

Scientology. Scientology is a body of beliefs and related practices created by science fiction writer L.
Ron Hubbard (1911–1986), beginning in 1952 as a successor to his earlier self-help system, Dianetics.[6] Hubbard characterized Scientology as a religion, and in 1953 incorporated the Church of Scientology in Camden, New Jersey.[7][8] Gold Base. Coordinates: Gold Base (also variously known as Gold, Int Base, or Int) is the international headquarters of the Church of Scientology.
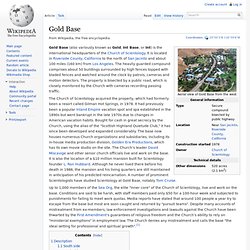
It is located in Riverside County, California to the north of San Jacinto and about 100 miles (160 km) from Los Angeles. The heavily guarded compound comprises about 50 buildings surrounded by high fences topped with bladed fences and watched around the clock by patrols, cameras and motion detectors. The property is bisected by a public road, which is closely monitored by the Church with cameras recording passing traffic. Departments. Office of Special Affairs. The Office of Special Affairs or OSA (formerly the Guardian's Office) is a department of the Church of Scientology.
According to the Church, the OSA is responsible for directing legal affairs, public relations, pursuing investigations, publicizing the Church's "social betterment works," and "oversee[ing its] social reform programs". Some observers outside the Church have characterized the department as an intelligence agency, comparing it variously to the CIA or the KGB.[1][2][3] The department has drawn criticism for its involvement in targeting critics of the Church for dead agent operations. OSA has mounted character assassination operations against many critics of the Church.[4][5] OSA is the successor to the now-defunct Guardian's Office,[6] which was responsible for Operation Snow White; both are in Department 20 in the Scientology Org-Chart. Sea Org. The Sea Organization, or Sea Org, is a paramilitary[3] wing of the Church of Scientology, comprising the church's most dedicated members.[4] It has also been described as a private naval force,[5] and has operated several vessels in its past.
As of 2009, it consisted of approximately 6,000 members, according to official Scientology statistics.[2] The Sea Org was established on 12 August 1967 by L. Ron Hubbard, the founder of Dianetics and Scientology, initially on board four ships, the Diana, the Athena, the Apollo, and the Excalibur. It moved to land-based organizations in 1975, though maritime customs persist, with many members wearing naval-style uniforms and addressing both male and female officers as "sir.
Scientology controversies. Since its inception in 1954, the Church of Scientology has been involved in a number of controversies.
When mainstream media outlets have reported alleged abuses, representatives of the church have tended to deny such allegations.[1] Many critics have called into question several of the practices and policies that the Scientology organization has in place in regard to its dealings with its critics and detractors.[2] Copyright and trademark laws[edit] The church maintains strict control over the use of its symbols, names and religious texts.[3] It holds copyright and trademark ownership over its cross and has taken legal action against individuals and organizations that have quoted short paragraphs of Scientology texts in print or on web sites. Individuals or groups who practice Scientology without affiliation with the church have been sued for violation of copyright and trademark law.
Operation Snow White. Operation Snow White was the Church of Scientology's internal name for a major criminal conspiracy during the 1970s to purge unfavorable records about Scientology and its founder L.
Ron Hubbard. This project included a series of infiltrations and thefts from 136 government agencies, foreign embassies and consulates, as well as private organizations critical of Scientology, carried out by Church members, in more than 30 countries.[1] It was the single largest infiltration of the United States government in history[2] with up to 5,000 covert agents.[3] This operation also exposed the Scientology plot 'Operation Freakout', because Operation Snow White was the case that initiated the US government investigation of the Church.[3] Under this program, Scientology operatives committed infiltration, wiretapping, and theft of documents in government offices, most notably those of the U.S. Internal Revenue Service. Background[edit] As early as 1960, L. Around this time L. Implementation[edit] Operation Freakout. Operation Freakout, also known as Operation PC Freakout, was a Church of Scientology covert plan intended to have the U.S. author and journalist Paulette Cooper imprisoned or committed to a mental institution.
List of Guardian's Office operations. From its establishment in 1966 to its demise in the early 1980s, the Guardian's Office (GO) of the Church of Scientology carried out numerous covert operations and programs against a range of perceived opponents of Scientology in the United States and around the world.
The GO sought to discredit, destroy or otherwise neutralize – or "depower", in Scientology jargon – any group or individual that it regarded as anti-Scientology. Instructions for such operations were distributed in the form of individually numbered "Guardian Program Orders", abbreviated as GPgmOs, which were distributed from the GO leadership to GO branches in Churches of Scientology and ultimately used to task agents.
Operations[edit] Operation Big Mouth[edit] Operation Big Mouth was a plan devised by the GO to discredit Nathan Dodell, an Assistant US Attorney who represented the government in several cases involving Scientology. Operation Bulldozer Leak[edit] Operation Bunny Bust[edit] Situation: St.