

Seeing Theory. BetterExplained - Quick Reference Guide. Factorization diagrams. Calculus 1 Help. Math: Free Courses Online. Calculus 1 Lecture 1 1 An Introduction to Limits. Numbers Index. The Secret to All Areas. The Math Major Who Never Reads Math. In college, I was one of those compulsive read-everything kids.
I even felt pangs of guilt when I skipped optional reading. But there was one gaping hole in this policy of mine, large enough to squeeze a whole degree through. I never did the reading for math. You know, my major. I’m not proud of it, but I know I’m not alone. Numberphile: Complete Episode List. Ben. Untitled. Algebra Calculator - MathPapa. Algebra Calculator is a calculator that gives step-by-step help on algebra problems. Disclaimer: This calculator is not perfect. Please use at your own risk, and please alert us if something isn't working. Thank you. Type your algebra problem into the text box.
For example, enter 3x+2=14 into the text box to get a step-by-step explanation of how to solve 3x+2=14. More Examples. Triangle Classifications. Our study of triangles begins with their different classifications.
But before we can do this, we must learn how to name triangles. Since triangles are defined by their three vertices, we use the triangle symbol, ? , followed by the three vertices (in any order). For instance, ? ABC describes a triangle whose vertices are the points A, B, and C. Area under a Curve. Calculus I - Definition of the Definite Integral. In this section we will formally define the definite integral and give many of the properties of definite integrals.

Let’s start off with the definition of a definite integral. Definite Integral The definite integral is defined to be exactly the limit and summation that we looked at in the last section to find the net area between a function and the x-axis. Free Math Help and Free Math Videos Online at MathVids.com. Free video lectures,Free Animations, Free Lecture Notes, Free Online Tests, Free Lecture Presentations.
Trig without Tears: Contents. Summary: Faced with the large number of trigonometric identities, students tend to try to memorize them all.

That way lies disaster. When you memorize a formula by rote, you have no way to know whether you’re remembering it correctly. I believe it is much more effective (and, in the long run, much easier) to understand thoroughly how the trig functions work, memorize half a dozen formulas, and work out the rest as needed. That’s what these pages show you how to do. Copying: You’re welcome to print copies of this page for your own use, and to link from your own Web pages to this page. Q. A. If you nonetheless have trouble reading the site, or something just looks strange, please let me know which browser you are using and what the problem is. contact info | site map. A MAGIC Hexagon. The three functions on the left are, historically, the three principal trigonometric functions.
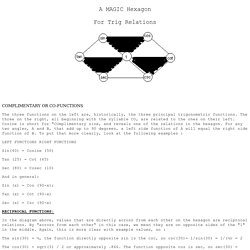
The three on the right, all beginning with the syllable CO, are related to the ones on their left. Cosine is short for "COmplimentary sine, and reveals one of the relations in the hexagon. For any two angles, A and B, that add up to 90 degrees, a left side function of A will equal the right side function of B. To put that more clearly, look at the following examples : Math.com - World of Math Online. My Math Forum - My Math Forum. Calculus Videos. Dave's Short Trig Course. Table of Contents Who should take this course?
Trigonometry for you Your background How to learn trigonometry Applications of trigonometry Astronomy and geography Engineering and physics Mathematics and its applications What is trigonometry? Trigonometry as computational geometry Angle measurement and tables Background on geometry The Pythagorean theorem An explanation of the Pythagorean theorem Similar triangles Angle measurement The concept of angle Radians and arc length Exercises, hints, and answers About digits of accuracy Chords What is a chord? Bewijzen van de Riemann-hypothese. Trigonometric and Geometric Conversions, Sin(A + B), Sin(A - B), Sin(AB) Ratios for sum angles As the examples showed, sometimes we need angles other than 0, 30, 45, 60, and 90 degrees.

In this chapter you need to learn two things: 1. Sin(A + B) is not equal to sin A + sin B. It doesn't work like removing the parentheses in algebra. 2. Geometry, Math, Maths. Free Online Courses From Top Universities. What is Calculus? Answered in an easy to understand way with pictures, diagrams and no fancy words! Math Functions - TI-Basic Developer. Calculators are built with one primary purpose: math.

Programming, game playing, and everything else is secondary. Thus, you will find a number of powerful math commands. Although it may seem that they are of no use to a programmer, programs sometimes need math functions, and many math functions can be used in clever ways. Pauls Online Math Notes. Cheat Sheets and Tables Here is list of cheat sheets and tables that I've written.

Most of these are pdf files and so you will need the Adobe Viewer to view them. You can download the latest version here. Algebra Cheat Sheet - [pdf] - This is as many common algebra facts, properties, formulas, and functions that I could think of. There is also a page of common algebra errors included. Calculus Why Calculus is Easy. Trigonometric Identities Solver - Symbolab. Symbolab Math Solver - Step by Step calculator. Untitled. Properties of Circles. Category:Elementary shapes. Lesson The Amazing Unit Circle: Trigonometric Identities. The unit circle definition of the trigonometric functions provides a lot of information The trigonometric functions sine and cosine are defined in terms of the coordinates of points lying on the unit circle x2 + y2 = 1.
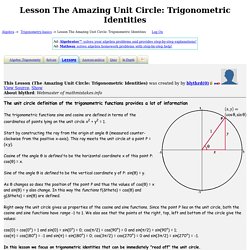
Start by constructing the ray from the origin at angle θ (measured counter-clockwise from the positive x-axis). This ray meets the unit circle at a point P = (x,y). Cosine of the angle θ is defined to be the horizontal coordinate x of this point P: cos(θ) = x. Sine of the angle θ is defined to be the vertical coordinate y of P: sin(θ) = y. As θ changes so does the position of the point P and thus the values of cos(θ) = x and sin(θ) = y also change.