

Galaxy clusters. The Hubble Deep Fields. One of the main scientific justifications for building Hubble was to measure the size and age of the Universe and test theories about its origin.

Images of faint galaxies give 'fossil' clues as to how the Universe looked in the remote past and how it may have evolved with time. The Deep Fields gave astronomers the first really clear look back to the time when galaxies were forming. The first deep fields – Hubble Deep Field North and South – gave astronomers a peephole to the ancient Universe for the first time, and caused a real revolution in modern astronomy. Subsequent deep imagery from Hubble, including the Hubble Ultra Deep Field, has revealed the most distant galaxies ever observed. Because of the time it has taken their light to reach us, we see some of these galaxies as they were just half a billion years after the Big Bang.
Kardashev scale. The Kardashev scale is a method of measuring a civilization's level of technological advancement, based on the amount of energy a civilization is able to utilize.[1] The scale has three designated categories called Type I, II, and III.
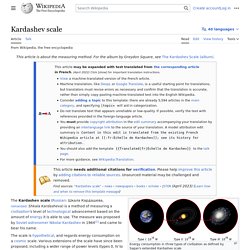
A Type I civilization uses only resources available on its home planet, Type II harnesses all needed energy from its local star, and Type III of its galaxy.[2] The scale is only hypothetical, but it puts energy consumption in a cosmic perspective. It was first proposed in 1964 by the Soviet astronomer Nikolai Kardashev. Various extensions of the scale have been proposed since, from a wider range of power levels (types 0, IV and V) to the use of metrics other than pure power. Definition[edit] Type I "Technological level close to the level presently attained on earth, with energy consumption at ≈4×1019 erg/sec (4 × 1012 watts) Type II Type III. Image Archive: Spacecraft.
AURA Study of Future Space-Based Telescopes. Return to Homepage AURA Study of Future Space-Based Telescopes January 21, 2015 The Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy has convened a group to investigate the possibilities for a next generation flagship UV-optical-NIR space telescope.

The committee, chaired by Julianne Dalcanton and Sara Seager, is exploring whether a single mission could meet the science goals of both the exoplanet and the general astronomy communities. The scientists, instrumentalists, and engineers on the committee are currently identifying high-value science opportunities and using these to narrow down the landscape of possible mission concepts and required technology investments. HubbleSite - Out of the ordinary...out of this world. What Would an Interstellar Spaceship Look Like? Project Icarus is an ambitious five-year study into launching an unmanned spacecraft to an interstellar destination.
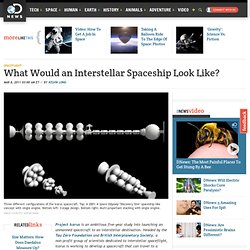
Headed by the Tau Zero Foundation and British Interplanetary Society, a non-profit group of scientists dedicated to interstellar spaceflight, Icarus is working to develop a spacecraft that can travel to a nearby star. In Part 1 of this two-part article, Kelvin Long, Design Lead for the Project Icarus Vehicle Configuration, describes the design constraints that were placed on the original Project Daedalus interstellar spacecraft.
WIDE ANGLE: Project Icarus: Reaching for Interstellar Space One of the most exciting parts of Project Icarus which is on everyone's mind with an interest in the project, is what will the spacecraft look like? Will it be very similar to the Daedalus design or radically different? Spaceplasma: Understanding Galaxies: An... Galaxy nomenclature. Galaxies contain varying numbers of planets, star systems, star clusters and types of interstellar clouds.
In between these objects is a sparse interstellar medium of gas, dust, and cosmic rays. List of Messier objects. The Messier objects are a set of astronomical objects catalogued by the French astronomer Charles Messier in his "Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d'Étoiles" ("Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters"), originally published in 1771, with the last addition (based on Messier's observations) made in 1966.[1] Because Messier was interested in finding only comets, he created a list of non-comet objects that frustrated his hunt for them.
The compilation of this list, in collaboration with his assistant Pierre Méchain, is known as the Messier catalogue. This catalogue of objects is one of the most famous lists of astronomical objects, and many Messier objects are still referenced by their Messier number.[2] The first edition included 45 objects, with Messier's final list totaling 103 objects. However, Messier 102 was not reported correctly, bringing the total to 102 objects. Messier objects[edit] Open cluster Globular cluster Nebula Planetary nebula Supernova remnant Galaxy Other.
Galaxies. COSMOS: A Spacetime odyssey. Chariots of the gods documentary. This video is currently unavailable.
Sorry, this video is not available on this device. by $author Share this playlist Cancel Play Pause Replay Stop live playback Playlist Next Previous Loop Shuffle Expand Collapse Like Dislike Full screen Exit full screen Share More More info Close. Universe or Multiverse Documentary. Through the wormhole. Astronomy Photographer of the Year : Exhibitions redirect : Visit. Take home the best of Astronomy Photographer of the Year The Royal Observatory has partnered with Collins to produce a beautiful hardback book featuring all the winning and shortlisted images from the 2013 Astronomy Photographer of the Year competition.
Order yours now from our shop. Royal Museums Greenwich Members receive 10% off items in all our shops.