

Sarah
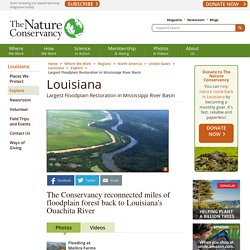
Largest Floodplain Restoration in Mississippi River Basin. US FWS manager, Kelby Ouchley, and TNC Board member, Tommy Barham, looking at the Mollicy floodplain.
Floodplains. Floodplain - The shape of the land, Forces and changes, Spotlight on famous forms, For More Information. Photo by: Torsten Dietrich Floodplains are landscapes shaped by running water.
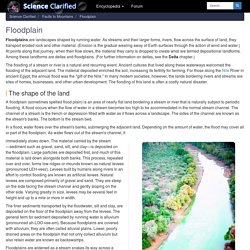
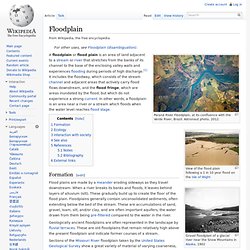
As streams and their larger forms, rivers, flow across the surface of land, they transport eroded rock and other material. (Erosion is the gradual wearing away of Earth surfaces through the action of wind and water.) At points along that journey, when their flow slows, the material they carry is dropped to create what are termed depositional landforms. Among these landforms are deltas and floodplains. The flooding of a stream or river is a natural and recurring event. The shape of the land A floodplain (sometimes spelled flood plain) is an area of nearly flat land bordering a stream or river that is naturally subject to periodic flooding. Floodplain. Paraná River Floodplain, at its confluence with the Verde River, Brazil.
Astronaut photo, 2012. What Is A Floodplain? For land use planning purposes, the regulatory floodplain is usually viewed as all lands within reach of a 100 year flood.
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) produces floodplain maps, defining what’s in and out of the 100-year (or “regulatory”) floodplain in order to implement the National Flood Insurance Program. Unfortunately, as Friends of the River flood policy expert Ronald Stork has noted, the regulatory floodplain and the federal insurance program have fostered a planning culture that allows people to be blind to geographic realities. “We need to have the entire floodplain mapped, not just an arbitrarily defined, 100- year flood zone,” says Stork.
What is a floodplain. How Sinkholes Form. Water supply Removing too much groundwater can leave underground holes, leading to sinkholes.

Frequently Asked Questions. Q: How dangerous are sinkholes?

A: Most sinkhole activity can be mitigated by identifying it quickly and working to correct it. Usually the notice of movement, the identification of sinkhole activity and its prescribed repair can happen well before and real dangerous movements of the soil or the structure can develop. This is most of the time. These Are The Places You Are Most Likely To Be Swallowed By A Sinkhole.
Photo: screenshot/ABC Last week a 30-foot-wide sinkhole opened in the ground in Florida and swallowed a man and his house.Things didn’t end up well for the man — the search for him was called off on Sunday night.
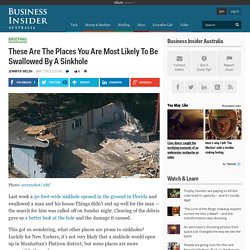
Clearing of the debris gave us a better look at the hole and the damage it caused. This got us wondering, what other places are prone to sinkholes? Luckily for New Yorkers, it’s not very likely that a sinkhole would open up in Manhattan’s Flatiron district, but some places are more susceptible than others. ” url=” are caused when underground water washes away soft rocks like limestone, carbonate rock and salt beds. The USGS calls areas like this “karst terrain.” According to the USGS, about 20 per cent of U.S. land is susceptible to sinkholes. The map below shows areas where underground cavities can form and catastrophic sinkholes can happen. UNICEF WCARO - Media Centre - EBOLA Outbreak in West Africa. EBOLA Outbreak in West Africa.

Ask Well: Can Pets Get Ebola? Ebola virus disease. Ebola Virus: Facts on Symptoms and the Latest Outbreak. Explicit cookie consent. Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa. The most widespread epidemic of Ebola virus disease (commonly known as "Ebola") in history is currently ongoing in three West African countries.[10][11] It has caused significant mortality, with reported case fatality rates of up to 70%[12][13][14][note 1] and specifically 57–59% among hospitalized patients.[15] Ebola virus disease was first described in 1976 in two simultaneous outbreaks in sub-Saharan Africa; this is the 26th outbreak and the first to occur in West Africa.
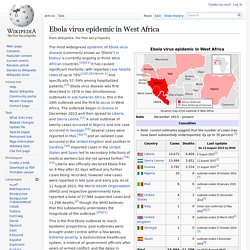
This is the first Ebola outbreak to reach epidemic proportions; past outbreaks were brought under control within a few weeks. Extreme poverty, a dysfunctional healthcare system, a mistrust of government officials after years of armed conflict, and the delay in responding to the outbreak for several months have all contributed to the failure to control the epidemic. Other factors include local burial customs that include washing of the body after death and the spread to densely populated cities.[22][23][24][25][26]
Questions and Answers on Ebola. General How do I protect myself against Ebola?
If you must travel to an area affected by the 2014 Ebola outbreak: Avoid contact with the blood and body fluids (such as urine, feces, saliva, sweat, urine, vomit, breast milk, semen, and vaginal fluids) of any person, particularly someone who is sick.Do not handle items that may have come in contact with an infected person’s blood or body fluids.Do not touch the body of someone who has died from Ebola.Do not have contact with the semen from a man who has recovered from Ebola (for example, avoid having oral, vaginal, or anal sex).Do not touch bats and nonhuman primates (apes and monkeys) or their blood and fluids and do not touch or eat raw meat prepared from these animals.Avoid facilities in West Africa where Ebola patients are being treated.
The U.S. Embassy or consulate is often able to provide advice on healthcare facilities that are suitable for your medical needs.