

Nano. Chem 570 Nanotechnology forTeachers_Page_06.jpg (1506×1121) Nanostructured nanowires appears to solve loss of superconductivity in very strong magnetic fields. Researchers have discovered a way to efficiently stabilize tiny magnetic vortices that interfere with superconductivity—a problem that has plagued scientists trying to engineer real-world applications for decades.
The discovery could remove one of the most significant roadblocks to advances in superconductor technology. When magnetic fields reach a certain strength, they cause a superconductor to lose its superconductivity. Self Assembly Nano Particles for RFID Tag (chemtrails) at NAMI. Wax-infused "nanoyarn" used to create artificial muscles. An international team of scientists based at the University of Texas, Dallas (UTD), has developed a new type of artificial muscle created from carbon “nanotubes” – tiny hollow cylinders constructed from the same graphite layers found in the core of a standard pencil.
Despite measuring 10,000 times less than the diameter of a human hair, the new muscles can lift more than 100,000 times their own weight, which amounts to approximately 85 times the power of a natural muscle of equivalent size. The new muscles are manufactured by taking a twisted yarn of the miniscule carbon cylinders, then introducing a volume-changing “guest,” in this case the paraffin wax used in candles. The wax-coated yarn is then heated either electrically, or with a flash of light, and this causes the wax to expand, with the yarn volume increasing, and the length of the material contracting as a result. This muscle contraction, or actuation, can occur in just 25 thousandths of a second. Dr. Source: UTD. Nanotechnology. Aging is a cellular process, so the only way to stop it (or reverse it) may be on the cellular level.
That’s where nanotechnology comes in. The term describes microscopic devices, materials, or even robots, that can revive cells, attack viruses, repair organs, even deliver precision drug or gene therapies. Nanorobots would also destroy cancer cells more effectively than any current treatment. For example, in 2004, researchers at Rice University sent gold “nanoshells” after tumors in mice.
Combining Nanowires and Memristors Could Lead to Brain-like Computing. For decades now, researchers have been trying to get computers to behave like artificial brains instead of merely binary data crunchers.
One of the obstacles in creating this capability has been that computers are based on silicon CMOS chips rather than the dendrites and synapses found in the human brain. One of the drawbacks with silicon chips is that they lack what is known as "plasticity" in which the brain's neurons adapt in order to learn and remember. To overcome such limitations, nanotechnology has been offering alternatives to silicon chip architecture that will more closely resemble the human brain. Nanotubes boost potential of salinity power as a renewable energy source. In November 2009, Norwegian state owned electricity company Statkraft opened the world’s first osmotic power plant prototype, which generates electricity from the difference in the salt concentration between river water and sea water.
While osmotic power is a clean, renewable energy source, its commercial use has been limited due to the low generating capacities offered by current technology – the Statkraft plant, for example, has a capacity of about 4 kW. Nanotechnology_diagram.jpg (902×700) The singularity is coming: 3 chips that meld man and machine. Nanotech ‘paints’ teeny tiny Mona Lisa. How Nanotechnology Could Reengineer Us - Keithley Instruments Inc. DARPA's Plan to Nanochip Soldiers Has a Darker Agenda Behind it 1/2. Nanotechnology.jpg (1034×776) Welcome to NanoSpace! Scientists observe your body's own self-assembling nanomachines in action. Repair DNA and Cells using Nanotech. Home > Press > Nanobotmodels Company offer vision of future DNA and cell-repair techniques Abstract: Five decades of research and practical application of computers in biomedicine has given rise to the discipline of medical informatics, which has made many advances in genomic and translational medicine possible.
Ukraine | Posted on March 15th, 2010 Developments in nanotechnology and nanorobotics are opening up the prospects for nanomedicine and regenerative medicine where informatics and DNA computing can become the catalysts enabling health care applications at sub-molecular or atomic scales. While nanomedicine promises a new exciting frontier for clinical practice and biomedical research, issues involving cost-effectiveness studies, clinical trials and toxicity assays, drug delivery methods, and the implementation of new personalized therapies still remain challenging. DNA repair nanorobotics will utilize the same tasks that living systems already prove possible. Nanotechnology - Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies. The Most Interesting Developments in Nanotechnologies. Nanomachine, nanogenerator, nanoelectronics – but most of all, the innovations relate to the field of nanomedicine.
