

Quantum Physics: Werner Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle of Quantum Mechanics. Werner Heisenberg Biography. Quantum Physics: Werner Heisenberg The Wave Structure of Matter (WSM) explains Werner Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle as caused by incorrect 'particle' conception of Matter.
Heisenberg Biography, Pictures, Quotes Introduction: Werner Heisenberg The problems of the particle and thus the resulting paradox of the particle / wave duality, have caused great confusion within quantum physics over the past seventy years, as both Werner Heisenberg and Paul Davies explain; Both matter and radiation possess a remarkable duality of character, as they sometimes exhibit the properties of waves, at other times those of particles.
Now it is obvious that a thing cannot be a form of wave motion and composed of particles at the same time - the two concepts are too different. The idea that something can be both a wave and a particle defies imagination, but the existence of this wave-particle duality is not in doubt. .. Heisenberg / Uncertainty Principle - Werner Heisenberg and the Uncertainty Principle. Common Interpretation of Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle Is Proved False. By Geoff Brumfiel of Nature magazine Contrary to what many students are taught, quantum uncertainty may not always be in the eye of the beholder.
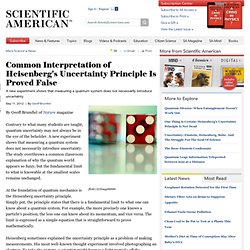
Uncertainty principle. Where ħ is the reduced Planck constant.
The original heuristic argument that such a limit should exist was given by Heisenberg, after whom it is sometimes named the Heisenberg principle. Quantum Physics and the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. Principe d'incertitude. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
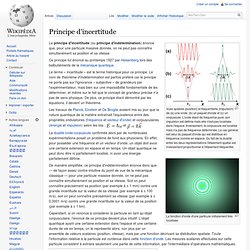
Vues spatiale (position) et fréquentielle (impulsion) de (a) une onde, (b) un paquet d'onde et (c) un corpuscule. L'onde étant de fréquence pure, son impulsion est définie mais elle n'est pas localisée dans l'espace. Inversement, le corpuscule est localisé mais n'a pas de fréquence déterminée. Le cas général est celui du paquet d'onde qui est distribué en fréquence comme en espace. Du fait de la dualité entre les deux représentations l'étalement spatial est inversement proportionnel à l'étalement fréquentiel. La fonction d'onde d'une particule initialement très localisée Le principe d'incertitude (ou principe d'indétermination) énonce que, pour une particule massive donnée, on ne peut pas connaître simultanément sa position et sa vitesse.
Ce principe fut énoncé au printemps 1927 par Heisenberg lors des balbutiements de la mécanique quantique. Le terme « incertitude » est le terme historique pour ce principe. Et , variant de -∞ à +∞. . Où choisi. Uncertainty Principle. What is Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle? Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle. Photograph: Alamy The uncertainty principle is one of the most famous (and probably misunderstood) ideas in physics. It tells us that there is a fuzziness in nature, a fundamental limit to what we can know about the behaviour of quantum particles and, therefore, the smallest scales of nature. Of these scales, the most we can hope for is to calculate probabilities for where things are and how they will behave.
Unlike Isaac Newton's clockwork universe, where everything follows clear-cut laws on how to move and prediction is easy if you know the starting conditions, the uncertainty principle enshrines a level of fuzziness into quantum theory. Werner Heisenberg's simple idea tells us why atoms don't implode, how the sun manages to shine and, strangely, that the vacuum of space is not actually empty. quanta. Uncertainty Principle. In classical physics, studying the behavior of a physical system is often a simple task due to the fact that several physical qualities can be measured simultaneously.

However, this possibility is absent in the quantum world. Mobile.rawstory. By Alok Jha, The GuardianSunday, November 10, 2013 9:02 EDT.
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle for Kids. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle for Kids When I throw a ball to you, you can see it coming because light from the sun (or a light bulb) bounces off the ball and into your eyes.
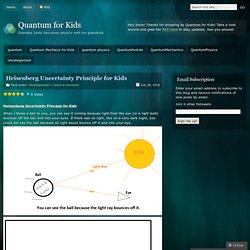
If there was no light, like on a very dark night, you could not see the ball because no light would bounce off it and into your eye. Theconversation. The term “uncertainty principle” suggests some grand philosophical idea, like “you can never be sure of anything”, or “there are some things you can never be sure of” and sometimes people use it as if this is what is meant.
In fact, this principle discovered by German theoretical physicist Werner Heisenberg in 1927, has a precise technical meaning that’s typically relevant only to microscopic particles. But it does have implications for how we understand the universe and our relation to it, and also to new technologies of the 21st century. Heisenberg - Quantum Mechanics, 1925-1927: Implications of Uncertainty.
There were also far-reaching implications for the concept of causality and the determinacy of past and future events.

These are discussed on the page about the origins of uncertainty. Because the uncertainty relations are more than just mathematical relations, but have profound scientific and philosophical implications, physicists sometimes speak of the "uncertainty principle. " A Science Odyssey: People and Discoveries: Heisenberg states the uncertainty principle.