

History of Vietnam. During the foreign domination of North Vietnam, several Indianized civilizations flourished in the central and south of what we know as Vietnam, particularly the Funanese and Cham.
The founders and rulers of these governments, however, were not native to Vietnam. From the 10th century onwards, the Vietnamese, emerging in their heartland of the Red River Delta, began to conquer these civilizations. When Ngô Quyền (King of Vietnam, 939–944) restoring sovereign power in the country, the next millennium was advanced by the accomplishments of successive dynasties: Ngôs, Đinhs, Prior Lês, Lýs, Trầns, Hồs, Posterior Trầns, Later Lês, Mạcs, Trịnhs, Nguyễns, Tây Sơns and again Nguyễns. At various points during these 1,000 years of imperial dynasties, Vietnam was ravaged and divided by civil wars and repeatedly attacked by the Songs, Mongol Yuans, Chams, Mings, Dutch, Manchus, French, and the Americans. Vietnam: The Ten Thousand Day War. Vietnam: The Ten Thousand Day War, a 26-part Canadian television documentary on the Vietnam War, was produced in 1980 by Michael Maclear.
The documentary series was consolidated into 13 hour-long episodes for American television syndication. The series was released on videocassette format by Embassy and won a National Education Association award for best world documentary. The military, political, and social repercussions of the Vietnam War continue to be felt, in the ways in which it altered the landscape of American life forever.
Written by CNN correspondent Peter Arnett, the 13 episodes of Vietnam: The Ten Thousand Day War trace the entire course of the conflict, from the closing days of World War II when Ho Chi Minh first began to assemble his revolutionary army, to the fall of Saigon in 1975. Documentary filmmaking simply doesn't get much better than this. History of Iraq. History of Iran. History of Japan. PBS OPB Japans Killer Quake 9.0 NOVA 3 30 2011 prt1a.
The Samurai. History of India. History of China. Chinese civilization originated in various regional centers along both the Yellow River and the Yangtze River valleys in the Neolithic era, but the Yellow River is said to be the cradle of Chinese civilization.
With thousands of years of continuous history, China is one of the world's oldest civilizations.[1] The written history of China can be found as early as the Shang Dynasty (c. 1700–1046 BC),[2] although ancient historical texts such as the Records of the Grand Historian (ca. 100 BC) and Bamboo Annals assert the existence of a Xia Dynasty before the Shang.[2][3] Much of Chinese culture, literature and philosophy further developed during the Zhou Dynasty (1045–256 BC). The Zhou Dynasty began to bow to external and internal pressures in the 8th century BC, and the kingdom eventually broke apart into smaller states, beginning in the Spring and Autumn Period and reaching full expression in the Warring States period.
Prehistory. History of China. Zheng He. Zheng He (1371–1433), formerly romanized as Cheng Ho, was a Hui court eunuch, mariner, explorer, diplomat, and fleet admiral during China's early Ming Dynasty.
Zheng commanded expeditionary voyages to Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and East Africa from 1405 to 1433. As a favorite of the Yongle Emperor, whose usurpation he assisted, he rose to the top of the imperial hierarchy and served as commander of the southern capital Nanjing (the capital was later moved to Beijing by Yongle). These voyages were long neglected in official Chinese histories but have become well known in China and abroad since the publication of Liang Qihao's Biography of Our Homeland's Great Navigator, Zheng He[3] in 1904.[4] A trilingual stele left by the navigator was discovered on the island of Sri Lanka shortly thereafter. Family[edit] Zheng He was the second son of a family from Kunyang,[a] Yunnan.[5] He was originally born with the name Ma He.[1][6] His family were Hui people. Confucius - Words of Wisdom part 1 of 5 Du Weiming Wei-ming Tu Harvard University. Discovery Atlas: China Revealed.
In one of the few times in its 5,000-year history, the oldest, most populous nation on earth has opened its doors to the rest of the world.
Coupling insightful storytelling with spectacular and groundbreaking photographic techniques, Discovery Atlas: China Revealed brings to life the fascinating and complex contemporary life of this extraordinary country. In today's China, the economics of feudalism and communism are out, while capitalism is in... with a Chinese twist. Old walls are being torn down, and a futuristic landscape of glass and steel is shooting up in their place.
History of Mongolia. Prehistory[edit] Mongolia has been inhabited for over 850,000 years with Homo erectus.[1] Important prehistoric sites are the paleolithic cave drawings of the Khoid Tsenkheriin Agui (Northern Cave of Blue) in Khovd province,[2] and the Tsagaan Agui (White Cave) in Bayankhongor province.[3] A neolithic farming settlement has been found in Dornod province.
Contemporary findings from western Mongolia include only temporary encampments of hunters and fishers. Kublai Khan. Genghis Khan. Genghis Khan (/ˈɡɛŋɡɪs ˈkɑːn/ or /ˈdʒɛŋɡɪs ˈkɑːn/,[5][6] Mongol: [tʃiŋɡɪs xaːŋ] ( ); Chingis/Chinghis Khan; 1162?
– August 1227), born Temujin, was the founder and Great Khan (emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous empire in history after his demise. Before Genghis Khan died, he assigned Ögedei Khan as his successor and split his empire into khanates among his sons and grandsons.[7] He died in 1227 after defeating the Western Xia. He was buried in an unmarked grave somewhere in Mongolia at an unknown location[citation needed].
His descendants went on to stretch the Mongol Empire across most of Eurasia by conquering or creating vassal states out of all of modern-day China, Korea, the Caucasus, Central Asian countries, and substantial portions of modern Eastern Europe, Russia and the Middle East. Beyond his military accomplishments, Genghis Khan also advanced the Mongol Empire in other ways. Early life Lineage Birth Early life and family Marriage to Börte Religion. History of Asia. Detail of Chinese silk from the 4th century BCE.
The characteristic trade of silk through the Silk Road connected various regions from China, India, Central Asia, and the Middle East to Europe and Africa. Pashtun people. Often characterised as a warrior and martial race, their history is spread amongst various countries of South, Central and Western Asia, centred around their traditional seat of power in medieval Afghanistan.
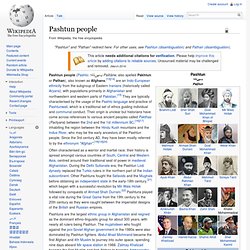
During the Delhi Sultanate era, the Pashtun Lodi dynasty replaced the Turkic rulers in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. Other Pashtuns fought the Safavids and the Mughals before obtaining an independent state in the early-18th century,[21] which began with a successful revolution by Mir Wais Hotak followed by conquests of Ahmad Shah Durrani.[22] Pashtuns played a vital role during the Great Game from the 19th century to the 20th century as they were caught between the imperialist designs of the British and Russian empires. Pashtuns are the largest ethnic group in Afghanistan and reigned as the dominant ethno-linguistic group for about 300 years, with nearly all rulers being Pashtun. They made up the majority of the Taliban and the current Afghan government. History of Pakhtuns/Pashtuns/Pathans.