

Olietønder og brugte autodele skal give vindkraft i Tanzania – og på Roskilde Festival. Meteora.ucsd.edu/~jnorris/presentations/climate_model_clouds.pdf. Carbon Footprint Calculator. From Tobacco to Climate Change: How Doubt-Mongers Systematically Undermine Public Policy. In a videotaped lecture (see below), Naomi Oreskes discusses the upcoming book, Merchants of Doubt: How a Handful of Scientists Obscured the Truth on Issues from Tobacco Smoke to Global Warming (Bloomsbury USA), which she has coauthored with Erik Conway.

Oreskes is a professor of history and science studies at the University of California, San Diego. According to the publisher's spring catalog [PDF], the book tells "the troubling story of how a cadre of influential scientists have clouded public understanding of scientific facts to advance a political and economic agenda. " It continues: "The U.S. scientific community has long led the world in research on such areas as public health, environmental science, and issues affecting quality of life. Our scientists have produced landmark studies on the dangers of DDT, tobacco smoke, acid rain, and global warming. The Montreal Protocol. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are chemicals that were once the main ingredients of refrigerants, aerosol spray propellants, cleaning solvents, and bubbles injected into foams.

Through the 1970s and 1980s, scientific evidence mounted that release of these chemicals was depleting the ozone layer (which absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation) in Earth’s upper atmosphere. [1] In 1985, 28 states negotiated the Vienna Convention on Protection of the Ozone Layer to provide a framework for international regulations on ozone-depleting substances. Black carbon. Not to be confused with Carbon black.
For the cell phone model, see Samsung SGH-D900 Black carbon is found worldwide, but its presence and impact are particularly strong in Asia. Black carbon is in the air and circulates the globe. Chemically, black carbon or BC is a component of fine particulate matter (PM ≤ 2.5 µm in aerodynamic diameter). Black Carbon consists of pure carbon in several linked forms. Black carbon causes human morbidity and premature mortality.[1] In climatology black carbon or BC is a climate forcing agent. The term black carbon is also used in soil sciences and geology, referring either to deposited atmospheric BC or to directly incorporated BC from vegetation fires.[3][4] Especially in the tropics, BC in soils significantly contributes to fertility as it is able to absorb important plant nutrients.[5] Overview[edit] Early mitigation attempts[edit] Influence on Earth's atmosphere[edit] Most of the developments mentioned above relate to air quality in urban atmospheres.
You Doubt Monger, You. February 25, 2011 at 7:37 pm Over at Climate-Resistance.org Ben Pile has authored a brilliant analysis of attempts by UK newspaper columnist George Monbiot to blame climate skepticism on a big-oil-funded denial machine.
Although the post addresses Monbiot specifically, these criticisms also apply to many other green activists. Pile points out that, when environmentalists organize themselves, fund-raise, and try to spread their message this is considered legitimate democratic activity. How much has atmospheric CO2 increased in the past 150 years? Your math is incorrect, Bubba.
Tsk, tsk. CO2 lags temperature - what does it mean? Earth’s climate has varied widely over its history, from ice ages characterised by large ice sheets covering many land areas, to warm periods with no ice at the poles.
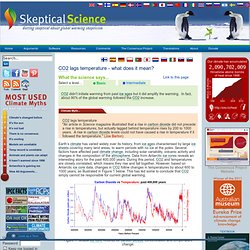
Several factors have affected past climate change, including solar variability, volcanic activity and changes in the composition of the atmosphere. Data from Antarctic ice cores reveals an interesting story for the past 400,000 years. During this period, CO2 and temperatures are closely correlated, which means they rise and fall together. However, based on Antarctic ice core data, changes in CO2 follow changes in temperatures by about 600 to 1000 years, as illustrated in Figure 1 below. This has led some to conclude that CO2 simply cannot be responsible for current global warming. Figure 1: Vostok ice core records for carbon dioxide concentration and temperature change. This statement does not tell the whole story. Are CO2 levels increasing? Currently, humans are emitting around 29 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere per year.
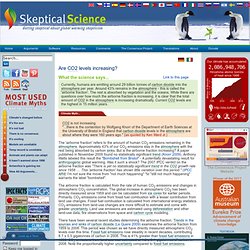
Around 43% remains in the atmosphere - this is called the 'airborne fraction'. The rest is absorbed by vegetation and the oceans. While there are questions over how much the airborne fraction is increasing, it is clear that the total amount of CO2 in the atmosphere is increasing dramatically. Current CO2 levels are the highest in 15 million years. The 'airborne fraction' refers to the amount of human CO2 emissions remaining in the atmosphere. CO2 lags temperature - what does it mean? A brief history of climate science. By Ed Hawkins, University of Reading Climate change is often seen as a recent phenomenon, but its roots are actually far older – the effects of human activity on the global climate have been discussed for more than 150 years.
In the 1820s, the French mathematician Joseph Fourier was trying to understand the various factors that affect Earth’s temperature. But he found a problem – according to his calculations, the Earth should have been a ball of ice. The most obvious factor, the Sun, did not seem to provide enough energy to raise the temperature of Earth above freezing. Sea Level Rise.