

Neurosurgeons use adult stem cells to grow neck vertebrae. New drug could cure nearly any viral infection. Most bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics such as penicillin, discovered decades ago.
However, such drugs are useless against viral infections, including influenza, the common cold, and deadly hemorrhagic fevers such as Ebola. Now, in a development that could transform how viral infections are treated, a team of researchers at MIT’s Lincoln Laboratory has designed a drug that can identify cells that have been infected by any type of virus, then kill those cells to terminate the infection.
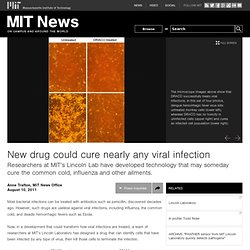
The microscope images above show that DRACO successfully treats viral infections. In the left set of four photos, rhinovirus (the common cold virus) kills untreated human cells (lower left), whereas DRACO has no toxicity in uninfected cells (upper right) and cures an infected cell population (lower right). The drug works by targeting a type of RNA produced only in cells that have been infected by viruses. New composite material may restore damaged soft tissue. 'Super antibody' fights off flu.
29 July 2011Last updated at 08:49 By James Gallagher Health reporter, BBC News A jab protecting against all flu viruses is considered a holy grails of vaccine research The first antibody which can fight all types of the influenza A virus has been discovered, researchers claim.
Experiments on flu-infected mice, published in Science Express, showed the antibody could be used as an "emergency treatment". New Virus Jumps From Monkeys to Lab Worker. Superhuman Hearing Possible, Experiments Suggest. How a jab of gel could be the surgery-free solution to your bad back. By Fiona Macrae Updated: 10:29 GMT, 20 May 2011 Clinical trials likely to start in three years Excruciating: Eighty per cent of Britons suffer with back pain at some point in their lives An injection that could ease the misery of back pain for millions has been invented by British scientists.

It contains thousands of microscopic sponge-like particles that inflate and gel together inside the body, repairing damaged and worn-away spinal discs. Almost everyone over the age of 50 has degeneration of the intervertebral discs, which cushion the vertebrae that make up the various sections of the spine. Special Report - An end to AIDS? By Kate Kelland LONDON (Reuters) - For his doctors, Timothy Ray Brown was a shot in the dark.
An HIV-positive American who was cured by a unique type of bone marrow transplant, the man known as "the Berlin patient" has become an icon of what scientists hope could be the next phase of the AIDS pandemic: its end. Dramatic scientific advances since HIV was first discovered 30 years ago this week mean the virus is no longer a death sentence. Thanks to tests that detect HIV early, new antiretroviral AIDS drugs that can control the virus for decades, and a range of ways to stop it being spread, 33.3 million people around the world are learning to live with HIV. People like Vuyiseka Dubula, an HIV-positive AIDS activist and mother in Cape Town, South Africa, can expect relatively normal, full lives. Nonetheless, on the 30th birthday of HIV, the global scientific community is setting out with renewed vigour to try to kill it. Experiment aboard shuttle Atlantis will test novel therapy to build bone during space travel.
Public release date: 6-Jul-2011 [ Print | E-mail Share ] [ Close Window ] Contact: Bonnie Prescottbprescot@bidmc.harvard.edu 617-667-7306Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center BOSTON – Astronauts lose a significant amount of bone mass during space travel and with long duration flights there is concern that this bone loss could lead to an increased risk of fractures.

When the final mission of NASA's 30-year Space Shuttle program is launched on July 8, an animal experiment to test a novel therapy to increase bone mass will be on board. "Mechanical loading is required to maintain musculoskeletal health," explains Co-Principal Investigator Mary Bouxsein, PhD, a scientist in BIDMC's Center for Advanced Orthopaedic Studies and Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery at Harvard Medical School.
Historic first images of rod photoreceptors in the living human eye. Public release date: 8-Jun-2011 [ Print | E-mail Share ] [ Close Window ] Contact: Angela Starkastark@osa.org 202-416-1443Optical Society of America WASHINGTON, June 8—Scientists today reported that the tiny light-sensing cells known as rods have been clearly and directly imaged in the living eye for the first time.

Using adaptive optics (AO), the same technology astronomers use to study distant stars and galaxies, scientists can see through the murky distortion of the outer eye, revealing the eye's cellular structure with unprecedented detail. This innovation, described in two papers in the Optical Society's (OSA) open access journal Biomedical Optics Express, will help doctors diagnose degenerative eye disorders sooner, leading to quicker intervention and more effective treatments.
Drug makes hearts repair themselves. 8 June 2011Last updated at 18:00 By James Gallagher Health reporter, BBC News More people are surviving heart attacks, but that means more are living with heart failure A drug that makes hearts repair themselves has been used in research on mice.
The damage caused by a heart attack had previously been considered permanent. But a study in the journal Nature showed the drug, thymosin beta 4, if used in advance of a heart attack, was able to "prime" the heart for repair. The British Heart Foundation described repair as the "holy grail of heart research", but said any treatment in humans was years away. Due to advances in health care the number of people dying from coronary heart disease is falling. Electromagnetic radiation and the brain 5 of 5.
Cell phones and Brain Cancer. Electromagnetic Radiation Warning to Humanity. 3D Human Anatomy. Stem cells coaxed into forming partial eyeball - life - 06 April 2011. Mouse stem cells have been coaxed into forming a partial eyeball, and the method may one day lead to retina transplants.
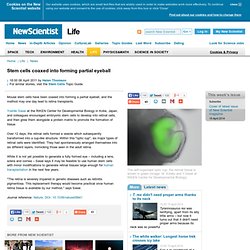
Yoshiki Sasai at the RIKEN Center for Developmental Biology in Kobe, Japan, and colleagues encouraged embryonic stem cells to develop into retinal cells, and then grew them alongside a protein matrix to promote the formation of tissue. Over 12 days, the retinal cells formed a vesicle which subsequently transformed into a cup-like structure. Within this "optic cup", six major types of retinal cells were identified. They had spontaneously arranged themselves into six different layers, mimicking those seen in the adult retina.