

Mathematics : Secondary: Oxford University Press. The Four Basic Mathematical Operations. The Four Basic Mathematical Operations Key Terms o Term o Sum o Commutative o Negative o Difference o Factor o Product o Dividend o Divisor o Quotient Objectives o Review addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division for positive and negative numbers o Make note of the relationships between the operations o Identify which operations are commutative The four basic mathematical operations--addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division--have application even in the most advanced mathematical theories.
If you have difficulty performing the basic operations for simple numbers, one way to improve is through the use of flash cards. 8) and the answer (24, for our example) on the other. Addition and Subtraction Addition and subtraction are two complementary operations--we can actually define subtraction in terms of addition. The above diagram is an illustration of the process of addition. Furthermore, note that the order in which we add the squares makes no difference. MathSteps: Grade 4: Order of Operations: What Is It? When children initially learn addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, they begin by performing operations on two numbers.

But what happens when an expression requires multiple operations? Over time, mathematicians have developed a set of rules called the order of operations to determine which operation to do first. The rules are: Multiply and divide from left to right. Add and subtract from left to right. ESL math. How to Teach Math to English Language Learners. Teachers across the country have increasing numbers of English language learners (ELLs) in their classrooms.
As a result, teachers need strategies that will help them reach all of their students and ensure that students learn what they need to know. Many lessons in existing curricula are designed for native speakers of English and do not support second language acquisition. This is particularly true for math instruction. Students need specific vocabulary to talk about and do math. Top educator-tested teaching strategies from veterans who have been through it... Answers to many teachers’ frequently asked questions, as well as a few teaching... Here's how to make your student teaching experience a success. Classroom management ways to spice up boring seat work and make it a little bit... A quick guide to help you in the classroom management assessment process to... What instructional math goals should I have for my ELL students? How do specific strategies help ELL students learn math skills? Maths and English Practice.
Developmental Math Topic Text. Solving Multi-Step Equations Learning Objective(s) · Use properties of equality together to isolate variables and solve algebraic equations. · Use the properties of equality and the distributive property to solve equations containing parentheses, fractions, and/or decimals.
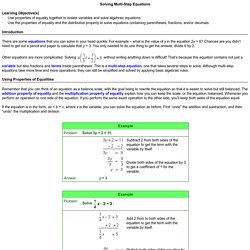
Other equations are more complicated. Solving Using Properties of Equalities If the equation is in the form, ax + b = c, where x is the variable, you can solve the equation as before. If the equation is not in the form, ax + b = c, you will need to perform some additional steps to get the equation in that form. Some equations may have the variable on both sides of the equal sign. Here are some steps to follow when you solve multi-step equations.
The examples below illustrate this sequence of steps. Solving Equations Involving Parentheses, Fractions, and Decimals More complex multi-step equations may involve additional symbols such as parentheses. Complex, multi-step equations often require multi-step solutions. Interweaving mathematics and pedagogy in task design: a tale of one task. Authors.
International Journal of Education in Mathematics, Science and Technology. A Case Study of E-tutors’ Teaching Practice: Does Technology Drive Pedagogy?

Hsueh-Hua ChuangFull Text Abstract Transfer of Learning in Mathematics, Science, and Reading among Students in Turkey: A Study Using 2009 PISA DataMack Shelley, Atila YildirimFull Text Abstract Representations of Fundamental Chemistry Concepts in Relation to the Particulate Nature of MatterZübeyde Demet Kırbulut, Michael Edward BeethFull Text Abstract Analysis of Scientific Epistemological Beliefs of Eighth GradersNilgün Yenice, Barış ÖzdenFull Text Abstract. Mathematical problem solving: Issues in research.
Journal for Research in Mathematics Education on JSTOR. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education. Vol. 47, No. 4, July 2016 Kateri Thunder, Charlottesville City Schools; and Robert Q.
Berry III, University of Virginia Mathematics education has benefited from qualitative methodological approaches over the past 40 years across diverse topics. Although the number, type, and quality of qualitative research studies in mathematics education has changed, little is known about how a collective body of qualitative research findings contributes to our understanding of a particular topic within the field. Through a process of qualitative research metasynthesis, our knowledge base can be broadened to provide insights into attitudes, perceptions, interactions, structures, and behaviors relevant for mathematics teaching and learning. Katherine E. Although approximately 5–8% of students have a mathematical learning disability (MLD), researchers have yet to develop a consensus operational definition. Kimberly Cervello Rogers, Bowling Green State University; and Michael D. Reviewed by Elizabeth L.