

Getting the most out of BIM_A guide for clients.pdf. Ductwork.pdf (application/pdf Object) EXACTLY how a car engine works - 3D animation ! How A Car Engine Works 3D Animation. How Differential Gear works (BEST Tutorial) Butterfly valve. Duplex valve in wafer butterfly configuration.
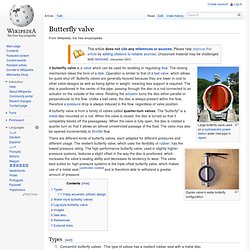
A butterfly valve is from a family of valves called quarter-turn valves. The "butterfly" is a metal disc mounted on a rod. When the valve is closed, the disc is turned so that it completely blocks off the passageway. When the valve is fully open, the disc is rotated a quarter turn so that it allows an almost unrestricted passage of the fluid. The valve may also be opened incrementally to throttle flow. There are different kinds of butterfly valves, each adapted for different pressures and different usage. Types[edit] Throttle. A throttle is the mechanism by which the flow of a fluid is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (i.e., by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term throttle has come to refer, informally and incorrectly, to any mechanism by which the power or speed of an engine is regulated. What is often termed a throttle (in an aviation context) is more correctly called a thrust lever. For a steam engine, the steam valve that sets the engine speed/power is often known as a regulator. Internal combustion engines[edit] VFD Application. MAXVENT® Louvre Return Air Grilles - Return Air Diffusion Products from Securimax.
Cooke Industries - Home. Oke Industries - Air Distribution Products - Air Diffusion. Trox_Ceiling_Diffuser_DLQ_ADLQ_2-11-EN-5.pdf (application/pdf Object) Pressure Units Online Converter. Convert Length - Unit Converter. Flow Units Converter. Friction Loss in Ducts. Ventilation. ASHRAE - American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers ASHRAE Standards Air - Altitude, Density and Specific Volume The density and the specific volume of air varies with the elevation above sea level Air Change Rate How to calculate air change rates - air change rate equations in imperial and SI units Air Change Rates for typical Rooms and Buildings Fresh air requirements - recommended air change rates - ACH - for some typical rooms and buildings - auditoriums, kitchens, churches and more.

Fantech on-line ventilation fans & noise control product catalogue. Heating, Ventilation, Air-Conditioning… In Thermal management, fans are classified as objects that forces air at a volumetric rate to cool certain devices, like a CPU microprocessor. There are numerous types of air moving products including axial, propeller, and tubeaxial fans. Other air movers consist of impellers and blowers (centrifugal & crossflow).
Fans, impellers, and blowers could be distinguished by their size, shape, but more importantly, the flow of air (measured in CFM) given the static air pressure. A fan can basically have a high output of CFM, but at a lower level of air pressure, whereas blowers and impellers move smaller amounts of air at a greater level of pressure. Basic Description of Fans, Impellers, and Blowers Fans: Tubeaxial fans could vary in many sizes, from 20x20mm (0.79" inches) to 172x51mm (6.77 inches). Impellers: Impellers have the best performance when it comes to noise. Shyuan Ya Fan Composition Shyuan Ya sells both inductive AC and brushless DC fans. Housing: Impellers: Rotor: Bearing: PC Board:
Sensible heat. Sensible heat is heat exchanged by a body or thermodynamic system that changes the temperature, and some macroscopic variables of the body, but leaves unchanged certain other macroscopic variables, such as volume or pressure.[1][2][3][4] The term is used in contrast to a latent heat, which is the amount of heat exchanged that is hidden, meaning it occurs without change of temperature.
For example, during a phase change such as the melting of ice, the temperature of the system containing the ice and the liquid is constant until all ice has melted. The terms latent and sensible are correlative. That means that they are defined as a pair, depending on which other macroscopic variables are held constant during the process. The sensible heat of a thermodynamic process may be calculated as the product of the body's mass (m) with its specific heat capacity (c) and the change in temperature ( Sensible heat and latent heat are not special forms of energy. See also[edit] References[edit] Refrigeration & air conditioning technology - William C. Whitman, William M. Johnson, John Tomczyk. Trane Trace 700 v 6.0. Ceiling diffusers. Ceiling diffusers type DD / DDRQ / DDQ.
Sheet Metal Calculators.