

Voile et Electronique : Christian Couderc. Problématique Identifier en permanence la position d'une personne (ou d'un animal) dans une pièce pour divers motifs : Élément de sécurité pour empêcher un opérateur d'approcher d'une machine ou d'une zone dangereuse pendant les opérations.
Ouvrir et refermer automatiquement des portes de sas, par exemple pour ne laisser passer qu'un convoyeur de fonds identifié (ou sa valise) dans un couloir sécurisé, commander l'éclairage automatique par zones de locaux peu fréquentés (faible précision requise). Piloter avec une très grande précision un spot de poursuite automatique centrant un artiste très mobile sur scène. Tester les réactions d'un téléspectateur pour voir combien de temps il est aller faire pipi pendant la pub... Avec un animal, il vaudra mieux commencer par un gros, une vache sera plus facile à équiper (et à repérer dans un couloir) qu'une souris ou qu'un poisson rouge.
Principe de la triangulation La solution simple est d'équiper la cible d'un boîtier accroché à sa ceinture. Weaponsgrade Kavelaars - Open Source Sentry Gun - Guide. Ultrasonic Batgoggles. Wish you were bat?
Want to Experience Echolocation? Want to try to "see" with your ears? For my first Instructable, I will show you how to build your own ultrasonic batgoggles using an Arduino microcontroller clone, Devantech ultrasonic sensor and welding goggles for around $60 or less if you already have standard electronics components. You could also skip the electronics and make a simple bat-mask perfect to wear to the next Batman movie. In that case, the cost would only be about $15. These goggles allow you to experience what it is like to use auditory cues like a bat and is intended for children in a science center setting to learn about echolocation.
To keeps costs and size low, an Arduino clone is built used however, but this project works just as well with pre-built Arduino microcontrollers. These goggles were built for "Dynamic User-centered Research and Design" course in the Arts, Media & Engineering program at Arizona State University. Color Detection Using RGB LED.
A Cheap Ultrasonic Range Finder. How does it work & Circuit schematic Everybody knows the speed of the sound in the dry air is around 340 m/s.
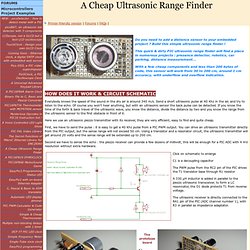
Send a short ultrasonic pulse at 40 Khz in the air, and try to listen to the echo. Of course you won't hear anything, but with an ultrasonic sensor the back pulse can be detected. If you know the time of the forth & back travel of the ultrasonic wave, you know the distance, divide the distance by two and you know the range from the ultrasonic sensor to the first obstacle in front of it. Here we use an ultrasonic piezzo transmitter with its receiver, they are very efficient, easy to find and quite cheap. First, we have to send the pulse : it is easy to get a 40 Khz pulse from a PIC PWM output.
Second we have to sense the echo : the piezzo receiver can provide a few dozens of millivolt, this will be enough for a PIC ADC with 4 mV resolution without extra hardware. Source code Here is the mikroC source code : I tested it with an EasyPic4 development board : E-Field Sensor Contest.