

Cognitive dissonance. In psychology, cognitive dissonance is the mental stress or discomfort experienced by an individual who holds two or more contradictory beliefs, ideas, or values at the same time, or is confronted by new information that conflicts with existing beliefs, ideas, or values.[1][2] Leon Festinger's theory of cognitive dissonance focuses on how humans strive for internal consistency.

When inconsistency (dissonance) is experienced, individuals tend to become psychologically uncomfortable and they are motivated to attempt to reduce this dissonance, as well as actively avoiding situations and information which are likely to increase it.[1] Relationship between cognitions[edit] Individuals can adjust their attitudes or actions in various ways. Neuroscience of free will. Neuroscience of free will is the part of neurophilosophy that studies the interconnections between free will and neuroscience.
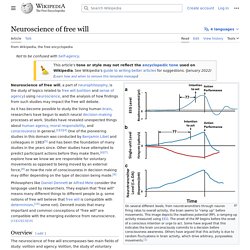
As it has become possible to study the living brain, researchers have begun to watch decision making processes at work. Findings could carry implications for our sense of agency and for moral responsibility and the role of consciousness in general.[1][2][3] Relevant findings include the pioneering study by Benjamin Libet and its subsequent redesigns; these studies were able to detect activity related to a decision to move, and the activity appears to begin briefly before people become conscious of it.[4] Other studies try to predict activity before overt action occurs.[5] Taken together, these various findings show that at least some actions - like moving a finger - are initiated unconsciously at first, and enter consciousness afterward.[6] A monk meditates. Electromagnetic theories of consciousness.
The electromagnetic theories of consciousness propose that consciousness can be understood as an electromagnetic phenomenon.
Overview[edit] Theorists differ in how they relate consciousness to electromagnetism. Electromagnetic field theories (or "EM field theories") of consciousness propose that consciousness results when a brain produces an electromagnetic field with specific characteristics. Susan Pockett[1] [2]and Johnjoe McFadden[3][4][5] have proposed EM field theories; William Uttal[6] has criticized McFadden's and other field theories. Some electromagnetic theories are also quantum mind theories of consciousness; examples include quantum brain dynamics (QBD) approaches of Mari Jibu and Kunio Yasue[7] and of Giuseppe Vitiello.[8] In general, however, quantum mind theories other than these QBD approaches do not treat consciousness as an electromagnetic phenomenon.