The most interesting developments (till now) in nanotechnologies in are: Nanomachine Researchers from the University of Groningen in the Netherlands and the Swiss Research Laboratory of Materials Science and Technology created a prototype of nano-sized car. Nanoneural Upgrade. You've always been told that you can "improve your mind" by learning, but a group of European scientists have decided to be more direct about it.

They've learned that neural activity can be increased by grafting brain cells onto nano-tubes, thereby creating something that's half brain, half ultra-tech, all awesome. The work clamps a bunch of hippocampus cells to a fullerene nanotube. Trials have shown that the brain cells grow very effectively on the nanomaterial, indicating that this junction could be a biocompatible link between mind and machine. Even better, the single-walled nanotubes can actually accelerate signaling between neural cells. For Autodesk, a Step Into a Nanoscale World. Nano: The Next Dimension. Future looks bright for carbon nanotube solar cells (June 18. Light from the sun creates charges in an ultrathinfilm of carbon nanotubes (blue), which are extracted by fullerene C60 (brown) in this schematic of the groundbreaking proof-of-concept solar cell with greater than 1 percent efficiency.
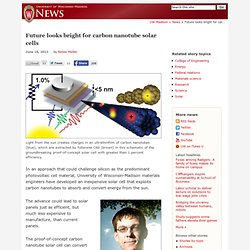
In an approach that could challenge silicon as the predominant photovoltaic cell material, University of Wisconsin-Madison materials engineers have developed an inexpensive solar cell that exploits carbon nanotubes to absorb and convert energy from the sun. Michael Arnold The advance could lead to solar panels just as efficient, but much less expensive to manufacture, than current panels. The proof-of-concept carbon nanotube solar cell can convert nearly 75 percent of the light it absorbs into electricity, says Michael Arnold, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at UW-Madison and a pioneer in developing carbon nanotube-based materials for solar energy applications.
Nanotech tea bag creates safe drinking water instantly, for less than a penny. World's Smallest Ear Can Hear Germs. A pin dropping is pretty quiet.
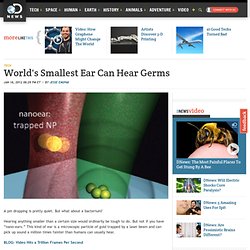
But what about a bacterium? Hearing anything smaller than a certain size would ordinarily be tough to do. But not if you have “nano-ears.” This kind of ear is a microscopic particle of gold trapped by a laser beam and can pick up sound a million times fainter than humans can usually hear. BLOG: Video Hits a Trillion Frames Per Second Sound waves happen when air is compressed and decompressed by pressure waves. Nanotechnology could help fight diabetes: Injectable nanogel can monitor blood-sugar levels, secrete insulin when needed.
Injectable nanoparticles developed at MIT may someday eliminate the need for patients with Type 1 diabetes to constantly monitor their blood-sugar levels and inject themselves with insulin. The nanoparticles were designed to sense glucose levels in the body and respond by secreting the appropriate amount of insulin, thereby replacing the function of pancreatic islet cells, which are destroyed in patients with Type 1 diabetes. Ultimately, this type of system could ensure that blood-sugar levels remain balanced and improve patients' quality of life, according to the researchers. "Insulin really works, but the problem is people don't always get the right amount of it. With this system of extended release, the amount of drug secreted is proportional to the needs of the body," says Daniel Anderson, an associate professor of chemical engineering and member of MIT's Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research and Institute for Medical Engineering and Science.
Nanotechnology and DNA Sequencing for Cancer Treatment. Cancer is still Canada’s number one killer. “Cancer affects everybody,” says Laura Syron, VP of Community Programs at the Princess Margaret Cancer Foundation. Fine-tuning Nanotech to Target Cancer.