

Viande : l'environnement, la santé et les animaux.
The different topics and websites. Slavery in America - Black History. The South would reach the breaking point the following year, when Republican candidate Abraham Lincoln was elected as president.

Within three months, seven southern states had seceded to form the Confederate States of America; four more would follow after the Civil War (1861-65) began. Though Lincoln’s antislavery views were well established, the central Union war aim at first was not to abolish slavery, but to preserve the United States as a nation. African-American Slavery - American History - Quatr.us. Civil Rights for Kids: History of Slavery in the United States including slave codes, abolitionism, free states vs. slave states, the Underground Railroad, Emancipation Proclamation, and the 13th amendment. James Hopkinsons Plantation Slaves Planting Sweet Potatoesby Henry P.
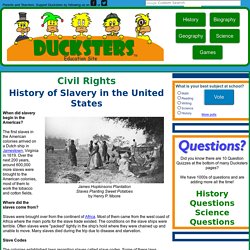
Moore. Slavery in America: Cotton, Slave Trade and the Southern Response. The United Sates was conceived on the idea of freedom and the rights of all people, but early on, an institution took hold that was the exact opposite of that idea.
In this lesson, find out the roots of slavery in the States, how it took hold, how slaves lived, and how they resisted the bonds of slavery. Explore our library of over 10,000 lessons Click "next lesson" whenever you finish a lesson and quiz. Got It You now have full access to our lessons and courses. Life on a Southern Plantation, 1854. Life on a Southern Plantation, 1854 The moral inconsistency of slavery existing within a nation founded upon the sanctity of individual freedom was well recognized in the early days of America's history.
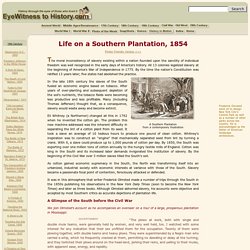
All 13 colonies legalized slavery at the beginning of America's War of Independence in 1775. By the time the nation's Constitution was ratified 13 years later; five states had abolished the practice. In the late 18th century the slaves of the South fueled an economic engine based on tobacco. After years of over-planting and subsequent depletion of the soil's nutrients, the tobacco fields were becoming less productive and less profitable. Eli Whitney (a Northerner) changed all this in 1792 when he invented the cotton gin.
Slave Plantations *** Slave PlantationsWhat were Slave Plantations?

Definition of Slave Plantations: Slave Plantations can be defined as large farms in the colonies that used the enforced labor of slaves to harvest cotton, rice, indigo, sugar, tobacco and other farm produce for trade and export. Typical Slave Plantations ranged from 500 to 1,000 acres and each acre produced about 5,000 plants. Resistance on the Plantations: The Abolition of Slavery Project. On the plantations, many enslaved Africans tried to slow down the pace of work by pretending to be ill, causing fires or ‘accidentally' breaking tools.

Whenever possible, enslaved Africans ran away. Some escaped to South America, England or North America. All of these acts made slavery less profitable. Some enslaved Africans fought back after they had escaped. Slave%20Life%20on%20a%20Southern%20Plantation. Bristol and Transatlantic Slavery. Enslaved Africans resisted, or rebelled, against their position as slaves in many different ways.
Each expression of resistance by enslaved individuals or groups counted as acts of rebellion against the system of slavery. The many instances of resistance show that slaves were not victims of slavery who accepted their situation. Instead they proved their strength and determination in fighting for their freedom. Uprising, or rebellion, was the most dramatic and bloody way that slaves could resist their enslavement. 3 Major Ways Slaves Showed Resistance to Slavery. By Lisa Vox.

Abolitionist Movement for kids *** Abolitionist Movement Facts for kidsInteresting Abolitionist Movement Facts and Timeline for kids are detailed below.
The history of Abolitionist Movement is told in a factual timeline sequence consisting of a series of short facts providing a simple method of relating the famous people and events of Abolitionism. Also refer to the Underground Railroad, the Underground Railroad Symbols & Secret Codes and Underground Railroad Maps Abolitionist Movement - Racial Discrimination and SegregationFor additional facts about racial discrimination and segregation refer to detailed information on Black Segregation History and for brief, fast facts refer to the Segregation History Timeline.
Black History for kids: Important People and EventsFor visitors interested in African American History refer to Black History - People and Events. Abolitionist. Abolitionism was a movement in several nations of the 19th century that sought to abolish slavery and the slave trade.

