

Paasmaker - Platform as a Service.
Management. ScriptRock. OpenNebula. OpenQRM. Support. Red Hat - Open Shift. OpenShift gives developers more choice—of interfaces, languages, frameworks, services, clouds, elasticity, and infrastructure.
It also offers multiple interaction models, which let developers use a rich set of command-line tools, a powerful multidevice web console, or an Eclipse-based IDE like Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio. Scale applications automatically to handle increased traffic and demand on your applications. Through OpenShift, you can deploy an application with scaling either enabled or disabled. If you deploy your application with scaling disabled, what you deploy is what you'll have, whether it's in 1 gear or several. Built with standard language and middleware runtimes, any application written on OpenShift can easily be moved to another environment that supports the same languages, which prevents lock-in. Built on fully open source technologies, you control your particular implementation. Pivotal - Cloud Foundry. Mirantis - OpenStack. OpenNebula Commercial Support. BIG DATA. Hadoop. PaaS. Development Platform as a Service (dPaaS) PaaS Magazine. Cloud Foundry. Iron Foundry. PaaS List.
AppScale. OpenShift by Red Hat. Pacific. Fortrabbit. Pagodabox. AppFog. IaaS. OpenStack. Chapter 1. Get started with OpenStack - OpenStack Cloud Administrator Guide - havana. Monitoring. Zenoss - Logical Model. This is the approved revision of this page, as well as being the most recent.
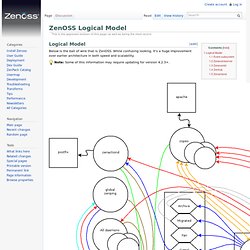
[edit] Logical Model Below is the ball of wire that is ZenOSS. While confusing looking, it's a huge improvement over earlier architecture in both speed and scalability. Note: Some of this information may require updating for version 4.2.3+. [edit] Event subsystem The event subsystem is built around rabbitmq-server, a message queuing daemon. To check the message queues, execute: # rabbitmqctl list_queues -p /zenoss This must be done as root. Example output: Sensu. Sensu is often described as the “monitoring router”.
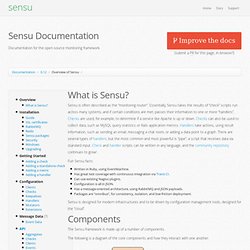
Essentially, Sensu takes the results of “check” scripts run across many systems, and if certain conditions are met; passes their information to one or more “handlers”. Checks are used, for example, to determine if a service like Apache is up or down. Checks can also be used to collect data, such as MySQL query statistics or Rails application metrics. Handlers take actions, using result information, such as sending an email, messaging a chat room, or adding a data point to a graph. There are several types of handlers, but the most common and most powerful is “pipe”, a script that receives data via standard input. Fun Sensu facts: Sensu is designed for modern infrastructures and to be driven by configuration management tools, designed for the “cloud”. The Sensu framework is made up of a number of components. The following is a diagram of the core components and how they interact with one another. Dependencies.