

The Robinson Projection – Robinson Map Library. Robinson called this the orthophanic projection (which means “right appearing”), but this name never caught on.
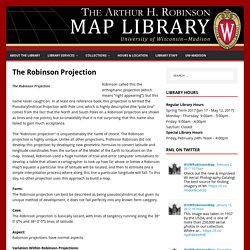
In at least one reference book, this projection is termed the Pseudocylindrical Projection with Pole Line, which is highly descriptive (the “pole line” comes from the fact that the North and South Poles on a Robinson projection are shown as lines and not points), but so unwieldily that it is not surprising that this name also failed to gain much acceptance. The “Robinson projection” is unquestionably the name of choice. The Robinson projection is highly unique. Unlike all other projections, Professor Robinson did not develop this projection by developing new geometric formulas to convert latitude and longitude coordinates from the surface of the Model of the Earth to locations on the map. Form: The Robinson projection can best be described as being pseudocylindrical, but given its unique method of development, it does not fall perfectly into any known form category. Distortions. Treasure hunt (game) - Wikipedia. Players searching for hidden treasure, buried in sand A treasure hunt is one of many different types of games with one or more players who try to find hidden objects or places by following a series of clues.
Treasure hunt games may be an indoor or outdoor activity. Outdoors they can be played in a garden or the treasure could be located anywhere around the world. Treasure hunts are sometimes organised as a game to be played at children's parties. The game could include searching for items, following clues as a group or splitting into teams to race to a prize. Mercator. The Mercator projection was first invented to help mariners.

They needed to be able to take a course and know the distance traveled, and draw a line on the map which showed the day's journey. In order to do this, Mercator invented a projection which preserved length, by projecting the earth's surface onto a cylinder, sharing the same axis as the earth itself. This caused all Latitude and Longitude lines to intersect at a 90° angle, thereby negating the problem that longitude lines get closer together at the poles. A Transverse Mercator projection takes the cylinder and turns it on its side. Now the cylinder's axis passes through the equator, and it can be rotated to line up with the area of interest. The UTM system was an attempt to set up a universal world wide system for mapping. Compare Map Projections. This website uses cookies to improve your experience.
More info Compare Map Projections Deutsch • English [info] Viewing options: Robinson. A Pseudocylindrical projection that preserves neither scale nor area, but which presents an aesthetically pleasing view of the entire world.

The Robinson projection is unlike most other projections in that it is not constructed by a mathematical formula used to transform coordinates systems. It is instead constructed by reference to a table of transformation parameters for meridians and parallels with an interpolation for locations between those given in the table. The table was created empirically to achieve a pleasing effect when the entire world is displayed. Scale Not true anywhere. Distortion Not free of distortion anywhere but the severe distortion near outer meridians at high latitudes seems less objectionable than in other pseudocylindrical projections.
Usage Overview maps of the entire world intended to present thematic data and not intended to be used for distance or area measurement. Origin Created by Arthur Robinson at the request of a commercial atlas publisher in the 1960’s. Geek Answers: Which map projection is 'best?' - Geek.com. What four things do map projections distort? There are four basic characteristics of a map that are distorted to some degree, depending on the map projection used.
These characteristics include distance, direction, shape, and area. My article is not to discuss the benefits of map projections but to look at how technology is contributing to skills and knowledge being lost. What four things do map projections distort? As a cartographer with over 25 years experience in the GeoSpatial Industry, I guess I have a slightly more critical eye when I see maps that are produced these days. It makes me cringe when I see maps that are missing some essential items like a scale, north point, legends, projection information or title. Are these basic elements being lost because it does not matter anymore or is it too easy to just rely on the technology and therefore too easy to overlook the basic elements. Cartografiando!!!: Proyecciones Cartograficas (IV) : Proyecciones Azimutales. Si de cartografiar los polos o completamente un hemisferio, sea el oriental o el occidental, la proyección mas indicada es la proyección azimutal.
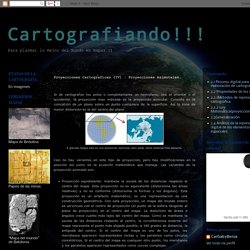
Consiste en la colocación de un plano sobre un punto cualquiera de la superficie. Así la zona de menor distorsión es la del centro del plano. Casi no hay variantes en este tipo de proyección, pero hay modificaciones en la posición así como en la ecuación matemática que maneja. Las variantes de la proyección azimutal son: Proyección equidistante: mantiene la escala de las distancias respecto al centro del mapa. Proyección estereográfica: es un sistema de representación gráfico en el cual se proyecta la superficie de una esfera sobre un plano mediante haces de rectas que pasan por un punto, o foco.
La Aventura de la Ciencia.