

Archaeologists find shrines to 2,000 year old Egyptian family. Before Brad Pitt and Angelina Jolie were 'Brangelina', there was Neferkhewe and Ruiuresti.
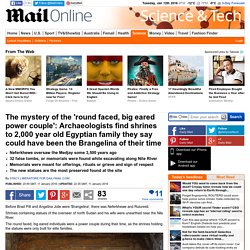
Shrines containing statues of the overseer of north Sudan and his wife were unearthed near the Nile River. The round faced, big eared individuals were a power couple during their time, as the shrines holding the statues were only built for elite families. Shrines containing statues of the oversee of north Sudan and his wife, along with another family, were found near the Nile River. The round faced, big eared individuals were a power couple during their time, as the shrines holding the statues were only built for elite families Gebel el Silsila Survey Project found carved alcoves, which were constructed as memorials for elite families, buried in the silt of the Nile River in Upper Egypt.
History says, Neferkhewe oversaw the Medjay, which is now northern Sudan, some 3,500 years ago when Pharaoh Thutmose III was ruler. They found that they ate a lot of barley and wheat over the long period. Hieroglyphs may finally solve 5th century disappearance of Persian army. Dutch professor believes he's solved the mystery of missing Persian armyProfessor Kaper claims the 50,000-strong army was defeated in battlePreviously it had been thought the army was swallowed by a sandstormBut new analysis of hieroglyphics reveals this story was merely a cover-upInstead they were defeated by a rebel army led by Petubastis III in 524 BC By Jonathan O'Callaghan Published: 16:13 GMT, 27 June 2014 | Updated: 19:53 GMT, 27 June 2014 Professor Kaper says that disappearance of a Persian army in 524 BC has been solved, thanks to deciphering ancient temple blocks (pictured) In 524 BC, a Persian army of 50,000 men sent by King Cambyses II marched into the Egyptian desert from Thebes - now known as Luxor.

But, after entering the desert, they were never heard from again. For centuries. it has been presumed they were swallowed by a sandstorm, but now a researcher claims that wasn’t the case - and instead they must have been defeated in battle. Ancient Egyptian creation myths. The sun rises over the circular mound of creation as goddesses pour out the primeval waters around it Ancient Egyptian creation myths are the ancient Egyptian accounts of the creation of the world.
The Pyramid Texts, tomb wall decorations and writings, dating back to the Old Kingdom (2780 – 2250 B.C.E) have given us most of our information regarding early Egyptian creation myths.[1] These myths also form the earliest religious compilations in the world.[2] The ancient Egyptians had many creator gods and associated legends. Thus the world or more specifically Egypt was created in diverse ways according to different parts of the country.[3] Common elements[edit] Another common element of Egyptian cosmogonies is the familiar figure of the cosmic egg, a substitute for the primeval waters or the primeval mound.
Cosmogonies[edit] Hermopolis[edit] Heliopolis[edit] Memphis[edit] The Memphite version of creation centered on Ptah, who was the patron god of craftsmen. Thebes[edit] History of ancient Egypt. The history of Ancient Egypt spans the period from the early predynastic settlements of the northern Nile Valley to the Roman conquest in 30 BC.
The Pharaonic Period is dated from around 3200 BC, when Lower and Upper Egypt became a unified state, until the country fell under Greek rule in 332 BC. Chronology[edit] Note For alternative 'revisions' to the chronology of Egypt, see Egyptian chronology. Egypt's history is split into several different periods according to the ruling dynasty of each pharaoh. Predynastic Period (Prior to 3100 BC)Protodynastic Period (Approximately 3100–3000 BC)Early Dynastic Period (1st–2nd Dynasties)Old Kingdom (3rd–6th Dynasties)First Intermediate Period (7th–11th Dynasties)Middle Kingdom (12th–13th Dynasties)Second Intermediate Period (14th–17th Dynasties)New Kingdom (18th–20th Dynasties)Third Intermediate Period (21st–25th Dynasties) (also known as the Libyan Period)Late Period (26th–31st Dynasties) Neolithic Egypt[edit] Neolithic period[edit]