

A VC: Subconscious Information Processing. It's fathers day and I thought I'd tell a story about my dad and something he taught me a long time ago.

I was in middle school and I had a school project due the next day and it came up at dinner that I had not done the project. My dad made me stay up very late that night until I had completed it. And he stayed up with me. Seeing in the Dark. Credit: cliff1066tm.
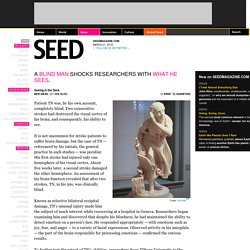
Patient TN was, by his own account, completely blind. Two consecutive strokes had destroyed the visual cortex of his brain, and consequently, his ability to see. It is not uncommon for stroke patients to suffer brain damage, but the case of TN — referenced by his initials, the general practice in such studies — was peculiar. His first stroke had injured only one hemisphere of his visual cortex.
About five weeks later, a second stroke damaged the other hemisphere. The Unexpected Reason Facebook May Be Good For Older Adults. Spending time on Facebook has been shown to reduce stress levels, slow down heart rates and -- generally speaking -- just simply relax people. Now new research suggests that learning to use Facebook may have an additional benefit for adults over 65: a sharpening of mental abilities.
Janelle Wohltmann, a graduate student in the University of Arizona department of psychology, set out to see whether teaching older adults to use the popular social networking site could give a boost to their cognitive performance and make them feel more socially connected. Her preliminary findings, which she shared this month at the International Neuropsychological Society Annual Meeting in Hawaii, reveal that older adults, after learning to use Facebook, performed about 25 percent better on memory tasks. During her study, Wohltmann helped train 14 older adults who had never before -- or who had rarely used -- Facebook so that they ultimately amassed new online friends while posting daily on the site.
Memory Laboratory. Home. Creating False Memories. Elizabeth F.

Loftus In 1986 Nadean Cool, a nurse's aide in Wisconsin, sought therapy from a psychiatrist to help her cope with her reaction to a traumatic event experienced by her daughter. During therapy, the psychiatrist used hypnosis and other suggestive techniques to dig out buried memories of abuse that Cool herself had allegedly experienced. In the process, Cool became convinced that she had repressed memories of having been in a satanic cult, of eating babies, of being raped, of having sex with animals and of being forced to watch the murder of her eight-year-old friend.
She came to believe that she had more than 120 personalities-children, adults, angels and even a duck-all because, Cool was told, she had experienced severe childhood sexual and physical abuse. When Cool finally realized that false memories had been planted, she sued the psychiatrist for malpractice. False Childhood Memories My research associate, Jacqueline E. Imagination Inflation Impossible Memories The Author. Learn About the MST. Scientists capture the first image of memories being made.
The ability to learn and to establish new memories is essential to our daily existence and identity; enabling us to navigate through the world.

A new study by researchers at the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital (The Neuro), McGill University and University of California, Los Angeles has captured an image for the first time of a mechanism, specifically protein translation, which underlies long-term memory formation. The finding provides the first visual evidence that when a new memory is formed new proteins are made locally at the synapse - the connection between nerve cells - increasing the strength of the synaptic connection and reinforcing the memory. The study published in Science, is important for understanding how memory traces are created and the ability to monitor it in real time will allow a detailed understanding of how memories are formed. (Photo Credit: Science) The biology of dreaming. O one would normally consider David Maurice, Ph.D., professor of ocular physiology in the Department of Ophthalmology at Columbia-Presbyterian Medical Center, a revolutionary.

Nevertheless, he has reignited a decades-long controversy that could spark a revolutionary re-evaluation of an entire field of behavioral research. Dr. Maurice has developed a startling new line of scientific inquiry that, when added to other findings, could change our understanding of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and the nature of dreams. What Maurice has done is to suggest an alternative explanation for the phenomenon known as REM sleep, the stage in which the eyes rapidly move and most dreams occur. Dr. The 5 Weirdest Sixth Senses Humans Have (Without Knowing It) Every attempt to prove that humans have some kind of telepathic sixth sense shows it to be complete bullshit.
But we still shouldn't sell ourselves short -- we have all sorts of "extra" senses that we either never use or don't notice when we do. And some of them come pretty damned close to mind reading. For instance ... #5. The Science of Word Recognition. The Brain—Information about the Brain. 1 Introduction “I think, therefore I am.”

—René Descartes, 17th-century philosopher Few of us question the crucial importance of the brain. It is vital to our existence. Our brains enable us to think, as René Descartes so skillfully pointed out nearly 400 years ago. The brain makes up only 2 percent of our body weight, but it consumes 20 percent of the oxygen we breathe and 20 percent of the energy we consume. Scientists have worked for many years to unravel the complex workings of the brain. Despite these and other significant advances in the field of brain research, most of the processes responsible for the integrated functioning of billions of brain cells remain a mystery.
Explanation: How Brain Training Can Make You Significantly Smarter.