

FlashAndVideo Add-On. We hope you enjoy this FireFox Add-On!

How to use this Mozilla Firefox Add-On ? Now, in order to download a Video or a Flash Game/Video, go to any of your favorite Video/Flash websites and wait for it to load. Once loaded, the little gray arrow icon in the Add-On bar and/or in the Tool-bar will light up to blue for any flash file found on the page; If a Video file was found on the page, the litte gray arrow icon will turn into blue as well but with an added small image of a clapboard, which means there are Videos available to download as well. Use that icon to download any desired Flash Game or Video. Enjoy! What people say about us: This is an excellent add-on which is very good at what it does. "this is by far the best flash down loader that I have ever used. it is simple and easy to use. " "Incredible. Altistart 01 - Soft starters for simple machines from 0.37 to 75 kW - Products overview - Schneider Electric.
1sxu000083d0201.pdf. Motor Starting - Electronic Soft Start. Loading, please wait.
Breathing a sigh of relief, we are now onto the final motor starting system in the series. Before talking about electronic soft starting, is is worth mentioning that the development of power electronics has and continues to revolutionize that way motors are used and applications to which they can be applied.
You could write books (and some people have) on the application of power electronics to the running and control of motors. This is outside the scope of what we are looking at, and I will only be talking about the application to starting (and then in only a very general way). While primarily discussing electronic soft starters, lets remember that more advanced devices (variable speed drives for example) have this functionality in-built.
Power Electronics. Power Electronics is the study of switching electronic circuits in order to control the flow of electrical energy.
Power Electronics is the technology behind switching power supplies, power converters, power inverters, motor drives, and motor soft starters. Eaton Soft Starter.pdf. Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motors.pdf. Induction motors - Electrical Installation Guide - Loads. SynchronousMach.pdf (application/pdf Object) Induction motor. Three-phase totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC) induction motor, with and, at right, without end cover to show cooling fan.
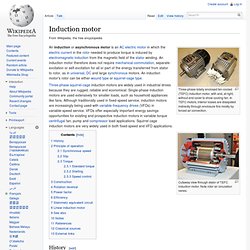
In TEFC motors, interior losses are dissipated indirectly through enclosure fins mostly by forced air convection. Three-phase squirrel-cage induction motors are widely used in industrial drives because they are rugged, reliable and economical. Synchronous motor. A synchronous motor-generator set for AC to DC conversion.
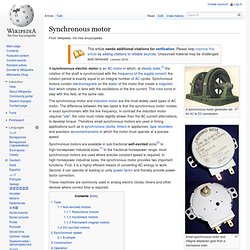
Small synchronous motor and integral stepdown gear from a microwave oven Synchronous motors are available in sub-fractional self-excited sizes[2] to high-horsepower industrial sizes.[1] In the fractional horsepower range, most synchronous motors are used where precise constant speed is required. In high-horsepower industrial sizes, the synchronous motor provides two important functions. First, it is a highly efficient means of converting AC energy to work.
Second, it can operate at leading or unity power factor and thereby provide power-factor correction. These machines are commonly used in analog electric clocks, timers and other devices where correct time is required. Type[edit] Electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction is the production of a potential difference (voltage) across a conductor when it is exposed to a varying magnetic field.

