

Immune System - National Library of Medicine - PubMed Health. Definition of leukocyte by Medical dictionary. Leukocyte [loo´ko-sīt] a type of bloodcellthatlackshemoglobinand is thereforecolorless.Leukocytesarelarger in sizeandfewer in numberthanerythrocytes; normallythebloodhasabout8000 of themper mm3.
In contrast to erythrocytes,leukocytescanmoveaboutundertheirownpowerwithameboid movement. Theirchieffunctionsare to act as scavengersand to helpfightinfections.Calledalsowhitecell or corpuscleandwhitebloodcell or corpuscle.adj. ,adjleukocyt´ic. Leukocytes may be classified in two main groups: the granular leukocytes are the basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils, and the nongranular leukocytes are the lymphocytes and monocytes. Leukocytes are actively engaged in the destruction or neutralization of invading microorganisms and are quickly transported to the vicinity of infection or inflammation, so that they can move through the blood vessel wall to reach the site of injury.
Types of leukocytes. agranular l's nongranular leukocyte. leu·ko·cyte (lū'kō-sīt), [leuko- + G. kytos, cell] also leucocyte. Bone Marrow and the Immune System. What is bone marrow?
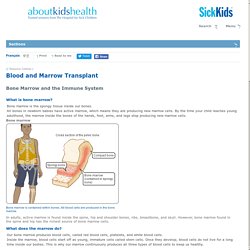
Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside our bones. All bones in newborn babies have active marrow, which means they are producing new marrow cells. By the time your child reaches young adulthood, the marrow inside the bones of the hands, feet, arms, and legs stop producing new marrow cells. In adults, active marrow is found inside the spine, hip and shoulder bones, ribs, breastbone, and skull. However, bone marrow found in the spine and hip has the richest source of bone marrow cells. What does the marrow do? Our bone marrow produces blood cells, called red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells. Inside the marrow, blood cells start off as young, immature cells called stem cells.
Red blood cells These cells are red because they are filled with a protein called haemoglobin. Platelets Platelets are blood cells that help the blood coagulate (stick together) to help stop bleeding at sites on the body that have been cut or injured. Through the Microscope. (11111 Reads) Table of Contents| Chapter Article List| Printable Version | Printable Chapter [Prev] | [Next] The primary tissues of the immune system are the bone marrow and thymus and these are involved in the creation and maturation of immune cells.
The secondary tissues of the immune system are the spleen, lymphatic system, lymph nodes and MALT. These tissues contain mature immune cells and are the active part of the immune system. The immune system consists of a complex network of organs and tissues, connected by blood and lymphatic vessels, that work together to prevent infection. Many different organs and tissues in the body contribute to the function of the immune system. The tissues of the immune system fall into two groups based upon their role in host defense. This figure cannot be displayed because permission has not been granted yet. Figure 15.2. . [Prev] | [Next] Table of Contents| Chapter Article List| Printable VersionPrintable Chapter. Adenoids and Tonsils. What are adenoids and tonsils? This leaflet gives a brief overview of problems which may occur with tonsils and adenoids.
There are separate more detailed leaflets on related topics such as tonsillitis, glandular fever and sore throat. Tonsils Tonsils are lumps of soft tissue and are part of the immune system. You have two tonsils, one on either side at the back of the mouth. Tonsils vary in size from person to person. A main function of tonsils is to trap germs (bacteria and viruses) which you may breathe in.
You can normally see your tonsils by opening your mouth wide and looking in a mirror. Adenoids. Immune System. The immune system, which is made up of special cells, proteins, tissues, and organs, defends people against germs and microorganisms every day.
In most cases, the immune system does a great job of keeping people healthy and preventing infections. But sometimes problems with the immune system can lead to illness and infection. About the Immune System The immune system is the body's defense against infectious organisms and other invaders. Through a series of steps called the immune response, the immune system attacks organisms and substances that invade body systems and cause disease. The immune system is made up of a network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body.