

Dean-Mac - Cow Eye Anatomy. 1.

Sclera - Tough, white outer covering of the eyeball. 2. Optic Nerve - A bundle of nerve fibers carrying information from the retina to the brain. 3. Cornea - Covering the iris and the pupil, the cornea is a tough and clear covering that begins bending light to make an image. 4. Aqueous Humor - Clear fluid that helps the cornea maintain its shape. 5. Pupil - A dark circle in the center of the iris which allows light into the inner eye.
Magic Eye: Client Samples, Eye. Bending Beams of Light. Summary:Students will learn about light beams, the concept of refraction and bending.
Main Curriculum Tie: Science - 6th GradeStandard 6 Objective 2Describe how light can be produced, reflected, refracted, and separated into visible light of various colors. Materials:Activity #1 Bowl Coin or washer Water Glass Pencil Paperclip or thin wire Cans (both ends removed) Round bottles filled with water, Square bottles Concave and convex lenses Shoe box top or lens holder Flashlights Slit blocks Protractor Compass Several round bottles same size (spice bottles) Refraction Experiment Log or Journals Activity #2 Activity #3 Box – the kind copier paper come in is ideal Equilateral prism Cardboard cutters White paper Overhead projector Slide projector or strong light source Yarn or string Cardstock Compass Protractor Pencil with point Student Journal or Prisms and Rainbows Additional Resources Books Videos Light, Series in Elementary Science.
Attachments Lenses are used to bend light. Reflection & Refraction Light Lesson - Elementary Science Lessons & Worksheets - My Schoolhouse. Reflection occurs when light bounces off objects.

How much reflection depends upon how even the surface is. If the surface is rough, the light scatters. If the surface is smooth and flat, the light will bounce off it at equal angles. That is why a flat mirror reflects a good likeness of the object being reflected. Look at the diagrams below. Refraction occurs because light bends. The curved surface/surfaces of a lens bends the light. Directions: Answer the questions about reflection and refraction. occurs when light bounces off an object. occurs when light is bent. When light strikes a surface that is rough, the light will . When light strikes a surface that is smooth, the light will bounce off at equal . What type of material is a lens? Transparent translucent opaque The path of light through a concave lens is not directed to a single focal point directed to a single focal point The path of light through a convex lens is.
Lenses - How they work. By Chris Woodford.
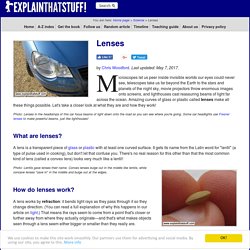
Last updated: May 7, 2017. Microscopes let us peer inside invisible worlds our eyes could never see, telescopes take us far beyond the Earth to the stars and planets of the night sky, movie projectors throw enormous images onto screens, and lighthouses cast reassuring beams of light far across the ocean. Amazing curves of glass or plastic called lenses make all these things possible. Let's take a closer look at what they are and how they work! Photo: Lenses in the headlamps of this car focus beams of light down onto the road so you can see where you're going. What are lenses? A lens is a transparent piece of glass or plastic with at least one curved surface.
Photo: Lentils gave lenses their name. How do lenses work? A lens works by refraction: it bends light rays as they pass through it so they change direction. Types of lenses There are two main types of lenses, known as convex (or converging) and concave (or diverging). Convex lenses Concave lenses Compound lenses.