

Twitter4rdf. RDF-Gravity. Sunil Goyal, Rupert Westenthaler {sgoyal, rwestenthaler}@salzburgresearch.at Salzburg Research, Austria RDF Gravity is a tool for visualising RDF/OWL Graphs/ ontologies.
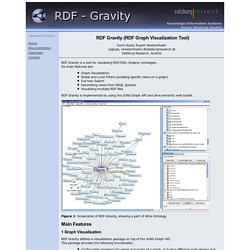
Its main features are: Graph VisualizationGlobal and Local Filters (enabling specific views on a graph) Full text SearchGenerating views from RDQL QueriesVisualising multiple RDF files RDF Gravity is implemented by using the JUNG Graph API and Jena semantic web toolkit. Figure 1: Screenshot of RDF-Gravity, showing a part of Wine Ontology 1 Graph Visualisation RDF Gravity defines a visualization package on top of the JUNG Graph API. Configurable renderers for edges and nodes of a graph, including different node shapes and edge decorations etc.A Renderer Factory allowing the configuration of the above node and edge renderers based on the type of an edge or node.
For graph layout, it uses the layout algorithms directly supported by the Jung API. 2 Global & Local Filters 3 Full Text Search 4 Visualising Multiple RDF Files. Provenance Vocabulary - trdf. Dave Beckett's Resource Description Framework (RDF) Resource Gui. RDFa Primer. Status of This Document This section describes the status of this document at the time of its publication. Other documents may supersede this document. A list of current W3C publications and the latest revision of this technical report can be found in the W3C technical reports index at This document is a Working Group Note produced jointly by the W3C Semantic Web Deployment Working Group [SWD-WG] and the W3C XHTML2 Working Group [XHTML2-WG].
This work is part of both the W3C Semantic Web Activity and the HTML Activity. This version of the RDFa Primer contains small editorial changes to the previous version as well as a short additional section (4.1) providing pointers to those wishing to create new relationship vocabularies. Comments on this Working Group Note are welcome and may be sent to public-rdf-in-xhtml-tf@w3.org; please include the text "comment" in the subject line. Publication as a Working Group Note does not imply endorsement by the W3C Membership. 1 Introduction. A Direct Mapping of Relational Data to RDF. Status of this Document This section describes the status of this document at the time of its publication.

Other documents may supersede this document. A list of current W3C publications and the latest revision of this technical report can be found in the W3C technical reports index at This is the First Public Working Draft of "A Direct Mapping of Relational Data to RDF" for review by W3C members and other interested parties. Sections 3 and 4 provide two normative definitions of the mapping from a relational database to an RDF graph.
Publication as a Working Draft does not imply endorsement by the W3C Membership. The W3C RDB2RDF Working Group is responsible for this document. Comments on this document should be sent to public-rdb2rdf-comments@w3.org, a mailing list with a public archive. This document was produced by a group operating under the 5 February 2004 W3C Patent Policy. 1 Introduction Strategies for mapping relational data to RDF abound. 2 Direct Mapping Description (Informative) RDFa Primer - Deutsche Übersetzung. Status dieses Dokuments Dieser Abschnitt beschreibt den Status dieses Dokuments zur Zeit seiner Veröffentlichung.

Andere Dokumente können dieses Dokument ersetzen. Eine Liste der aktuellen W3C-Veröffentlichungen und die aktuelle Version dieses Technischen Berichts kann im Index der Technischen Berichte des W3C unter gefunden werden. An Introduction to the Resource Description Framework. D-Lib MagazineMay 1998 ISSN 1082-9873An Introduction to the Resource Description Framework Eric Miller Research Scientist Online Computer Library Center, Inc.

Office of Research Dublin, Ohioemiller@oclc.org Abstract The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is an infrastructure that enables the encoding, exchange and reuse of structured metadata. RDF is an application of XML that imposes needed structural constraints to provide unambiguous methods of expressing semantics. RDF additionally provides a means for publishing both human-readable and machine-processable vocabularies designed to encourage the reuse and extension of metadata semantics among disparate information communities. The structural constraints RDF imposes to support the consistent encoding and exchange of standardized metadata provides for the interchangeability of separate packages of metadata defined by different resource description communities. Figure 5 This, in turn, could be syntactically represented as <? RDF- und RDFS-Editierung. Web 3.0 Content Authoring mit loomp - Home. RDF. Dublin Core (DC) Ziele für den Entwurf Einfachheit: durch Nicht-Experten benutzbarSemantische Kompatibilität: über Fachgrenzen hinweg benutzbarInternationaler Konsens: von Leuten aus über 30 Ländern erarbeitetErweiterbarkeit: offen für feinere Untergliederung der MetadatenAnwendbarkeit im Web: kompatibel mit RDF Die Bedeutung der Elemente ist wiederum durch die Spezifikation von ISO/ITEC 11179 Attributen festgelegt.

Syntax Die Core Elemente Titel Label: Title Definition: Name der Quelle. Beispiel: DC.Title="A Pilot's Guide to Aircraft Insurance" DC.Title="The Sound of Music" DC.Title="Green on Greens" DC.Title="AOPA's Tips on Buying Used Aircraft" Autor oder Erschaffer Label: Creator Definition: Körperschaft/Person, die für die Quelle inhaltlich verantwortlich ist.
FOAF. SIREn: Semantic Information Retrieval Engine.