

ScienceDirect.com - Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology - Chilling-injury and disturbance of ion homeostasis in the coxal muscle of the tropical cockroach (Nauphoeta cinerea) ScienceDirect.com - Journal of Insect Physiology - Stage-related variation in rapid cold hardening as a test of the environmental predictability hypothesis. Jeb.biologists.org/content/214/5/726.full.pdf. On the nature of pre-freeze mortality in insects:... [J Exp Biol. 2004. On the nature of pre-freeze mortality in insects: water balance, ion homeostasis and energy charge in the adults of Pyrrhocoris apterus.
Three acclimation groups [i.e. non-diapause (LD), diapause (SD) and diapause, cold-acclimated (SDA)] of the adult bugs Pyrrhocoris apterus differed markedly in their levels of chill tolerance. Survival time at a sub-zero, but non-freezing, temperature of –5°C (Lt50) extended from 7.6 days, through 35.6 days, to >60 days in the LD, SD and SDA insects, respectively. On the nature of pre-freeze mortality in insects: water balance, ion homeostasis and energy charge in the adults of Pyrrhocoris apterus. Three acclimation groups [i.e. non-diapause (LD), diapause (SD) and diapause, cold-acclimated (SDA)] of the adult bugs Pyrrhocoris apterus differed markedly in their levels of chill tolerance. Survival time at a sub-zero, but non-freezing, temperature of –5°C (Lt50) extended from 7.6 days, through 35.6 days, to >60 days in the LD, SD and SDA insects, respectively.
On the nature of pre-freeze mortality in insects: water balance, ion homeostasis and energy charge in the adults of Pyrrhocoris apterus. Three acclimation groups [i.e. non-diapause (LD), diapause (SD) and diapause, cold-acclimated (SDA)] of the adult bugs Pyrrhocoris apterus differed markedly in their levels of chill tolerance. Survival time at a sub-zero, but non-freezing, temperature of –5°C (Lt50) extended from 7.6 days, through 35.6 days, to >60 days in the LD, SD and SDA insects, respectively. The time necessary for recovery after chill-coma increased linearly with the increasing time of exposure to –5°C, and the steepness of the slope of linear regression decreased in the order LD>SD>SDA. The capacity to prevent/counteract leakage of Na+ down the electrochemical gradient (from haemolymph to tissues) during the exposure to –5°C increased in the order LD<SD<SDA.
As a result, the rates of counteractive outward movement of K+, and of the EK dissipation, decreased in the same order. Www.sciencemag.org/content/231/4735/234.full.pdf. Trends in Ecology & Evolution - Insects at low temperatures: an ecological perspective. To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription.
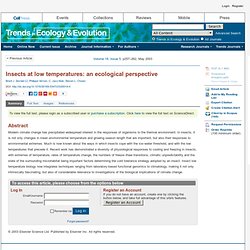
Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect. Fig. I Changes in the (a) water content, (b) melting point and (c) per-unit dry weight concentration of glycogen (solid line), trehalose (dashed line), and activity of trehalose-6-synthase (the enzyme responsible for the conversion between the two) (dotted line) when Onychiurus arcticus is cooled in the presence of ice from 5 to −5.5°C over a period of several days.
Summarized from [61,62] , Y-axis values for melting point and water content are approximate. Abstract Modern climate change has precipitated widespread interest in the responses of organisms to the thermal environment. To access this article, please choose from the options below Register an Account If you do not have an account, create one by clicking the button below, and take full advantage of this site's features. Www.units.muohio.edu/cryolab/publications/documents/Dollo2010.pdf. Www.units.muohio.edu/cryolab/projects/documents/ChenDenlingerLee87_PZ_2.pdf.