

High voltage charging systems. This Video Sequence is not available in the free CDX eTextbook Click this icon for more information about CDX Automotive Resource Kit Plus This Knowledge Check is not available in the free CDX eTextbook Click this icon for more information about CDX Automotive Resource Kit Plus This Lab Experiment is not available in the free CDX eTextbook Click this icon for more information about CDX Automotive Resource Kit Plus This Workshop Activity Sheet is not available in the free CDX eTextbook Click this icon for more information about CDX Automotive Resource Kit Plus This Assessment Checklist is not available in the free CDX eTextbook Click this icon for more information about CDX Automotive Resource Kit Plus This Handout Activity Sheet is not available in the free CDX eTextbook Click this icon for more information about CDX Automotive Resource Kit Plus As the number of electrical components increase, vehicles require increasing amounts of available electricity.
Electronic Stability Control. The Sending Unit - How Fuel Gauges Work. The sending unit is located in the fuel tank of the car.
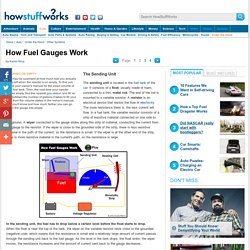
It consists of a float, usually made of foam, connected to a thin, metal rod. The end of the rod is mounted to a variable resistor. A resistor is an electrical device that resists the flow of electricity. The more resistance there is, the less current will flow. In a fuel tank, the variable resistor consists of a strip of resistive material connected on one side to the ground. In the sending unit, the fuel has to drop below a certain level before the float starts to drop. When the float is near the top of the tank, the wiper on the variable resistor rests close to the grounded (negative) side, which means that the resistance is small and a relatively large amount of current passes through the sending unit back to the fuel gauge.
This mechanism is one reason for the inaccuracy of fuel gauges. Something similar can happen when the float nears the bottom of the tank. Now let's see how the gauge works. LV07 Lubrication Systems. Work and power. Lead Acid battery construction. Definition: A lead-acid battery is a electrical storage device that uses a reversible chemical reaction to store energy.
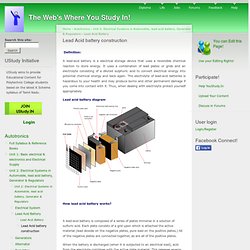
It uses a combination of lead plates or grids and an electrolyte consisting of a diluted sulphuric acid to convert electrical energy into potential chemical energy and back again. The electrolyte of lead-acid batteries is hazardous to your health and may produce burns and other permanent damage if you come into contact with it. Thus, when dealing with electrolyte protect yourself appropriately Lead acid battery diagram How lead acid battery works?
A lead-acid battery is composed of a series of plates immerse in a solution of sulfuric acid. When the battery is discharged (when it is subjected to an electrical load), acid from the elecrolyte combines with the active plate material. When a battery is recharged, the opposite occurs: the lead sulfate reverts back to active material, and the electrolyte becomes more acidic with a higher specific gravity. Discharge: Charge. Ballast resistor. Ballast resistor. "BCMV Engine Piston C Luke" Ballast resistor. Diesel-engine. Remix of "An inline engine is one where the pistons are. An inline engine is one where the pistons are arranged in a line next to each other.
This is probably the most common design, but it can take up a great deal of space because of the length of the cylinder block needed to hold the pistons. The inline unit is restricted by the number of cylinders it can use. Typically this would be four cylinders transversely mounted and six cylinders inline (rear wheel drive). Extending the cylinders above this number (even if room allowed) would result in more main bearings and journals supporting the crankshaft resulting in extra weight.disadvantages This type of engine uses low build cost during production; it also benefits from having very good 'balance' characteristics, by design. 1. smaller fly wheel (less weight). 2. engine fires more time daring rolation, porducing more mean torque. 3. engine can rev much higher due to reduced inertia ( smallaller componas).
Epicyclic gears. Aims and Objectives. Engines. Exhaust.