

Home - Franklin Electric Australia. SR Series 8-Inch - Franklin Electric Australia. Fe342_sr_6_8in_data.pdf. Fe564_8_sr_assembly.pdf. Bore Hole Pumps - Franklin Electric Australia. At Franklin Electric, we carry a large selection of submersible, industrial, and well water pumps for use in submerged and aboveground water systems.

Our pumps are typically installed for use in residential clean water, residential wastewater, industrial, light commercial, agricultural, and municipal water systems. For additional information about application, choose your preferred brand from the links on the left hand side of this page. Submersible water pumps (sometimes called “submergible pumps”) can be operated while completely submerged underwater. Mechanical seals are used to keep any water from entering the pump motor and short circuiting it.
Submersible pumps have many useful applications, but the typical use is to pump water from a certain source, such as a water well, to a different desired destination. 338383-751 37kW ENC 239 601 at 400V.pdf (application/pdf Object) Eaton S801 and S811 Soft Starters for Compact Applications. TR Industries - WEG Electric Motors and Drives. Lowara DOC 7 GT Submersible Pump with tube floatswitch (0.55kW, 240v-1Ph-50Hz) Doc7 » Single Phase » Lowara DOC Submersible Drainage Pumps » Lowara » Submersible Pumps » C & A Pumps Ltd. Motor controller. Applications[edit] Every electric motor has to have some sort of controller.
The motor controller will have differing features and complexity depending on the task that the motor will be performing. More complex motor controllers may be used to accurately control the speed and torque of the connected motor (or motors) and may be part of closed loop control systems for precise positioning of a driven machine. For example, a numerically controlled lathe will accurately position the cutting tool according to a preprogrammed profile and compensate for varying load conditions and perturbing forces to maintain tool position. Types of motor controllers[edit] Motor controllers can be manually, remotely or automatically operated. An electric motor controller can be classified by the type of motor it is to drive such as permanent magnet, servo, series, separately excited, and alternating current. Main_GE_catalogue.pdf (application/pdf Object)
Starters - Vynco. Understanding Induction Motor Nameplate Information. The U.S. motor industry has worked on a standardized basis for more than three-quarters of a century.

The standardization agency — National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) — was established in 1926 “… to promote the standardization of electrical apparatus and supplies.” As a result of this group's efforts, you can expect “standard” motors from different manufacturers to meet or exceed minimum performance parameters and, for the most part, be about the same size. A critical part of making motors interchangeable is ensuring that nameplate information is common among manufacturers. The common language of the motor nameplate enables installation and maintenance personnel to quickly understand and recognize exactly what type of motor they're dealing with during a new installation or replacement procedure. Industrial submersible pumps. SP submersible pumps. SP submersible pumps. Ms_mms_brochure.pdf (application/pdf Object) Grundfos Australia & New Zealand homepage.
Products A-Z TR Industries - WEG Electric Motors and Drives. TR Industries - WEG Electric Motors and Drives. Weg Motors 2012_Technical_Catalogue.PDF. How Bearings Work" Plain bearing. Plain bearing on a 1906 S-Motor showing the axle, bearing, oil supply and oiling pad.
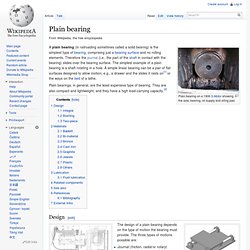
Plain bearings, in general, are the least expensive type of bearing. They are also compact and lightweight, and they have a high load-carrying capacity.[2] Design[edit] Rolling-element bearing. A sealed deep groove ball bearing A rolling element rotary bearing uses a shaft in a much larger hole, and cylinders called "rollers" tightly fill the space between the shaft and hole.
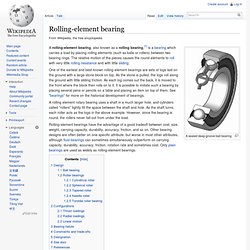
As the shaft turns, each roller acts as the logs in the above example. However, since the bearing is round, the rollers never fall out from under the load. Rolling-element bearings have the advantage of a good tradeoff between cost, size, weight, carrying capacity, durability, accuracy, friction, and so on. Main bearing. While some small single-cylinder engines have only one main bearing, designed to deal with the bending moment exerted by the crank as a result of the force from the connecting rod, most engines have at least two main bearings, one at each end of the crank shaft and may have as many as one more than the number of crank pins.
Increasing the number of bearings in an engine will generally increase the size and cost of the engine, but also provides stability to the crankshaft, which would otherwise have to endure greater bending moments from having the crank pin further from a bearing. The combination of bearing number and crankshaft design can also have an effect on engine balance; a more stable crankshaft will better avoid unbalance from flexing, but increasing the crankshaft length or girth to accommodate an additional bearing increases the rotational inertia of the crankshaft, which can have the opposite effect. Bearing (mechanical) The term "bearing" is derived from the verb "to bear";[1] a bearing being a machine element that allows one part to bear (i.e., to support) another.
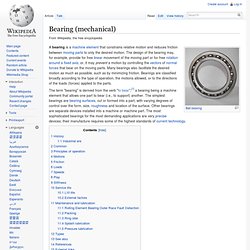
The simplest bearings are bearing surfaces, cut or formed into a part, with varying degrees of control over the form, size, roughness and location of the surface. Other bearings are separate devices installed into a machine or machine part. The most sophisticated bearings for the most demanding applications are very precise devices; their manufacture requires some of the highest standards of current technology. LV432641.pdf (application/pdf Object) Marelli - 30kW (40HP) 400V 3ph 4 Pole Foot Mounting AC Motor for Speed Control - AC Motors (Three Phase) Order Code: 21023 Product Brand: Marelli Part No: A4C200L4 B3 Obsolete product.
Alternatives may be available - see linked products below Description: Marelli 200 Frame - 30kW 3ph 4 Pole AC Motor for 400V or 660V 3 phase supply. Can be used over a 20:1 Speed Control range from 145RPM to 2930RPM, with suitable de-rating at the lower speeds. Fixed mains supply output is 30kW (40HP) x 1465RPM at 400V x 50Hz 3ph. Full Load Current - 58A at 400V. 360mm Wide x 723mm Long x 478mm high overall in its IP55 enclosure. Default.aspx (application/pdf Object) AC Motors (Three Phase) AC Motors (Three Phase) filtered by Power: 30kW.