

Machu-picchu-3.jpg (3648×2736) Llama_machu_picchu_1000.jpg (1000×750) Machu-picchu-c12.jpg (2376×3683) File:PompeiiStreet.jpg. File:Greek street - III century BC - Porta Rosa - Velia - Italy.JPG. Mayan-ruins-tikal.jpg (500×332) Machu-picchu-adrenaline-hikes.jpg (1200×1600) Top 10 Most Adrenaline Pumping Hiking Trails and Bridges machu-picchu-adrenaline-hikes – Top 10 Lists. Image Result for. Wheel. The earliest wheels were made of a solid piece of wood.
Etymology[edit] The English word wheel comes from the Old English word hweol, hweogol, from Proto-Germanic *hwehwlan, *hwegwlan, from Proto-Indo-European *kwekwlo-,[1] an extended form of the root *kwel- "to revolve, move around". Cognates within Indo-European include Greek κύκλος kúklos, "wheel" and Sanskrit chakra, both meaning "circle" or "wheel".[2] History[edit] A depiction of an onager-drawn cart on the Sumerian "battle standard of Ur" (c. 2500 BC) A figurine featuring the New World's independently invented wheel Evidence of wheeled vehicles appears from the second half of the 4th millennium BC, near-simultaneously in Mesopotamia (Sumerian civilization), the Northern Caucasus (Maykop culture) and Central Europe, so that the question of which culture originally invented the wheeled vehicle remains unresolved and under debate.
Early wheels were simple wooden disks with a hole for the axle. Mechanics and function[edit] Kuelap. View along fortress wall at Kuelap The fortress of Kuelap or Cuélap (Chachapoyas, Amazonas, Perú), associated with the Chachapoyas culture, consists of massive exterior stone walls containing more than four hundred buildings.
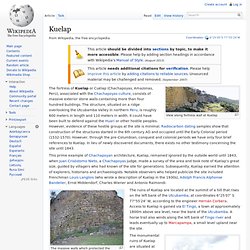
The structure, situated on a ridge overlooking the Utcubamba Valley in northern Peru, is roughly 600 meters in length and 110 meters in width. It could have been built to defend against the Huari or other hostile peoples. However, evidence of these hostile groups at the site is minimal. Radiocarbon dating samples show that construction of the structures started in the 6th century AD and occupied until the Early Colonial period (1532-1570). This prime example of Chachapoyan architecture, Kuelap, remained ignored by the outside world until 1843, when Juan Crisóstomo Nieto, a Chachapoyas judge, made a survey of the area and took note of Kuelap's great size, guided by villagers who had known of the site for generations. Cultural periods of Peru. This is a chart of cultural periods of Peru and the Andean Region developed by Edward Lanning and used by some archaeologists studying the area.
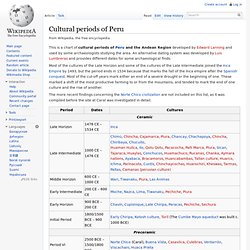
An alternative dating system was developed by Luis Lumbreras and provides different dates for some archaeological finds. Maya civilization. Uxmal, Nunnery Quadrangle Artist's copy of Bonampak Painting, Mexico, 700 C.E.
Throne 1 of Piedras Negras The Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for Maya script, the only known fully developed writing system of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as for its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Pre-Classic period (c. 2000 BC to AD 250), according to the Mesoamerican chronology, many Maya cities reached their highest state of development during the Classic period (c. Bronze Age. Diffusion of metallurgy in Europe and Asia Minor.
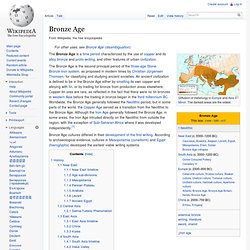
The darkest areas are the oldest. The Bronze Age is a time period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze and proto-writing, and other features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age Stone-Bronze-Iron system, as proposed in modern times by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen, for classifying and studying ancient societies. An ancient civilization is defined to be in the Bronze Age either by smelting its own copper and alloying with tin, or by trading for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Copper-tin ores are rare, as reflected in the fact that there were no tin bronzes in western Asia before the trading in bronze began in the third millennium BC.
Bronze Age cultures differed in their development of the first writing. History[edit] File:Collier de Penne.jpg. Bronze Age. The idea of a “Bronze” Age that succeeded a “Neolithic” or New Stone Age and preceded an “ Iron Age” was developed in the early nineteenth century and was based on the spectacular examples of bronze and gold objects placed in graves, rivers and bogs throughout Europe.
Modern archaeology has shifted the initial emphasis on metal craftsmanship to understanding how people inhabited the landscape. Whilst the importance of metal should not be denied, its role tends to be exaggerated as compared to more perishable materials such as wood, textiles and food. Taken together, the surviving evidence implies a multitude of inter-connected settled and mobile groups whose livelihoods relied on pastoral and arable agriculture as well as trade.
Africa. Europe. Americas. Asia.