

Get your Free Lizard Profile. Testimony of integrity. Testimony to integrity and truth, refers to the way many members of the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers) testify or bear witness to their belief that one should live a life that is true to God, true to oneself, and true to others.
To Friends, the concept of integrity includes personal wholeness and consistency as well as honesty and fair dealings. From personal and inward integrity flow the outward signs of integrity, which include honesty and fairness. It is not only about telling the truth - it is applying ultimate truth to each situation. For example, Friends (Quakers) believe that integrity requires avoiding statements that are technically true but misleading. The word testimony is used to refer to the ways in which Friends testify or bear witness to their faith in their everyday lives.
Also known as the Testimony of Truth, or Truth Testimony, the essence of the Testimony of Integrity is placing God at the center of one's life. Oaths and fair-dealing[edit] See also[edit] Punk subculture. Two UK punks in the 1980s The punk subculture, which centres on punk rock music, includes a diverse array of ideologies, fashions and forms of expression, including visual art, dance, literature and film.
The subculture is largely characterized by anti-establishment views and the promotion of individual freedom. The punk subculture emerged in the United Kingdom, Australia, and the United States in the mid-1970s. In the late 1970s, the subculture began to diversify, which led to the proliferation of factions such as new wave, 2 Tone, pop punk, hardcore punk, no wave, street punk and Oi!. Hardcore punk, street punk and Oi! The punk subculture is centered on a loud, aggressive genre of rock music called punk rock. Although punks are frequently categorised as having left-wing or progressive views, punk politics cover the entire political spectrum.
One of the biggest parts of punk was a creating explicitly outward identities of sexuality. The Beatles. The Beatles were an English rock band that formed in Liverpool, in 1960.
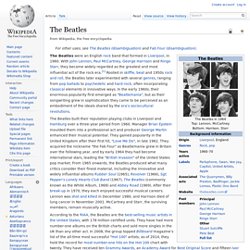
With John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr, they became widely regarded as the greatest and most influential act of the rock era.[1] Rooted in skiffle, beat and 1950s rock and roll, the Beatles later experimented with several genres, ranging from pop ballads to psychedelic and hard rock, often incorporating classical elements in innovative ways. In the early 1960s, their enormous popularity first emerged as "Beatlemania", but as their songwriting grew in sophistication they came to be perceived as an embodiment of the ideals shared by the era's sociocultural revolutions.
History. New Age. The New Age movement is a Western spiritual movement that developed in the second half of the 20th century. Its central precepts have been described as "drawing on both Eastern and Western spiritual and metaphysical traditions and infusing them with influences from self-help and motivational psychology, holistic health, parapsychology, consciousness research and quantum physics".[2] The term New Age refers to the coming astrological Age of Aquarius.[1] The movement aims to create "a spirituality without borders or confining dogmas" that is inclusive and pluralistic.[3] It holds to "a holistic worldview",[4] emphasising that the Mind, Body, and Spirit are interrelated[1] and that there is a form of monism and unity throughout the universe.[5] It attempts to create "a worldview that includes both science and spirituality"[6] and embraces a number of forms of mainstream science as well as other forms of science that are considered fringe.
History[edit] Origins[edit] Development[edit] History of the hippie movement. The hippie subculture began its development as a youth movement in the United States during the early 1960s and then developed around the world.
Its origins may be traced to European social movements in the 19th and early 20th century such as Bohemians, and the influence of Eastern religion and spirituality. From around 1967, its fundamental ethos — including harmony with nature, communal living, artistic experimentation particularly in music, and the widespread use of recreational drugs — spread around the world. Precursors[edit] Classical culture[edit] 19th- and early 20th-century Europe[edit]