It is described mathematically by Faraday's law of induction, named after Michael Faraday who is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831. History[edit] A diagram of Faraday's iron ring apparatus. Change in the magnetic flux of the left coil induces a current in the right coil.[1] How Electric Motors Work" To understand how an electric motor works, the key is to understand how the electromagnet works.
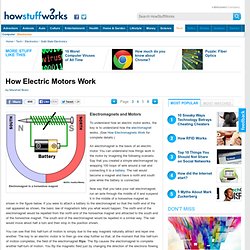
(See How Electromagnets Work for complete details.) An electromagnet is the basis of an electric motor. You can understand how things work in the motor by imagining the following scenario. Electromagnet. A simple electromagnet consisting of a coil of insulated wire wrapped around an iron core.
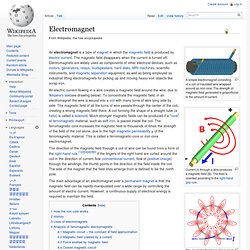
The strength of magnetic field generated is proportional to the amount of current. Current (I) through a wire produces a magnetic field (B). The field is oriented according to the right-hand grip rule. The magnetic field lines of a current-carrying loop of wire pass through the center of the loop, concentrating the field there. Electric generator. U.S.
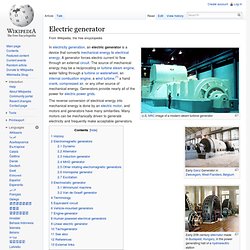
NRC image of a modern steam turbine generator The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by an electric motor, and motors and generators have many similarities. Many motors can be mechanically driven to generate electricity and frequently make acceptable generators. History[edit] Before the connection between magnetism and electricity was discovered, electrostatic generators were used. Induction generator. An induction generator or asynchronous generator is a type of AC electrical generator that uses the principles of induction motors to produce power.
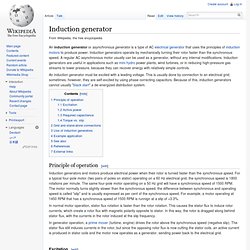
Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their rotor faster than the synchronous speed. A regular AC asynchronous motor usually can be used as a generator, without any internal modifications. Induction generators are useful in applications such as mini hydro power plants, wind turbines, or in reducing high-pressure gas streams to lower pressure, because they can recover energy with relatively simple controls. Ac Generator. How generator works by Khurram Tanvir. Engine. Terminology[edit] "Engine" was originally a term for any mechanical device that converts force into motion. Hence, pre-industrial weapons such as catapults, trebuchets and battering rams were called "siege engines".
The word "gin," as in "cotton gin", is short for "engine. " The word derives from Old French engin, from the Latin ingenium, which is also the root of the word ingenious. Most mechanical devices invented during the industrial revolution were described as engines—the steam engine being a notable example. In modern usage, the term engine typically describes devices, like steam engines and internal combustion engines, that burn or otherwise consume fuel to perform mechanical work by exerting a torque or linear force to drive machinery that generates electricity, pumps water, or compresses gas. Pump. A small, electrically powered pump A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps.[1] Torque.
Torque, moment or moment of force (see the terminology below), is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis,[1] fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist to an object. Mathematically, torque is defined as the cross product of the lever-arm distance vector and the force vector, which tends to produce rotation. Loosely speaking, torque is a measure of the turning force on an object such as a bolt or a flywheel.
For example, pushing or pulling the handle of a wrench connected to a nut or bolt produces a torque (turning force) that loosens or tightens the nut or bolt. The symbol for torque is typically τ, the Greek letter tau. Armature (electrical engineering) A DC armature. In electrical engineering, an armature generally refers to one of the two principal electrical components of an electromechanical machine — generally in a motor or generator — but it may also mean the pole piece of a permanent magnet or electromagnet, or the moving iron part of a solenoid or relay.
The other component is the field winding or field magnet. The role of the "field" component is simply to create a magnetic field (magnetic flux) for the armature to interact with, thus the field component can comprise either permanent magnets, or electromagnets formed by a conducting coil. Alternator. In principle, any AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually the term refers to small rotating machines driven by automotive and other internal combustion engines. An alternator that uses a permanent magnet for its magnetic field is called a magneto. Alternators in power stations driven by steam turbines are called turbo-alternators. History[edit] Alternating current generating systems were known in simple forms from the discovery of the magnetic induction of electric current in the 1830s. The early machines were developed by pioneers such as Michael Faraday and Hippolyte Pixii.
Stator. Electric motors and generators. Electric motors, generators, alternators and loudspeakers are explained using animations and schematics. Motor Formulas. Electric Motor Formula. Fleming's left-hand rule for motors. Connecting electronic VSDs (slightly OT) U need to be careful just cutting off the power of a VSD. 2 pole motor vs 4 pole motor. 2 pole or 4 pole motor? Electric motor. Various electric motors, compared to 9 V battery.