

Retrograde Neurotransmitter. Nicotine. In smaller doses (an average cigarette yields about 1 mg of absorbed nicotine), the substance acts as a stimulant in mammals, while high amounts (50–100 mg) can be harmful.[5][6][7] This stimulant effect is likely to be a major contributing factor to the dependence-forming properties of tobacco smoking, nicotine patches, nicotine gum, nicotine inhalers and liquid nicotine vaporizers.
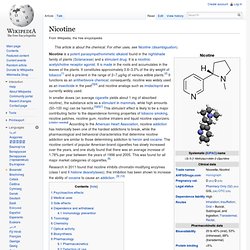
[citation needed] According to the American Heart Association, nicotine addiction has historically been one of the hardest addictions to break, while the pharmacological and behavioral characteristics that determine nicotine addiction are similar to those determining addiction to heroin and cocaine. The nicotine content of popular American-brand cigarettes has slowly increased over the years, and one study found that there was an average increase of 1.78% per year between the years of 1998 and 2005. This was found for all major market categories of cigarettes.[8] Nootropic. Nootropics (/noʊ.əˈtrɒpɨks/ noh-ə-TROP-iks), also referred to as smart drugs, memory enhancers, neuro enhancers, cognitive enhancers, and intelligence enhancers, are drugs, supplements, nutraceuticals, and functional foods that improve one or more aspects of mental function, such as working memory, motivation, and attention.[1][2] The word nootropic was coined in 1972 by the Romanian Dr.
Corneliu E. Giurgea,[3][4] derived from the Greek words νους nous, or "mind", and τρέπειν trepein meaning to bend or turn.[5] Availability and prevalence[edit] At present, there are only a few drugs which have been shown to improve some aspect of cognition in medical reviews. [citation needed] Many more are in different stages of development.[6] The most commonly used class of drug is stimulants, such as caffeine.[7] Academic use[edit] Surveys suggest that 3–11% of American students and 0.7–4.5% of German students have used cognitive enhancers in their lifetime.[11][12][13] Side effects[edit]
Citicoline. Citicoline (INN), also known as cytidine diphosphate-choline (CDP-Choline) & cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine is a psychostimulant/nootropic.
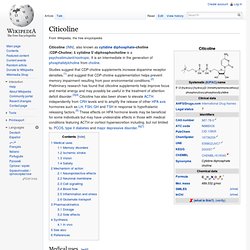
It is an intermediate in the generation of phosphatidylcholine from choline. Medical uses[edit] Citicoline is available as a supplement online and in stores. It is sold in over 70 countries under a variety of brand names: Ceraxon, Cognizin, NeurAxon, Somazina, Synapsine, etc. When taken as a supplement citicoline is hydrolyzed into choline and cytidine in the intestine.[8] Once these cross the blood–brain barrier it is reformed into citicoline by the rate-limiting enzyme in phosphatidylcholine synthesis, CTP-phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase.[9][10] Memory disorders[edit] In the hippocampi of rats with induced Alzheimer’s Disease, citicoline counteracts neuronal degeneration and reduces the number of apoptotic cells present.
Ischemic stroke[edit] Vision[edit] Satiety[edit] Mechanism of action[edit] Enzymes involved in reactions are identified by numbers.