the function of gene groups involved in panic disorder. Additionally, scientists have implicated miR-22 and miR-488 within the regulation of anxiety related pathways. Micro-RNA’s contribute to risk for panic disorder. New NeuroFocus headset gets closer to the Mynd. New Model For Neurodegeneration. Mind vs. Machine - Magazine. In the race to build computers that can think like humans, the proving ground is the Turing Test—an annual battle between the world’s most advanced artificial-intelligence programs and ordinary people.
The objective? To find out whether a computer can act “more human” than a person. In his own quest to beat the machines, the author discovers that the march of technology isn’t just changing how we live, it’s raising new questions about what it means to be human. Bryan Christie. Cannabis use precedes the onset of psychotic symptoms in young people, study finds. Cannabis use during adolescence and young adulthood increases the risk of psychotic symptoms, while continued cannabis use may increase the risk for psychotic disorder in later life, concludes a new study published online in the British Medical Journal.
Cannabis is the most commonly used illicit drug in the world, particularly among adolescents, and is consistently linked with an increased risk for mental illness. However, it is not clear whether the link between cannabis and psychosis is causal, or whether it is because people with psychosis use cannabis to self medicate their symptoms. So a team of researchers, led by Professor Jim van Os from Maastricht University in the Netherlands, set out to investigate the association between cannabis use and the incidence and persistence of psychotic symptoms over 10 years. The study took place in Germany and involved a random sample of 1,923 adolescents and young adults aged 14 to 24 years. W.sns. Early top-down control of visual processing predic... [J Cogn Neurosci. 2010] - PubMed result.
A Photocleavable Rapamycin Conjugate for Spatiotemporal Control of Small GTPase Activity - Journal of the American Chemical Society. Department of Cell Biology, Center for Cell Dynamics, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland 21205, United States, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan, and CREST, JST, 3-5, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, Japan J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133 (1), pp 12–14 DOI: 10.1021/ja108258d Publication Date (Web): December 13, 2010 Copyright © 2010 American Chemical Society Section: Abstract. Neuron - The Many Faces of Tau. Depression: The Yin of Happiness. In my mind, authentic and long-lasting happiness requires what positive psychologist Tal Ben-Sahar calls, “a permission to experience the full range of human emotions.”
This permission includes what are sometimes thought of as “negative” states of mind such as grief, anger, or sadness (the exact opposite of what we would usually consider to be “happiness”). As paradoxical as it sounds, I believe those lows can sometimes be necessary to help define our highs. Like darkness and light, or yin and yang, happiness and depression are interdependent; you can’t have one concept without implying the other. In fact, even the happiest of individuals occasionally go through bouts of sadness and depression, and I think in many ways we need to occasionally engage with those states if we want to find true bliss in our lives. A common theme that I try to emphasize on this blog is that all emotions are resources. Let me relate this to a personal experience of mine. So what is the takeaway? Directly Restores Neurons Critical to Cognition. Huge Differences Discovered In Cost-Efficient Functioning Of Brain Networks, Over Half Of Which Explained By Genes.
Training The Athletic Brain. Zeo-Sleep-Infographic-FFunction.jpg (JPEG Image, 750x3260 pixels) - Scaled (19. Neuron - A Cytokine-Dependent Switch for Glial-Neuron Interactions. Virginia Tech Announces Football Helmet Ratings for Reducing Concussion Risk. Virginia Tech released today the results of a new rating system of adult football helmets that is designed to reduce the risk of concussions. One currently manufactured helmet received the top “5 star” rating, and a total of five helmets received the very good “4-star” rating. This biomechanical impact data study on football helmets represents the first time researchers have provided the public with comparative test results. Mapping The Human Brain With 'Connectomics' Brain Research : Change blindness in profoundly deaf individuals and cochlear implant recipients.
New light-sensing mechanism found in neurons. A UC Irvine research team led by Todd C. Holmes has discovered a second form of phototransduction light sensing in cells that is derived from vitamin B2. This discovery may reveal new information about cellular processes controlled by light. An On-Off Switch for Anxiety. Stanford scientists create neurons with symptoms of Parkinson's disease from patient's skin cells. Illuminating-brain-0128. There are about 100 billion neurons in the human brain, and each one belongs to elaborate networks that control our behavior, thoughts and emotions. Neuron - Excitatory Projection Neuron Subtypes Control the Distribution of Local Inhibitory Interneurons in the Cerebral Cortex. Scientists use light to move molecules within living cells. Using a light-triggered chemical tool, Johns Hopkins scientists report that they have refined a means of moving individual molecules around inside living cells and sending them to exact locations at precise times.
Dancecult: Journal of Electronic Dance Music Culture. Hearing the voices of colours. Weight Loss Improves Memory.