

The Feynman Lectures on Physics Vol. I Ch. 37: Quantum Behavior. 37–1Atomic mechanics In the last few chapters we have treated the essential ideas necessary for an understanding of most of the important phenomena of light—or electromagnetic radiation in general.

(We have left a few special topics for next year. Specifically, the theory of the index of dense materials and total internal reflection.) What we have dealt with is called the “classical theory” of electric waves, which turns out to be a completely adequate description of nature for a large number of effects. We have not had to worry yet about the fact that light energy comes in lumps or “photons.” We would like to take up as our next subject the problem of the behavior of relatively large pieces of matter—their mechanical and thermal properties, for instance. Antistatic agent - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. An antistatic agent is a compound used for treatment of materials or their surfaces in order to reduce or eliminate buildup of static electricity generally caused by the triboelectric effect.
Its role is to make the surface or the material itself slightly conductive, either by being conductive itself, or by absorbing moisture from the air, so some humectants can be used. The molecules of an antistatic agent often have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas, similar to those of a surfactant; the hydrophobic side interacts with the surface of the material, while the hydrophilic side interacts with the air moisture and binds the water molecules. Internal antistatic agents are designed to be mixed directly into the material, external antistatic agents are applied to the surface.
Antistatic agents are also added to some military jet fuels, to impart electrical conductivity to them and avoid buildup of static charge that could lead to sparks igniting fuel vapors. See also[edit] Notes[edit] What Is Stati Electricity and How Can It Be Neutralized? What Is Static Electricity and How Can It Be Neutralized?

An introduction to ION CORD Static Eliminator What is static electricity? All matter is made of atoms that have a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. Normally the positive and negative charges are exactly equal so there is no net charge. When two surfaces touch, it means that the electrons in their surface atoms have gotten close enough to repel each other. There are powerful forces that occur between charges. Static is often a major problem on machinery that processes non-conductive materials.
Anionic, nonionic, cationic — what do they all mean? As a young boy growing up on Long Island, I remember watching my mother frantically trying to clean up some unknown food or drink spill from our carpet before company came.
She’d scrub and scrub, actually spreading the spill instead of cleaning it. And, of course, with no carpet spot remover in the house, she would be forced to try whatever was handy, such as laundry detergent, dish soap, maybe even some alkaline degreaser from my dad’s workroom. “Shouldn’t you use carpet cleaner on that?” Measuring Conductivity. Measuring Conductivity The purpose of this experiment is to build a conductivity tester, to use it to test the conductivity of several substances, and to draw conclusions about the presence of ions in these substances.

Electrolytes are substances which dissolve in water to produce a solution which conducts an electrical current. Such substances produce ions when dissolved in water, and it is the ions which carry the current through the solution. Nonelectrolytes are substance whose aqueous solutions do not contain ions and hence do not conduct an electrical current. Electrolytes are classified as either strong electrolytes or weak electrolytes. NaCl(s) ®Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Www.pedagogics.ca/files/REVIEW/IB Physics Review.pdf.
What is superposition? - Definition from WhatIs.com. Superposition is a principle of quantum theory that describes a challenging concept about the nature and behavior of matter and forces at the sub-atomic level.
The Physics Behind Schrödinger's Cat Paradox. His feline paradox thought experiment has become a pop culture staple, but it was Erwin Schrödinger's work in quantum mechanics that cemented his status within the world of physics.
The Nobel prize-winning physicist would have turned 126 years old on Monday and to celebrate, Google honored his birth with a cat-themed Doodle, which pays tribute to the paradox Schrödinger proposed in 1935 in the following theoretical experiment. A cat is placed in a steel box along with a Geiger counter, a vial of poison, a hammer, and a radioactive substance. ZOOM . activities . sci . Electroscope. Are you charged up for the science scoop?
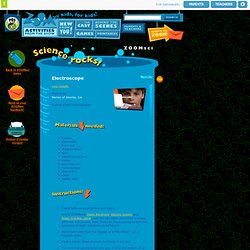
Because electrons have a negative charge, the foil ball and the pie pan both become negatively charged after touching a staticky object. When two things have the same charge, they repel, or push away from one another, which is what the foil ball does when it moves away from the pie pan. If you put your finger towards the foil ball, the foil ball will move towards it. How many coulombs of charge are on the electrons in a nickel coin? - Yahoo! Answers. Rice creates first long, strong, flexible, and conductive carbon nanotube thread. Chemical and nanoengineers at Rice University have become the first team to create long (hundreds of meters), macroscopic, mass-producible carbon nanotube thread. How to Stop Static on a Dress Clinging to You: 11 Steps - wikiHow. 3 Ways to Get Rid of Static Cling - wikiHow. Edit Article Edited by Teresa, Jack Herrick Three Methods:Methods to Remove Static QuicklyMethods to Remove Static in AdvancePrepping Yourself Static cling is the result of electrical charges that build up in your clothes due to dryness, friction, and other similar causes.
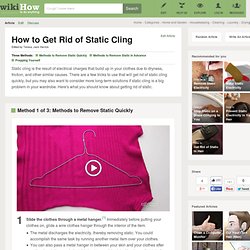
There are a few tricks to use that will get rid of static cling quickly, but you may also want to consider more long-term solutions if static cling is a big problem in your wardrobe. Here's what you should know about getting rid of static. Ad Steps. Types of Static Removal Devices. IB Physics. Chris Hamper IB Physics.
Electromagnetism.