Members of this movement are known as abolitionists. The chief philosophical ground for abolition has been the idea of human rights --- that human beings are too valuable to be property, as well as the idea that human beings ought to control their own destiny. Much of this philosophy stems from religious views, although Christians, Jews and Muslims have all practiced slavery in the past. Belief in abolition has contributed to the foundation of some denominations such as the Free Methodist Church. Another ground for abolishing slavery has been economic, and much ink has been spilled describing how various crusaders or factions have sought to profit financially by outlawing slavery. What is Slavery?: The Abolition of Slavery Project. Slavery refers to a condition in which individuals are owned by others, who control where they live and at what they work.
Slavery had previously existed throughout history, in many times and most places. The ancient Greeks, the Romans, Incas and Aztecs all had slaves. What does it mean to be a slave or enslaved person? To be a slave is to be owned by another person. A slave is a human being classed as property and who is forced to work for nothing. What does it mean to be a Chattel Slave? A chattel slave is an enslaved person who is owned for ever and whose children and children's children are automatically enslaved. Chattel slavery was supported and made legal by European governments and monarchs.
Abolitionist movement. Civil War for Kids: Emancipation Proclamation. History >> Civil War The Emancipation Proclamation was an order given on January 1, 1863 by Abraham Lincoln to free the slaves. Were all the slaves immediately free? No. Emancipation Proclamation. Click here for the text of this historical document. As early as 1849, Abraham Lincoln believed that slaves should be emancipated, advocating a program in which they would be freed gradually. Early in his presidency, still convinced that gradual emacipation was the best course, he tried to win over legistators. To gain support, he proposed that slaveowners be compensated for giving up their "property.
" Support was not forthcoming. Emancipation Proclamation. Emancipation Proclamation Definition:Lincoln issued the proclamation Jan. 1, 1863. Kids Encyclopedia. Ku Klux Klan. The Ku Klux Klan (KKK) is one of several white supremacy organizations in the United States, which are dedicated to opposing civil rights for Blacks, Jews, and other ethnic, racial, social or religious groups. They also oppose Catholicism, and 'left' groups such as the IWW, and the gay rights movement. Ku Klux Klan. The Ku Klux Klan is a hate group.[1] It was started in the southern United States on 3 March 1865.
Ku Klux Klan - Facts & Summary. Ku Klux Klan History *** Kid's Biography: Martin Luther King, Jr. Martin Luther King, Jr. Martin Luther King, Jr. Martin Luther King, Jr. Martin Luther King Day. Rosa Parks for Kids. Biography Rosa Parksby Unknown. Rosa Parks Facts and Information for Kids. Rosa Parks Biography for Kids – The First Lady of Freedom « Remembering Rosa Parks. Teaching Kids NewsNearly 60 Years Ago Rosa Parks Refused To Change Seats On The Bus. Rosa Parks: Civil Rights Pioneer. Protestation aux Jeux Olympiques de Mexico par deux athlètes américains.
Mexico 68: Smith et Carlos un poing levé contre le racisme. Black Panther Party. The Black Panthers. The Black Panthers. The Black Panther Party for Self-Defense. Angela Davis. Angela Davis - Academic, Civil Rights Activist, Scholar, Women's Rights Activist. Angela Davis Biography - Women's History. Angela Davis Facts. Angela Davis. Racial segregation in the United States. Racial Segregation History for Kids *** Jim Crow Laws - Separate Is Not Equal. Civil Rights for Kids: Jim Crow Laws. Jim Crow Laws: Facts, List and Examples *** Kids Encyclopedia. Jim crow laws for kids. Racial segregation. Harlem. Ghettos in new york. So-called Black Ghetto Cool: From the Color Line to the Colorblind. Ghetto America. The Harlem gentrification: From black to white. African-American culture. Top 10 TED Talks for K-12 Teachers.
Ghetto. Jesse Owens Bio. Jesse Owens Biography: Olympic Athlete. JesseOwens.com. 1936 Olympics from Berlin with Hitler and Jesse Owens. Jesse Owens. African-American music. African-American culture. 100 Free Things: African American Culture. Opposingviews. Harlem Renaissance Facts: US History for Kids *** 1920s. Black History in America. Barack Obama - U.S. President, Lawyer, U.S. Senator. Sans titre. Barack Obama. Meet Barack Obama. Biography of President Barack Obama for Kids.