

Black Hole Hosts Universe's Most Massive Water Cloud. Weighing in at 40 billion times the mass of Earth, the giant cloud of mist swaddles a type of actively feeding supermassive black hole known as a quasar.

Among the brightest and most energetic objects in the universe, quasars are black holes at the centers of galaxies that are gravitationally consuming surrounding disks of material while burping back out powerful energy jets. "As this disk of material is consumed by the central black hole, it releases energy in the form of x-ray and infrared radiation, which in turn can heat the surrounding material, resulting in the observed water vapor," said study co-author Eric Murphy, an astronomer with the Carnegie Observatories in Pasadena, California. {sciences²} Einstein Les physiciens de l'expérience internationale Opera ont mesuré des particules allant plus vite que la lumière, pourtant considérée jusqu'à présent comme une limite infranchissable.

De quoi chambouler la théorie de la relativité ? J'ai publié un article ce matin dans Libération, il sera en ligne demain sur le blog. En attendant, voici le tchat réalisé cet après-midi sur le site web de Libération. Proton: la presse ne s’emballe t-elle pas un peu vite? Sylvestre Huet: L’importance de cette mesure très étrange car en contradiction avec une des théories les plus solides et vérifiées de la physique n’a pas été fixée par les journalistes. Billboquet: Avant de se demander si on s’emballe, peut on savoir ce qui se passe?
Or, lorsque, en mars dernier, le responsable de cette partie de l’expérience a regardé de près ses Schema OPERA mesures, il s’est rendu compte que les neutrinos arrivaient trop vite. Scientists Discover The Oldest, Largest Body Of Water In Existence. Scientists have found the biggest and oldest reservoir of water ever--so large and so old, it’s almost impossible to describe.

The water is out in space, a place we used to think of as desolate and desert dry, but it's turning out to be pretty lush. Researchers found a lake of water so large that it could provide each person on Earth an entire planet’s worth of water--20,000 times over. NASA research team reveals the Moon has earthlike core. Transparent Photovoltaic Cells Turn Windows Into Solar Panels. Paul Zerdin, ventriloquist without a dummy. 5347118082_fa66767410_z.jpg (JPEG Image, 640×318 pixels) News - Technology & Science - 1st habitable distant planet found. Two planets previously discovered around Gliese 581 had a very small chance of being habitable because they were right on the edge of the habitable zone.

Awesome death spiral of a bizarre star. I sometimes think I’ve seen everything there is in the sky, with nothing new left to see.
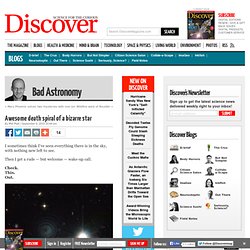
Then I get a rude — but welcome — wake-up call. Check. This. Out. [Click to enspiralnate.] When I first saw this picture, my reactions, in order, were: 1) What the frak is that? Followed immediately by 2) This must be a fake! Saturn's Strange Hexagon Recreated in the Lab. Saturn boasts one of the solar system's most geometrical features: a giant hexagon encircling its north pole.

Though not as famous as Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, Saturn's Hexagon is equally mysterious. Now researchers have recreated this formation in the lab using little more than water and a spinning table—an important first step, experts say, in finally deciphering this cosmic mystery. Saturn’s striped appearance comes from jet streams that fly east to west through its atmosphere at different latitudes.
Most jets form circular bands, but the Voyager spacecraft snapped pictures of an enormous hexagonally shaped one (each side rivals Earth's diameter) when it passed over the planet's north pole in 1988. Stumped scientists first attributed the shape to a huge, stormlike vortex along one of the hexagon’s sides, which Voyager also spotted during its journey. Beginning and end of the universe.
8 Wonders of the Solar System, Made Interactive: Scientific Amer. U.K. astronomers find new type of star. Scale_of_universe.swf (application/x-shockwave-flash Object) 10,000 Suns -Most Dense Star Cluster in Milky Way Located. With a mass of more than 10 000 suns packed into a volume with a diameter of a mere three light-years, the massive young star cluster in the nebula NGC 3603 is one of the most compact stellar clusters in the Milky Way and a natural lab to test theories for their formation, revealing whether the stars were in the process of drifting apart, or about to settle down.

The cluster, formally known as the NGC 3603 Young Cluster, is about 20 000 light-years from the Sun which makes these measurements extraordinarily difficult. It is necessary to compare images that were made years or even decades apart. The telescope and camera used must give very sharp images and be extremely stable over long periods. A team of astronomers from the Max-Planck Institute for Astronomy in Heidelberg and the University of Cologne led by Wolfgang Brandner realized that the Hubble Space Telescope was the best for the job.